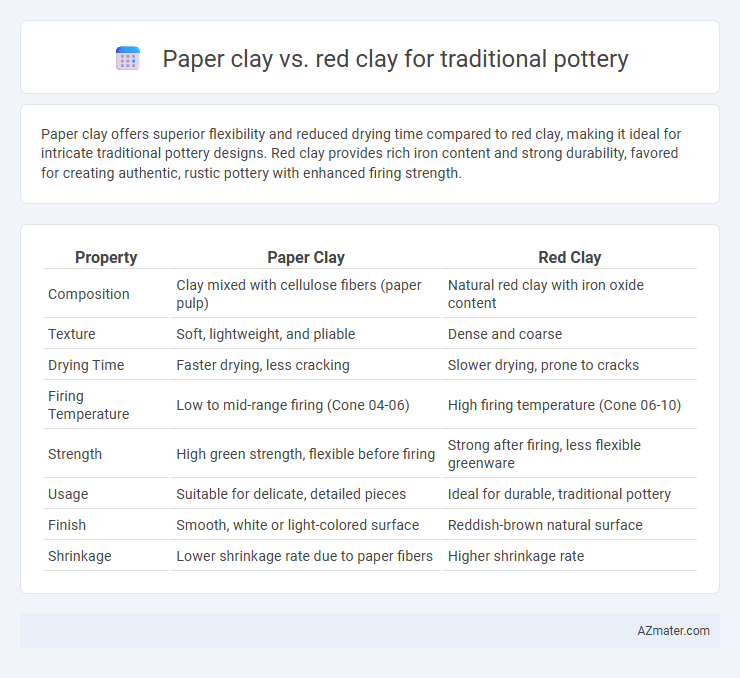
Paper clay offers superior flexibility and reduced drying time compared to red clay, making it ideal for intricate traditional pottery designs. Red clay provides rich iron content and strong durability, favored for creating authentic, rustic pottery with enhanced firing strength.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Paper Clay | Red Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay mixed with cellulose fibers (paper pulp) | Natural red clay with iron oxide content |
| Texture | Soft, lightweight, and pliable | Dense and coarse |
| Drying Time | Faster drying, less cracking | Slower drying, prone to cracks |
| Firing Temperature | Low to mid-range firing (Cone 04-06) | High firing temperature (Cone 06-10) |
| Strength | High green strength, flexible before firing | Strong after firing, less flexible greenware |
| Usage | Suitable for delicate, detailed pieces | Ideal for durable, traditional pottery |
| Finish | Smooth, white or light-colored surface | Reddish-brown natural surface |
| Shrinkage | Lower shrinkage rate due to paper fibers | Higher shrinkage rate |
Introduction to Paper Clay and Red Clay
Paper clay combines refined clay with cellulose fiber, enhancing its strength, flexibility, and drying properties, making it ideal for delicate and intricate pottery designs. Red clay, rich in iron oxide, offers natural durability and a distinctive reddish hue prized in traditional pottery for its earthy aesthetic and robust firing characteristics. Both clays serve unique roles in pottery, with paper clay favored for sculptural detail and red clay valued for classic, durable ceramic ware.
Historical Background of Traditional Pottery Clays
Traditional pottery has relied on various clays such as paper clay, known for its lightweight and porous structure, and red clay, prized for its rich iron oxide content that imparts a distinctive color and durability. Historical records document red clay as the primary medium in ancient civilizations like the Indus Valley and Mesopotamia, used extensively for utilitarian and ceremonial vessels. Paper clay, developed more recently, offers improved workability and reduced cracking, influencing modern adaptations of traditional pottery techniques.
Composition: Paper Clay vs Red Clay
Paper clay is composed of traditional clay mixed with cellulose fibers derived from paper pulp, enhancing its workability and drying strength. Red clay, primarily composed of iron oxide-rich natural clay minerals, boasts a higher plasticity suited for traditional pottery shaping and firing. The cellulose in paper clay improves crack resistance and repairability, whereas red clay's mineral composition provides durability and a characteristic reddish hue after firing.
Workability and Sculpting Differences
Paper clay offers enhanced workability for traditional pottery due to its lightweight, flexible texture, allowing finer detail and easier joining of pieces compared to red clay. Red clay, denser and more plastic, is preferred for robust sculpting and structural stability in larger forms but can be less forgiving during delicate shaping. The inclusion of paper fibers in paper clay reduces cracking during drying, enabling more intricate, complex designs that are difficult to achieve with the coarser, more shrink-prone red clay.
Drying Time and Shrinkage Rates
Paper clay typically dries faster than red clay due to its fibrous composition, which allows moisture to evaporate more quickly while maintaining structural integrity. Red clay often exhibits higher shrinkage rates during drying, sometimes up to 12-15%, causing potential warping or cracking in traditional pottery. Paper clay's lower shrinkage rate, usually around 5-7%, enhances durability and reduces the risk of damage during the drying process.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Paper clay offers enhanced strength and flexibility compared to traditional red clay due to its fiber content, which reduces cracking during drying and firing. Red clay, known for its natural iron oxide content, provides robust durability and a rich, earthy finish but is more prone to brittleness and fracture under stress. The combination of paper fibers in paper clay results in higher resistance to physical impact, making it preferable for intricate or thin-walled pottery designs.
Firing Temperatures and Kiln Requirements
Paper clay and red clay differ significantly in firing temperatures and kiln requirements for traditional pottery. Paper clay typically fires at lower temperatures, around cone 06 to cone 04 (999degC to 1060degC), making it suitable for electric kilns with controlled atmospheres. Red clay, often fired at higher temperatures between cone 04 and cone 10 (1060degC to 1300degC), requires kilns capable of reaching and maintaining these elevated temperatures, such as gas or wood-fired kilns, to achieve optimal strength and durability.
Surface Texture and Aesthetic Results
Paper clay offers a smoother, more refined surface texture compared to red clay, allowing for intricate detailing and a delicate finish in traditional pottery. Red clay, known for its coarse and earthy texture, provides a rustic, organic aesthetic that highlights natural imperfections and raw beauty. The choice between paper clay and red clay significantly influences the tactile quality and visual appeal of pottery, with paper clay lending itself to polished elegance and red clay emphasizing traditional, rugged charm.
Suitability for Various Pottery Techniques
Paper clay offers enhanced flexibility and is highly suitable for hand-building techniques like coiling and slab construction, allowing potters to create intricate shapes with reduced cracking. Red clay, known for its dense and coarse texture, excels in wheel throwing and sculptural pottery, providing durability and rich earthy tones after firing. Both clays serve distinct purposes: paper clay suits experimental and detailed work, while red clay is ideal for robust, traditional pottery forms.
Choosing the Right Clay for Traditional Pottery
Choosing the right clay for traditional pottery hinges on the desired texture and firing properties; paper clay, infused with cellulose fibers, offers enhanced strength and reduced cracking, making it ideal for intricate designs and lightweight vessels. Red clay, rich in iron oxide, provides a natural earthy hue and excellent plasticity, preferred for robust, durable pottery with traditional aesthetics. Understanding the functional differences and firing requirements of paper clay versus red clay ensures optimal results in handcrafted ceramic art.
Infographic: Paper clay vs Red clay for Traditional pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com