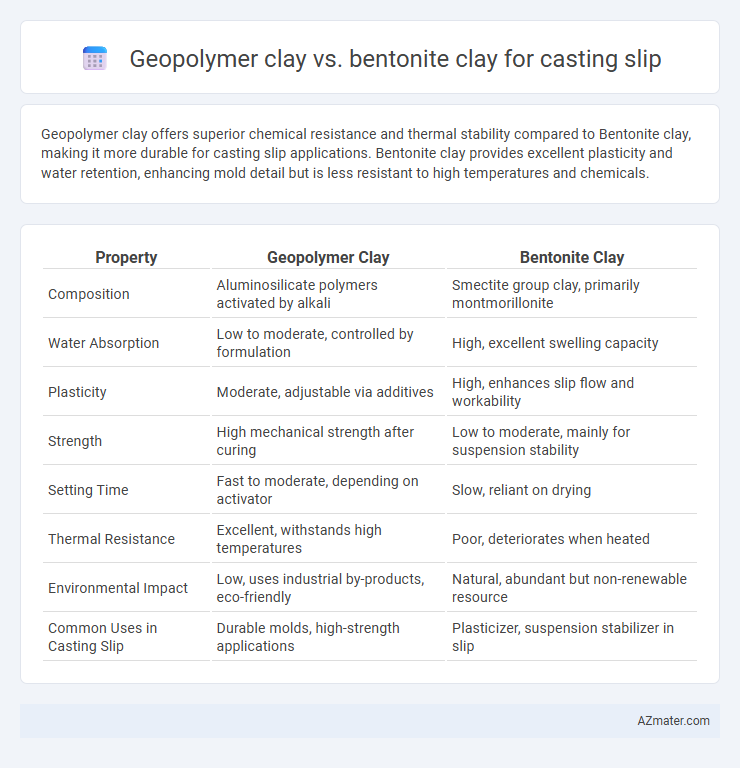
Geopolymer clay offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to Bentonite clay, making it more durable for casting slip applications. Bentonite clay provides excellent plasticity and water retention, enhancing mold detail but is less resistant to high temperatures and chemicals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Geopolymer Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate polymers activated by alkali | Smectite group clay, primarily montmorillonite |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate, controlled by formulation | High, excellent swelling capacity |
| Plasticity | Moderate, adjustable via additives | High, enhances slip flow and workability |
| Strength | High mechanical strength after curing | Low to moderate, mainly for suspension stability |
| Setting Time | Fast to moderate, depending on activator | Slow, reliant on drying |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent, withstands high temperatures | Poor, deteriorates when heated |
| Environmental Impact | Low, uses industrial by-products, eco-friendly | Natural, abundant but non-renewable resource |
| Common Uses in Casting Slip | Durable molds, high-strength applications | Plasticizer, suspension stabilizer in slip |
Introduction to Clay Types in Casting Slip
Geopolymer clay and bentonite clay serve distinct purposes in casting slip formulations due to their unique properties. Geopolymer clay offers enhanced chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making it suitable for industrial ceramics and refractory applications. Bentonite clay, known for its strong plasticity and excellent suspension properties, is widely used to improve the viscosity and workability of ceramic casting slips.
What is Geopolymer Clay?
Geopolymer clay is an advanced inorganic material composed of aluminosilicate polymers formed through the alkali activation of materials like metakaolin or fly ash, offering superior strength and thermal stability compared to traditional bentonite clay. Unlike bentonite, which is primarily composed of montmorillonite and used for its swelling properties in casting slips, geopolymer clay provides enhanced durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance ceramic applications. Its innovative composition allows for more precise mold casting with improved dimensional stability and reduced shrinkage during firing processes.
Understanding Bentonite Clay
Bentonite clay, a highly absorbent and plastic type of clay composed mainly of montmorillonite, offers superior suspension and binding properties for casting slips compared to geopolymer clay. Its ability to increase viscosity and improve particle dispersion enhances the slip's stability and reduces settling during the casting process. Understanding the mineralogical characteristics and hydration behavior of bentonite clay is essential for optimizing slip formulations in ceramic and mold-making applications.
Composition Differences: Geopolymer vs Bentonite
Geopolymer clay consists primarily of aluminosilicate materials activated by alkaline solutions, forming a network of silicon-oxygen and aluminum-oxygen bonds that provide high thermal stability and structural integrity. Bentonite clay is largely composed of montmorillonite, a layered silicate mineral rich in magnesium and calcium ions, which imparts excellent water absorption and swelling properties but lower mechanical strength compared to geopolymers. The key compositional difference lies in geopolymer's synthetic aluminosilicate matrix versus bentonite's natural smectite mineral structure, influencing their performance in casting slip applications.
Workability and Handling in Casting Slip
Geopolymer clay offers superior workability in casting slip due to its smooth consistency and excellent flow properties, allowing for easy mold filling and reduced air entrapment. Bentonite clay provides enhanced plasticity and suspension stability, improving slip coherence but can lead to higher viscosity and more challenging handling during casting. Choosing between the two depends on the specific casting requirements, where geopolymer clay favors fluidity and bentonite clay ensures structural integrity in the slip.
Drying and Shrinkage Rates
Geopolymer clay exhibits significantly lower drying shrinkage rates compared to Bentonite clay, making it ideal for casting slip applications where dimensional stability is critical. Bentonite clay tends to absorb more water, leading to higher shrinkage and cracking risks during drying, whereas geopolymer formulations maintain better structural integrity due to their chemical bonding properties. The controlled drying process of geopolymer clay enhances reduced warping and improved durability in finished ceramic or casting slip products.
Strength and Durability of Final Casts
Geopolymer clay exhibits superior strength and durability compared to bentonite clay when used in casting slip, due to its high silica and alumina content that forms a robust aluminosilicate network upon curing. Bentonite clay, while effective for plasticity and water retention, tends to produce casts with lower mechanical strength and decreased resistance to environmental degradation. The enhanced chemical bonding in geopolymer-based slips leads to final casts that outperform bentonite-based ones in hardness, fracture toughness, and long-term structural integrity.
Environmental Impact: Geopolymer vs Bentonite
Geopolymer clay significantly reduces environmental impact compared to bentonite clay by utilizing industrial byproducts like fly ash and slag, lowering carbon emissions during production. Bentonite extraction involves substantial land degradation and water consumption, contributing to ecosystem disruption and higher ecological footprints. Choosing geopolymer clay for casting slip promotes sustainable practices with reduced resource depletion and waste generation.
Cost-effectiveness for Casting Applications
Geopolymer clay offers enhanced cost-effectiveness for casting slip due to its lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during curing compared to bentonite clay. Bentonite clay, while traditional and widely used, often incurs higher costs related to processing and longer drying times, impacting overall production efficiency. For industrial-scale casting applications, geopolymer clay provides a more economical alternative by minimizing material costs and accelerating turnaround times.
Choosing the Right Clay: Applications and Recommendations
Geopolymer clay offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature casting slip applications and industrial molds. Bentonite clay provides excellent plasticity and swelling properties, which enhance slip suspension and improve cast surface details in pottery and ceramic casting. Selecting the right clay depends on application requirements: geopolymer clay suits structural and heat-resistant casts, while bentonite clay is preferred for fine-detail ceramics and traditional casting techniques.
Infographic: Geopolymer clay vs Bentonite clay for Casting slip
 azmater.com
azmater.com