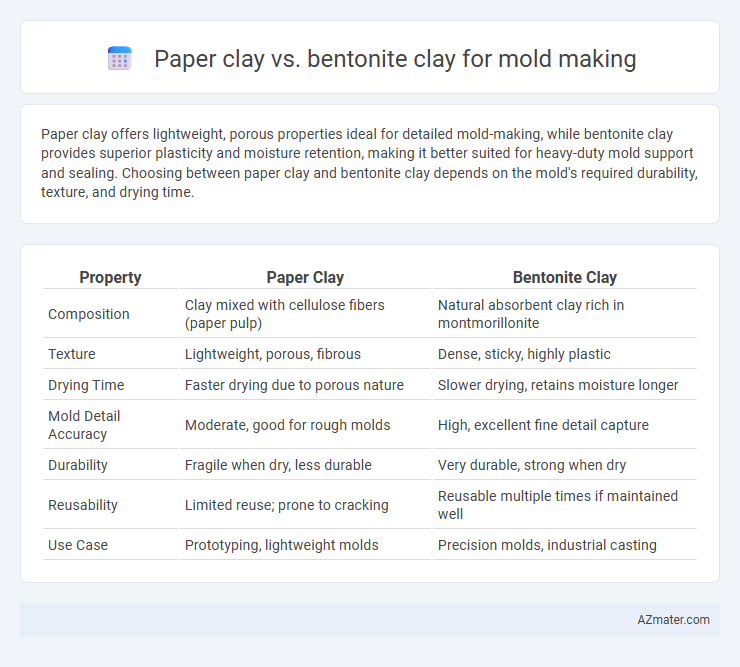
Paper clay offers lightweight, porous properties ideal for detailed mold-making, while bentonite clay provides superior plasticity and moisture retention, making it better suited for heavy-duty mold support and sealing. Choosing between paper clay and bentonite clay depends on the mold's required durability, texture, and drying time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Paper Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay mixed with cellulose fibers (paper pulp) | Natural absorbent clay rich in montmorillonite |
| Texture | Lightweight, porous, fibrous | Dense, sticky, highly plastic |
| Drying Time | Faster drying due to porous nature | Slower drying, retains moisture longer |
| Mold Detail Accuracy | Moderate, good for rough molds | High, excellent fine detail capture |
| Durability | Fragile when dry, less durable | Very durable, strong when dry |
| Reusability | Limited reuse; prone to cracking | Reusable multiple times if maintained well |
| Use Case | Prototyping, lightweight molds | Precision molds, industrial casting |
Introduction to Paper Clay and Bentonite Clay
Paper clay combines traditional clay with cellulose fibers, enhancing plasticity and allowing lighter, stronger molds ideal for detailed sculpting and lightweight casting. Bentonite clay is highly absorbent with excellent swelling properties, commonly used in mold making to create flexible, durable molds that withstand repeated use and high temperatures. Understanding the distinct composition and functional benefits of paper clay versus bentonite clay helps artists and mold makers select the optimal material for precision and durability in casting projects.
What is Paper Clay?
Paper clay is a lightweight, pliable material composed of traditional ceramic clay mixed with cellulose fibers such as paper pulp, enhancing its strength and reducing shrinkage during drying and firing. Unlike bentonite clay, which is a natural absorbent clay known for its high plasticity and swelling properties, paper clay offers improved flexibility and easier manipulation for mold making. The fibrous composition of paper clay allows for durable, crack-resistant molds that are ideal for detailed casting and model building.
What is Bentonite Clay?
Bentonite clay is a natural, highly absorbent clay composed primarily of montmorillonite, widely used in mold making for its excellent plasticity and swelling properties when hydrated. It provides superior mold release, durability, and fine detail capture, making it ideal for casting ceramics, metal, and plaster. Unlike paper clay, which incorporates fibers for added strength, bentonite clay offers a smoother, more malleable consistency essential for precise and reusable molds.
Comparing Material Properties
Paper clay offers lightweight and flexible characteristics due to its cellulose fiber content, making it ideal for delicate mold designs that require easy handling. Bentonite clay exhibits exceptional plasticity and water absorption, providing superior durability and detailed surface capture in mold making. The choice between paper clay and bentonite clay depends on the mold's required strength, texture fidelity, and ease of manipulation during the creation process.
Workability and Ease of Molding
Paper clay offers superior workability due to its lightweight texture and flexibility, making it easier to shape and carve for detailed mold designs. Bentonite clay, while excellent for capturing fine textures, tends to be heavier and stickier, which can complicate molding and require more skill to handle effectively. Artists and mold makers often prefer paper clay for intricate, smooth forms and bentonite clay for robust, durable molds with sharp detail retention.
Drying and Shrinkage Differences
Paper clay typically contains cellulose fibers that reduce drying shrinkage and improve strength, resulting in less cracking during mold making compared to bentonite clay. Bentonite clay, composed primarily of montmorillonite, absorbs water and swells significantly, causing greater shrinkage and deformation as it dries. The slower drying time of bentonite clay often leads to higher dimensional changes, whereas paper clay's fiber integration provides more controlled drying and minimal shrinkage for accurate mold replication.
Strength and Durability in Molds
Bentonite clay exhibits superior strength and durability compared to paper clay when used for mold making, due to its high plasticity and cohesive properties that allow it to withstand repeated use without cracking. Paper clay, while lightweight and easy to shape, tends to be less durable, often requiring reinforcement or sealing to prevent damage during multiple casting cycles. The mineral-rich composition of bentonite ensures long-lasting molds suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Cost Considerations
Paper clay generally offers cost advantages for mold making due to its lightweight nature, reducing shipping and handling expenses compared to Bentonite clay, which tends to be heavier and bulkier. Bentonite clay, though more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and reusability, potentially lowering long-term costs for repeated mold production. Careful evaluation of project scale and frequency of use is essential to balance the initial material costs against overall mold lifespan and performance.
Ideal Applications for Each Clay
Paper clay excels in mold making for lightweight, detailed sculptures and prototypes due to its enhanced strength and flexibility when dry. Bentonite clay is ideal for molds requiring high plasticity and water retention, making it suitable for casting materials like plaster, concrete, or ceramics. Choosing between paper clay and bentonite clay depends on the mold's functional demands, such as durability, moisture handling, and the intricacy of the design.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Clay for Mold Making
Paper clay offers lightweight flexibility and ease of shaping, making it ideal for detailed and delicate mold projects, especially where drying and firing are required. Bentonite clay provides superior plasticity and excellent moisture retention, making it suitable for reusable molds and applications needing durability and fine texture. Selecting the best clay depends on project requirements: paper clay suits artistic, porous molds, while bentonite clay excels in heavy-duty, reusable, and water-resistant mold making.
Infographic: Paper clay vs Bentonite clay for Mold making
 azmater.com
azmater.com