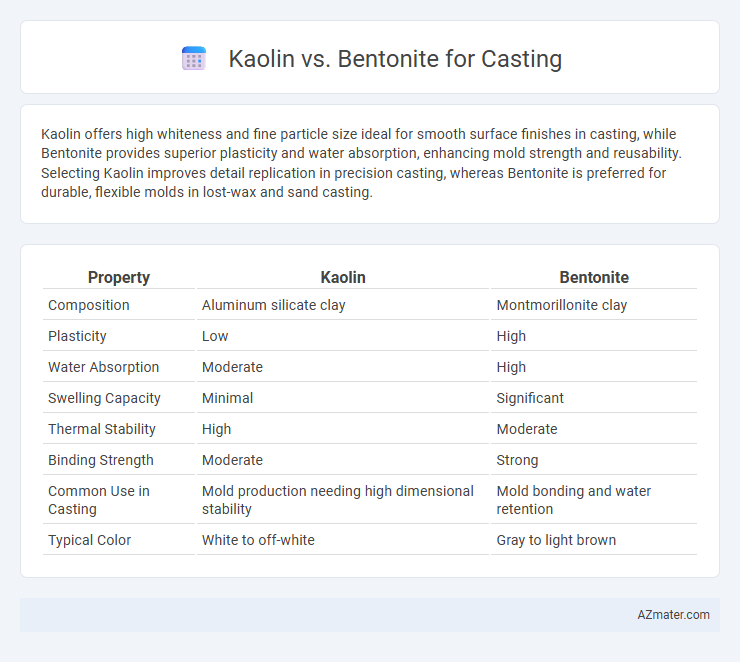
Kaolin offers high whiteness and fine particle size ideal for smooth surface finishes in casting, while Bentonite provides superior plasticity and water absorption, enhancing mold strength and reusability. Selecting Kaolin improves detail replication in precision casting, whereas Bentonite is preferred for durable, flexible molds in lost-wax and sand casting.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Kaolin | Bentonite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminum silicate clay | Montmorillonite clay |
| Plasticity | Low | High |
| Water Absorption | Moderate | High |
| Swelling Capacity | Minimal | Significant |
| Thermal Stability | High | Moderate |
| Binding Strength | Moderate | Strong |
| Common Use in Casting | Mold production needing high dimensional stability | Mold bonding and water retention |
| Typical Color | White to off-white | Gray to light brown |
Introduction to Casting Clays
Kaolin and Bentonite are key clays used in casting processes, each offering unique properties vital for mold making. Kaolin, a white, fine-grained clay, provides smooth surfaces and high refractory strength, ideal for precision casting molds. Bentonite, rich in montmorillonite, enhances plasticity and water absorption, improving mold flexibility and binding capacity in foundry applications.
What is Kaolin?
Kaolin is a fine, white clay primarily composed of the mineral kaolinite, known for its high purity and low levels of impurities like iron oxide. Its fine particle size and chemical inertness make it ideal for ceramic casting molds, providing smooth surfaces and excellent refractory properties. Kaolin's low plasticity and ability to withstand high temperatures without significant deformation distinguish it from bentonite, which offers higher plasticity but less thermal stability.
What is Bentonite?
Bentonite is a highly absorbent clay consisting primarily of montmorillonite, widely used in casting for its excellent binding properties and ability to retain moisture, which enhances mold strength and surface finish. Its fine particle size and plasticity make it ideal for forming detailed molds in metal casting, particularly sand casting processes. Compared to kaolin, bentonite offers superior cohesion and expansion when wet, improving mold durability and reducing defects in castings.
Key Differences Between Kaolin and Bentonite
Kaolin and bentonite differ primarily in their mineral composition and plasticity, with kaolin being a white, non-plastic clay rich in kaolinite, while bentonite contains montmorillonite, offering higher plasticity and swelling properties. In casting, kaolin is preferred for its refractory qualities and smooth finish, ideal for porcelain and fine ceramics, whereas bentonite is favored for its binding strength and water absorption, making it suitable for sand molds and foundry applications. The thermal stability of kaolin surpasses that of bentonite, which can deform under high temperatures, influencing their specific uses in casting processes.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Kaolin primarily consists of the mineral kaolinite with the chemical formula Al2Si2O5(OH)4, featuring a layered silicate structure rich in aluminum and silicon. Bentonite is predominantly composed of montmorillonite, a smectite group mineral with a formula roughly represented as (Na,Ca)0.33(Al,Mg)2Si4O10(OH)2*nH2O, characterized by high sodium and calcium content and significant water absorption capacity. The distinct chemical compositions influence their casting properties, with kaolin offering lower plasticity and bentonite providing superior swelling and binding due to its clay mineral structure.
Physical Properties and Performance
Kaolin exhibits a fine particle size and low plasticity, providing excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy in casting molds, while bentonite offers higher plasticity and greater swelling capacity, enhancing mold strength and moisture retention. Kaolin's lower shrinkage rate reduces defects during drying and firing, whereas bentonite's superior adhesion improves sand bond strength but may cause increased shrinkage and cracking risks. In performance, kaolin ensures smoother mold surfaces for precision casting, whereas bentonite's binding properties make it ideal for heavy-duty molds needing durability and flexibility.
Applications in Casting Industries
Kaolin and bentonite are essential clays used in casting industries, with kaolin prized for its high purity and fine particle size that provides smooth surface finishes in precision moldings. Bentonite's superior swelling properties and excellent binding capacity make it ideal for sand casting, enhancing mold strength and moisture retention. Both clays are crucial for producing durable molds and consistent casting quality in metal foundries and ceramics manufacturing.
Advantages of Kaolin in Casting
Kaolin offers superior plasticity and fine particle size, resulting in smoother mold surfaces and enhanced detail accuracy in casting applications. Its low impurity levels contribute to higher refractoriness and reduced defects, improving overall casting quality. Kaolin's excellent thermal stability also minimizes thermal expansion, ensuring dimensional consistency and reducing mold cracking during metal pouring.
Benefits of Bentonite for Casting Processes
Bentonite offers superior plasticity and binding properties, making it ideal for precision casting molds. Its excellent moisture retention enhances mold stability and surface finish, reducing defects and improving dimensional accuracy. The high swelling capacity of bentonite ensures better mold compaction and strength during metal pouring, optimizing casting quality.
Choosing the Right Clay: Kaolin vs Bentonite
Kaolin and Bentonite are key clays in casting, where Kaolin provides superior smoothness and high refractory properties, making it ideal for precision molds and fine details. Bentonite offers excellent plasticity and water retention, enhancing mold strength and durability for larger or more robust castings. Selecting between Kaolin and Bentonite depends on the required mold surface finish, heat resistance, and mechanical strength in casting applications.
Infographic: Kaolin vs Bentonite for Casting
 azmater.com
azmater.com