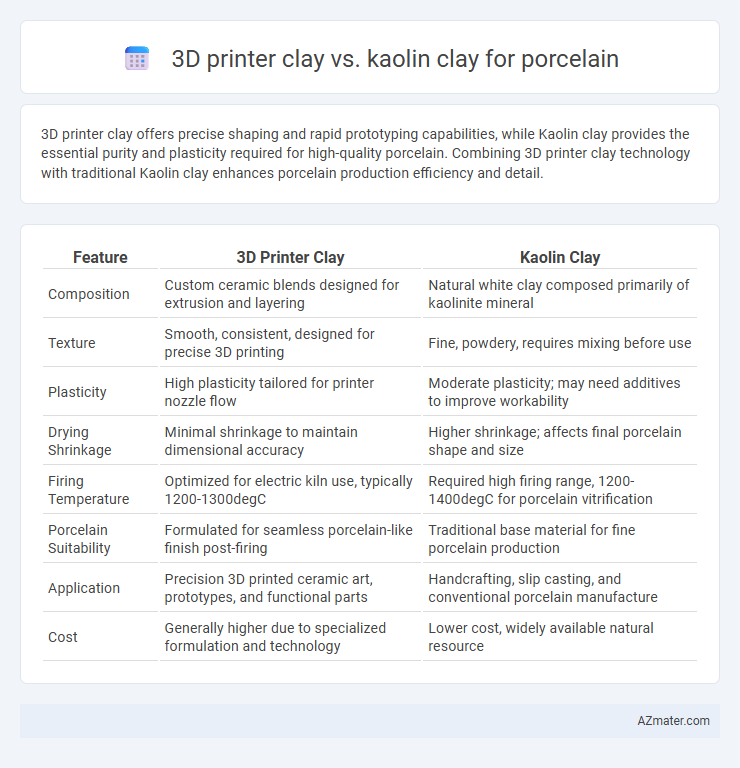
3D printer clay offers precise shaping and rapid prototyping capabilities, while Kaolin clay provides the essential purity and plasticity required for high-quality porcelain. Combining 3D printer clay technology with traditional Kaolin clay enhances porcelain production efficiency and detail.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Kaolin Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Custom ceramic blends designed for extrusion and layering | Natural white clay composed primarily of kaolinite mineral |
| Texture | Smooth, consistent, designed for precise 3D printing | Fine, powdery, requires mixing before use |
| Plasticity | High plasticity tailored for printer nozzle flow | Moderate plasticity; may need additives to improve workability |
| Drying Shrinkage | Minimal shrinkage to maintain dimensional accuracy | Higher shrinkage; affects final porcelain shape and size |
| Firing Temperature | Optimized for electric kiln use, typically 1200-1300degC | Required high firing range, 1200-1400degC for porcelain vitrification |
| Porcelain Suitability | Formulated for seamless porcelain-like finish post-firing | Traditional base material for fine porcelain production |
| Application | Precision 3D printed ceramic art, prototypes, and functional parts | Handcrafting, slip casting, and conventional porcelain manufacture |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized formulation and technology | Lower cost, widely available natural resource |
Introduction to 3D Printer Clay and Kaolin Clay for Porcelain
3D printer clay, designed for additive manufacturing, offers precise control and customization in creating porcelain objects, utilizing a mixture optimized for extrusion and layering during the printing process. Kaolin clay, a primary component of traditional porcelain, is valued for its high purity, fine particle size, and excellent plasticity, which contribute to the strength and translucency of finished porcelain products. Comparing 3D printer clay to kaolin highlights the intersection of modern technology with classic materials, emphasizing adaptability in porcelain fabrication.
Composition Differences: 3D Printer Clay vs Kaolin Clay
3D printer clay for porcelain typically consists of a blend of fine clay particles, binders, and additives engineered to enhance plasticity and flow through printer nozzles, while kaolin clay is primarily composed of pure kaolinite mineral with high alumina and silica content, which provides whiteness and stability. The 3D printer clay's composition is optimized to prevent clogging and ensure layer adhesion in additive manufacturing, whereas kaolin clay's mineral purity supports the traditional firing process, contributing to the strength and translucency of porcelain. The key difference lies in 3D printer clay's tailored particle size distribution and binder systems, contrasting with kaolin clay's natural, unmodified mineral composition essential for classic porcelain craftsmanship.
