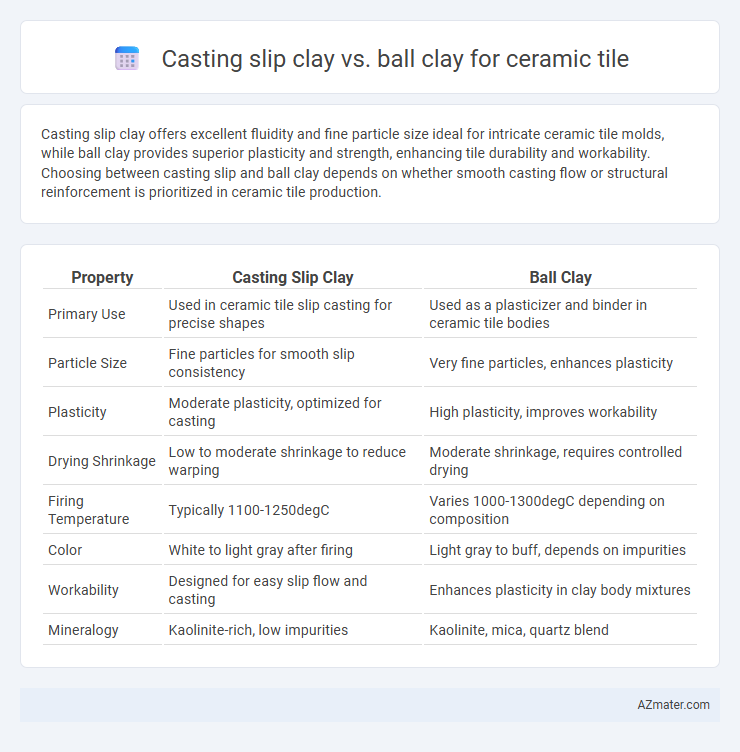
Casting slip clay offers excellent fluidity and fine particle size ideal for intricate ceramic tile molds, while ball clay provides superior plasticity and strength, enhancing tile durability and workability. Choosing between casting slip and ball clay depends on whether smooth casting flow or structural reinforcement is prioritized in ceramic tile production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Casting Slip Clay | Ball Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Used in ceramic tile slip casting for precise shapes | Used as a plasticizer and binder in ceramic tile bodies |
| Particle Size | Fine particles for smooth slip consistency | Very fine particles, enhances plasticity |
| Plasticity | Moderate plasticity, optimized for casting | High plasticity, improves workability |
| Drying Shrinkage | Low to moderate shrinkage to reduce warping | Moderate shrinkage, requires controlled drying |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 1100-1250degC | Varies 1000-1300degC depending on composition |
| Color | White to light gray after firing | Light gray to buff, depends on impurities |
| Workability | Designed for easy slip flow and casting | Enhances plasticity in clay body mixtures |
| Mineralogy | Kaolinite-rich, low impurities | Kaolinite, mica, quartz blend |
Introduction to Ceramic Tile Materials
Casting slip clay, characterized by its fine particle size and high plasticity, is preferred for producing smooth, dense ceramic tiles with excellent surface quality. Ball clay contains a higher amount of kaolin and organic materials, providing strong plasticity but requiring careful blending to prevent excessive shrinkage or deformation during firing. Understanding the distinct physical properties and mineral compositions of casting slip clay versus ball clay is crucial for optimizing the formulation and performance of ceramic tile bodies.
Overview of Casting Slip Clay
Casting slip clay, primarily composed of fine particles and formulated for optimal fluidity, enables precise molding and uniform density in ceramic tile production. This clay type ensures minimal shrinkage and enhanced green strength, facilitating the manufacture of thin, complex shapes with smooth surfaces. Compared to ball clay, casting slip clay contains fewer impurities and lower plasticity, making it ideal for slip casting processes demanding high rheological control and consistency.
Overview of Ball Clay
Ball clay is a highly plastic and fine-grained sedimentary clay widely used in ceramic tile production to enhance workability and green strength. Its high kaolinite content provides excellent plasticity and plastic forming properties, making it ideal for casting slips in thin, intricate tile designs. Compared to other clays, ball clay improves the mechanical strength and firing durability of ceramic tiles while maintaining smooth surface quality.
Key Differences Between Casting Slip Clay and Ball Clay
Casting slip clay features finer particle size and lower plasticity compared to ball clay, enabling it to form smooth, uniform ceramic tiles through slip casting. Ball clay has higher plasticity and bonding properties, which improve the strength and flexibility of ceramic tile bodies but require more water and careful handling during processing. The key difference lies in casting slip's suitability for precise shaping and surface finish, while ball clay enhances mechanical strength and workability in tile production.
Role of Plasticity in Ceramic Tile Production
Casting slip clay exhibits lower plasticity than ball clay, facilitating easier flow and uniform layer formation during ceramic tile production. Ball clay's higher plasticity enhances green strength and machinability, crucial for shaping and drying processes. Optimizing plasticity balances workability and structural integrity, impacting tile quality and production efficiency.
Impact on Tile Strength and Durability
Casting slip clay features finer particle size and higher plasticity compared to ball clay, resulting in better particle packing and minimized porosity in ceramic tiles. Ball clay, though beneficial for plasticity, contains organic impurities that may weaken tile microstructure and reduce strength over time. Utilizing casting slip clay enhances tile density, improving strength and durability essential for high-performance ceramic applications.
Color Variations and Firing Characteristics
Casting slip clay typically exhibits a higher plasticity and finer particle size compared to ball clay, resulting in smoother surfaces and more consistent color variations after firing. Ball clay often contains higher organic content and impurities, leading to darker hues and less predictable changes during firing, especially in oxidation or reduction atmospheres. The firing characteristics of casting slip clay allow for more controlled shrinkage and vitrification, ideal for achieving uniform ceramic tile color and strength.
Workability and Production Techniques
Casting slip clay exhibits superior workability for ceramic tile production due to its finer particle size and higher plasticity, allowing for smooth mold filling and reduced defects during slip casting. Ball clay provides excellent plasticity and strength but often requires blending with other clays to optimize casting slip properties, enhancing drying shrinkage control and green strength. Production techniques favor casting slip clay in slip casting methods for intricate shapes, while ball clay's versatility supports both pressing and casting processes, influencing tile density and surface finish.
Cost Implications and Sourcing
Casting slip clay generally incurs higher costs due to its fine particle size and superior plasticity, which enhance moldability but require more refined processing techniques. Ball clay, being more abundant and widely sourced globally, offers a more economical option with sufficient plasticity and strength for ceramic tile production. Manufacturers often balance cost implications by blending ball clay with casting slip clay to optimize performance while minimizing raw material expenses.
Choosing the Right Clay for Ceramic Tile Applications
Casting slip clay offers superior fluidity and fine particle size, making it ideal for creating smooth, uniform ceramic tiles with intricate shapes and thin walls. Ball clay features high plasticity and excellent binding properties, enhancing tile strength and durability during forming and drying processes. Selecting the appropriate clay depends on balancing the need for detailed casting precision with structural integrity requirements in ceramic tile production.
Infographic: Casting slip clay vs Ball clay for Ceramic tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com