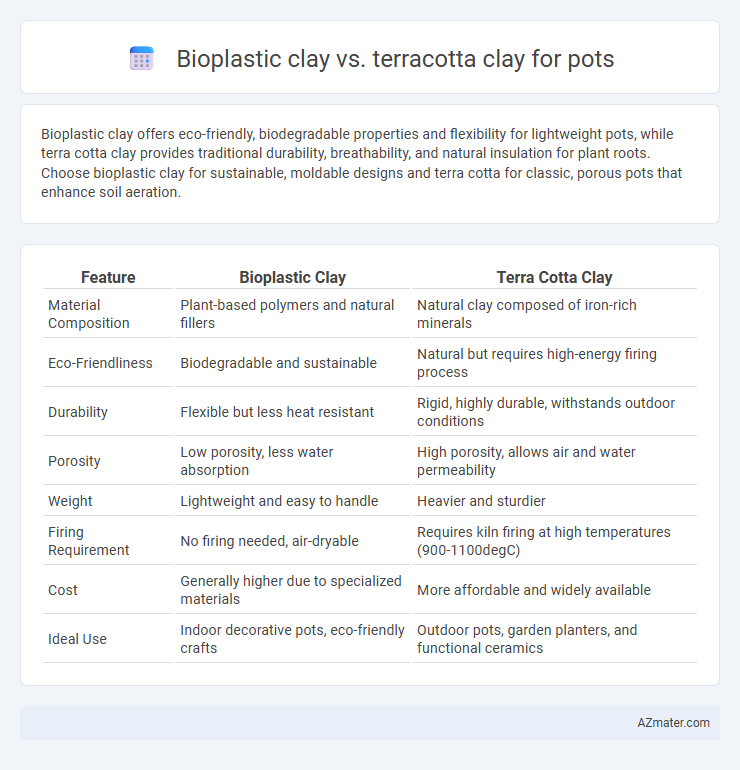
Bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly, biodegradable properties and flexibility for lightweight pots, while terra cotta clay provides traditional durability, breathability, and natural insulation for plant roots. Choose bioplastic clay for sustainable, moldable designs and terra cotta for classic, porous pots that enhance soil aeration.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioplastic Clay | Terra Cotta Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plant-based polymers and natural fillers | Natural clay composed of iron-rich minerals |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable and sustainable | Natural but requires high-energy firing process |
| Durability | Flexible but less heat resistant | Rigid, highly durable, withstands outdoor conditions |
| Porosity | Low porosity, less water absorption | High porosity, allows air and water permeability |
| Weight | Lightweight and easy to handle | Heavier and sturdier |
| Firing Requirement | No firing needed, air-dryable | Requires kiln firing at high temperatures (900-1100degC) |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized materials | More affordable and widely available |
| Ideal Use | Indoor decorative pots, eco-friendly crafts | Outdoor pots, garden planters, and functional ceramics |
Introduction to Bioplastic Clay and Terra Cotta Clay
Bioplastic clay is a biodegradable, eco-friendly material made from renewable resources such as starch and cellulose, offering flexibility and ease of shaping for pot-making. Terra cotta clay, a natural, porous material composed mainly of iron-rich earthenware, has been traditionally used for pottery due to its durability and ability to regulate soil moisture. Choosing between bioplastic clay and terra cotta clay for pots depends on factors like environmental impact, aesthetic preferences, and functional properties such as breathability and weight.
Understanding Bioplastic Clay: Composition and Properties
Bioplastic clay is primarily composed of natural polymers such as starch, cellulose, and biodegradable additives, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional clays. Its lightweight, flexible texture and non-toxic properties allow for easy molding and quick drying, which is ideal for decorative pots and crafts. Unlike terra cotta clay, which consists of naturally occurring clay minerals fired at high temperatures to achieve hardness and durability, bioplastic clay remains softer and less water-resistant, limiting its use for functional pottery.
What is Terra Cotta Clay? Key Features and History
Terra cotta clay, a porous and iron-rich earthenware clay, has been used for centuries in pottery due to its natural reddish-brown color and excellent thermal properties. Key features include high plasticity, ease of shaping, and durability after firing at lower temperatures compared to stoneware, making it ideal for traditional pots and sculptures. Originating in ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley, terra cotta clay remains a popular choice for artisan pottery and garden pots due to its breathability and rustic aesthetic.
Eco-Friendliness: Bioplastic Clay vs. Terra Cotta Clay
Bioplastic clay offers a more eco-friendly alternative to terra cotta clay due to its biodegradable properties and reduced reliance on natural resource extraction. Terra cotta clay requires extensive mining and firing at high temperatures, leading to higher carbon emissions and environmental degradation. Choosing bioplastic clay supports sustainable crafting by minimizing waste and promoting materials derived from renewable sources.
Pot Durability and Strength Comparison
Bioplastic clay offers moderate durability with flexibility, making it less prone to cracking but generally weaker than terra cotta clay, which is known for its high strength and long-lasting structural integrity in pots. Terra cotta clay undergoes firing at high temperatures, resulting in a dense, rigid material that withstands outdoor conditions and heavy loads better than bioplastic clay. While bioplastic clay is biodegradable and eco-friendly, terra cotta remains superior for pot durability and strength, especially in garden and outdoor applications.
Design Flexibility: Molding and Shaping Each Clay
Bioplastic clay offers superior design flexibility with its lightweight, pliable texture, allowing intricate molding and fine detailing that harden without cracking, ideal for custom-shaped pots. Terra cotta clay, while sturdy and breathable, is less forgiving during shaping, requiring more careful handling to prevent warping or cracking in complex designs. The malleability of bioplastic clay supports diverse artistic expressions and precise forms compared to the more traditional, rigid terra cotta clay.
Water Retention and Breathability in Pots
Bioplastic clay offers superior water retention compared to terra cotta clay, making it ideal for plants that require consistent moisture levels. Terra cotta clay is highly breathable, allowing for excellent air circulation and preventing root rot through natural evaporation. While bioplastic clay enhances moisture control, terra cotta's porous structure supports healthy root aeration, influencing the choice based on specific plant needs.
Aesthetic Appeal: Surface Texture and Color Differences
Bioplastic clay offers a smooth, consistent surface texture with vibrant, customizable colors, making it ideal for creating visually striking pots with modern aesthetics. Terra cotta clay features a porous, rustic texture and naturally warm, earthy red or brown hues that develop a charming, traditional patina over time. The choice between these clays significantly influences the pot's decorative appeal, with bioplastic clay suiting contemporary designs and terra cotta enhancing natural, classic styles.
Cost and Accessibility of Bioplastic and Terra Cotta Clays
Bioplastic clay generally costs more than terra cotta clay due to its synthetic composition and specialized manufacturing process, making it less accessible for large-scale pottery projects. Terra cotta clay remains widely available and affordable, benefiting from natural abundance and established supply chains globally. Choosing between them often depends on budget constraints and project scale, with terra cotta favored for cost-efficiency and bioplastic clay for specific, niche applications.
Conclusion: Which Clay is Best for Your Potting Needs?
Bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly advantages with its biodegradability and lightweight nature, making it suitable for decorative pots and short-term uses, whereas terra cotta clay provides superior durability, breathability, and natural insulation essential for healthy plant growth in long-term gardening. For functional and traditional pottery pots, terra cotta remains the preferred choice due to its porosity that helps regulate soil moisture and temperature. Choose bioplastic clay for sustainability and aesthetics in non-essential potting, and terra cotta clay for robust, practical plant housing that supports healthy root systems.
Infographic: Bioplastic clay vs Terra cotta clay for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com