Workability: Printing vs Traditional Hand Building
3D printer clay designed for porcelain offers superior workability by allowing precise layer-by-layer deposition, enabling intricate shapes and consistent texture difficult to achieve with traditional hand-building. Kaolin clay, the primary component of porcelain, demands manual skill for shaping, making it less adaptable but providing tactile feedback critical for artisans during hand-building. While 3D printing optimizes repetitive and complex designs through controlled extrusion, Kaolin clay's plasticity supports versatile hand manipulation and smooth joining techniques in conventional ceramics.
Drying and Shrinkage Comparison
3D printer clay designed for porcelain typically exhibits faster drying times due to its optimized composition, reducing the risk of cracking compared to traditional Kaolin clay, which dries slower and more unevenly. Shrinkage rates in 3D printer clay are carefully controlled, often ranging between 7-10%, ensuring dimensional accuracy during firing, whereas Kaolin clay can experience higher and less predictable shrinkage, potentially exceeding 12%. These differences make 3D printer clay more suitable for precision porcelain applications requiring consistent drying and minimal deformation.
Firing Temperatures and Porcelain Quality
3D printer clay formulated for porcelain typically requires precise firing temperatures around 1200degC to 1400degC to achieve optimal vitrification and translucency, similar to traditional porcelain standards. Kaolin clay, a primary ingredient in porcelain, fires at slightly lower temperatures (approximately 1150degC to 1300degC) but may produce less strength and translucency if used alone without additional fluxes and filler materials. Porcelain quality in 3D printed clay depends on the clay body's composition and firing profile, with optimized formulations yielding higher density, reduced porosity, and enhanced whiteness compared to pure kaolin firing.
Surface Finish: Smoothness and Glaze Compatibility
3D printer clay designed for porcelain offers a finely tuned particle size and consistency that enhances surface finish smoothness, reducing the need for extensive post-processing compared to Kaolin clay. Kaolin clay, a primary ingredient in traditional porcelain, provides excellent glaze absorption but often requires careful surface preparation to achieve comparable smoothness. While both materials are compatible with high-fire glazes, 3D printer clay formulations are optimized to ensure uniform glaze adherence and minimal defects, making it ideal for precise, smooth porcelain surfaces.
Strength and Durability of Finished Pieces
3D printer clay for porcelain is specifically formulated to enhance the strength and durability of printed pieces by incorporating fine particles and additives that improve cohesion and minimize cracking during firing. Kaolin clay, a key component of traditional porcelain, offers excellent plasticity and whiteness but may require precise processing to achieve comparable strength and durability in finished pieces. The optimized particle size distribution and controlled moisture content in 3D printer clays result in porcelain objects with superior mechanical properties and reduced porosity compared to standard kaolin-based formulations.
Best Uses and Applications for Each Clay Type
3D printer clay offers precise layer-by-layer control ideal for intricate porcelain prototypes and custom decorative pieces, enabling rapid and repeatable production with minimal material waste. Kaolin clay, a primary ingredient in traditional porcelain, excels in high-temperature firing applications, providing excellent whiteness, plasticity, and strength for fine china and ceramic art. For functional porcelain items requiring durability and a smooth, glassy finish, kaolin clay remains the preferred choice, while 3D printer clay suits experimental designs and small-batch manufacturing.
Cost and Availability Considerations
3D printer clay offers higher precision but tends to be more expensive and less readily available compared to Kaolin clay, which remains a cost-effective and abundant material widely used in porcelain production. Kaolin clay's natural abundance ensures consistent supply at lower prices, making it ideal for large-scale or traditional porcelain manufacturing. Cost efficiency and availability make Kaolin clay the preferred choice despite 3D printer clay's advantages in fine detail and customization.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Porcelain Project
When choosing the right clay for your porcelain project, 3D printer clay offers precise layering and customization ideal for intricate designs, while Kaolin clay provides a traditional, naturally white base essential for classic porcelain. Kaolin clay's fine particle size and high purity contribute to its durability and translucency when fired, making it the preferred choice for authentic porcelain craftsmanship. Evaluate your project's complexity and desired finish to decide between the innovative 3D printing methods or the time-tested qualities of Kaolin clay.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Kaolin clay for Porcelain
 azmater.com
azmater.com