Fire clay offers high thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature molding applications. Bentonite clay provides excellent plasticity and binding properties, commonly used for detailed molds but less heat-resistant than fire clay.
Table of Comparison
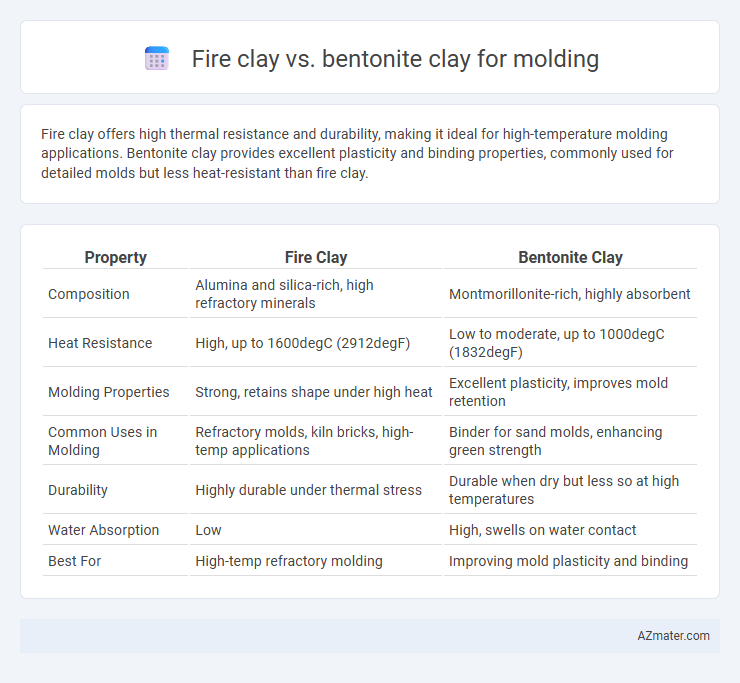
| Property | Fire Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alumina and silica-rich, high refractory minerals | Montmorillonite-rich, highly absorbent |
| Heat Resistance | High, up to 1600degC (2912degF) | Low to moderate, up to 1000degC (1832degF) |
| Molding Properties | Strong, retains shape under high heat | Excellent plasticity, improves mold retention |
| Common Uses in Molding | Refractory molds, kiln bricks, high-temp applications | Binder for sand molds, enhancing green strength |
| Durability | Highly durable under thermal stress | Durable when dry but less so at high temperatures |
| Water Absorption | Low | High, swells on water contact |
| Best For | High-temp refractory molding | Improving mold plasticity and binding |
Introduction to Fire Clay and Bentonite Clay
Fire clay is a highly refractory material known for its ability to withstand extreme heat, making it ideal for molding applications in foundries and ceramics manufacturing. Bentonite clay, composed mainly of montmorillonite, exhibits strong adhesive properties and excellent plasticity, enabling it to form smooth, precise molds that retain shape under pressure. Understanding the thermal resilience of fire clay and the binding strength of bentonite clay is essential for selecting the optimal material in high-temperature molding processes.
Composition and Properties of Fire Clay
Fire clay is composed primarily of kaolinite, alumina, and silica with a high melting point typically above 1,500degC, making it highly refractory and ideal for molding applications requiring heat resistance and durability. Its low impurity content enhances thermal stability and mechanical strength, contrasting with bentonite clay, which contains montmorillonite and has superior plasticity but lower refractory properties. Fire clay's dense structure and thermal shock resistance provide superior performance in molds subjected to extreme temperatures compared to the more absorbent and swell-prone bentonite.
Composition and Properties of Bentonite Clay
Bentonite clay, primarily composed of montmorillonite, exhibits high swelling capacity and excellent plasticity, making it ideal for molding applications that require flexibility and moisture retention. Its cation exchange properties enable strong bonding and durability in molds compared to fire clay, which is richer in alumina and silica, providing higher heat resistance but less plasticity. Bentonite's fine particle size and ability to absorb water contribute to superior adhesion and surface finish in casting molds.
Key Differences Between Fire Clay and Bentonite Clay
Fire clay, composed primarily of kaolinite and other refractory materials, offers high heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for molding applications requiring thermal stability. Bentonite clay, rich in montmorillonite, excels in plasticity and water absorption, providing superior binding and flexibility in molds but with lower heat resistance. The key differences lie in fire clay's refractory properties suited for high-temperature molding versus bentonite's excellent moldability and moisture retention for detailed casting work.
Strength and Plasticity Comparison
Fire clay exhibits superior high-temperature strength, making it ideal for moldings exposed to intense heat, while bentonite clay offers exceptional plasticity and binding properties that enhance mold detail and flexibility. Fire clay's coarse particle structure provides rigidity but less malleability compared to bentonite, which consists of finer particles that increase plastic deformation without compromising mold integrity. Combining bentonite with fire clay can optimize mold strength and plasticity, achieving a balance suitable for complex shaping and thermal resistance.
Water Absorption and Workability
Fire clay exhibits lower water absorption rates compared to bentonite clay, making it less prone to excessive swelling during molding processes. Bentonite clay offers superior workability due to its high plasticity and ability to retain moisture, allowing for easier shaping and fine detailing in molds. The balance between fire clay's dimensional stability and bentonite's enhanced moldability is crucial when selecting the optimal clay for specific molding applications.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Fire clay exhibits superior thermal resistance withstanding temperatures up to 1,600degC, making it ideal for high-heat molding applications such as refractory bricks and kiln linings. Bentonite clay has moderate thermal resistance, typically tolerating temperatures around 400degC to 600degC, which limits its use in high-temperature molding but excels in binding and plasticity due to its swelling properties. Performance-wise, fire clay provides durability and thermal stability, while bentonite offers excellent moldability and moisture retention, often enhancing the strength of molds in low to medium temperature casting processes.
Applications in Sand Molding Processes
Fire clay exhibits high refractory properties and thermal stability, making it ideal for sand cores and molds in high-temperature metal casting applications. Bentonite clay offers superior plasticity and water absorption, enhancing sand mold cohesiveness and strength, especially in green sand molding processes for iron and steel castings. Combining both clays optimizes mold durability and surface finish, crucial for precision casting industries.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Fire clay offers moderate cost and wide availability, making it a practical choice for molding applications requiring high heat resistance. Bentonite clay tends to be more expensive due to its superior plasticity and binding properties but can be limited in certain regions, affecting supply consistency. Cost considerations should weigh the trade-off between fire clay's affordability and bentonite's enhanced mold detail and reusability.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Molding Needs
Fire clay offers high heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for molds subjected to extreme temperatures and repeated firing, such as in ceramics and metal casting. Bentonite clay provides excellent plasticity and water retention, ensuring smooth surface details and ease of shaping, which suits delicate or intricate mold designs. Selecting the right clay hinges on the specific heat tolerance and detail requirements of your molding project, with fire clay favored for strength and bentonite for workability.
Infographic: Fire clay vs Bentonite clay for Molding
 azmater.com
azmater.com