Nano-enhanced clay offers superior strength, reduced drying time, and increased durability compared to traditional earthen clay. Its nano-scale additives improve plasticity and firing properties, making it ideal for high-performance pottery applications.
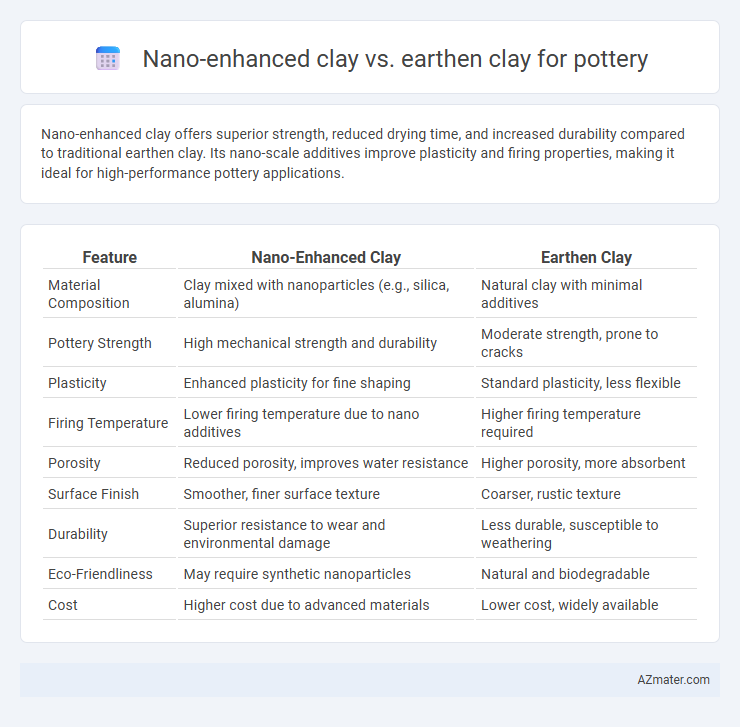
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nano-Enhanced Clay | Earthen Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay mixed with nanoparticles (e.g., silica, alumina) | Natural clay with minimal additives |
| Pottery Strength | High mechanical strength and durability | Moderate strength, prone to cracks |
| Plasticity | Enhanced plasticity for fine shaping | Standard plasticity, less flexible |
| Firing Temperature | Lower firing temperature due to nano additives | Higher firing temperature required |
| Porosity | Reduced porosity, improves water resistance | Higher porosity, more absorbent |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, finer surface texture | Coarser, rustic texture |
| Durability | Superior resistance to wear and environmental damage | Less durable, susceptible to weathering |
| Eco-Friendliness | May require synthetic nanoparticles | Natural and biodegradable |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced materials | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Pottery Materials: Nano-enhanced Clay vs Earthen Clay
Nano-enhanced clay incorporates nanoparticles that improve plasticity, strength, and drying time, offering superior performance in pottery compared to traditional earthen clay. Earthen clay, composed of natural soil minerals, provides organic texture and historical authenticity but often requires longer firing and has lower mechanical strength. Selecting between these materials impacts the durability, finish, and workability of ceramic pieces, making nano-enhanced clay ideal for modern, high-precision pottery.
Composition and Structure Differences
Nano-enhanced clay incorporates nanoparticles such as nano-silica or nano-alumina, which significantly alter the microstructure by improving particle packing density and enhancing mechanical strength compared to traditional earthen clay. Earthen clay consists primarily of naturally occurring minerals like kaolinite, illite, and quartz with larger, less uniform particles that result in a coarser texture and lower structural integrity. The nanoscale additives in nano-enhanced clay create a more homogenous matrix, reducing porosity and increasing thermal stability, making it superior for high-performance pottery applications.
Material Properties: Strength and Durability
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits significantly improved strength and durability compared to traditional earthen clay due to the incorporation of nanoparticles that reinforce the clay matrix, reducing porosity and increasing tensile strength. This nanocomposite structure enhances resistance to cracking, abrasion, and weathering, making it ideal for functional pottery subjected to mechanical stress. In contrast, earthen clay, while naturally plastic and workable, tends to have lower structural integrity and is more susceptible to chipping and wear over time.
Workability and Molding Techniques
Nano-enhanced clay improves workability by integrating nanoparticles that increase plasticity, enabling smoother shaping and finer detail retention during molding. Earthen clay, while traditional and widely used, often exhibits coarser particle distribution, which can limit precise molding and requires more water for pliability. The enhanced plasticity in nano-clay reduces cracking risks and allows for more innovative molding techniques compared to the bulkier texture of earthen clay.
Firing Temperatures and Kiln Requirements
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits higher thermal stability, allowing it to withstand firing temperatures up to 1300degC, compared to traditional earthen clay which typically fuses at around 1000degC. Kiln requirements for nano-enhanced clay include precise temperature control and slower ramp rates to optimize the enhanced particle dispersion and prevent cracking. Earthen clay, being less thermally stable, relies on conventional kilns with standard firing cycles, making it more accessible but less durable in high-temperature applications.
Aesthetic Outcomes: Texture and Finish
Nano-enhanced clay offers a significantly smoother texture and a more refined finish compared to traditional earthen clay, due to the ultra-fine particles that fill microscopic gaps, reducing surface roughness. This advanced composition allows potters to achieve intricate details and a polished, glossy aesthetic that is difficult to replicate with conventional earthen clay. Earthen clay, while prized for its natural, rustic appearance and tactile variations, tends to produce a coarser texture and matte finish, offering a distinctly organic feel favored in artisanal pottery.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nano-enhanced clay reduces resource consumption and waste by improving the material's strength and durability, leading to longer-lasting pottery with less frequent remakes. Earthen clay, sourced locally and often without chemical additives, supports traditional, low-impact extraction methods but may require more energy in firing due to its natural porosity and lower strength. Nano-enhanced clay's potential for recycling and lower carbon footprint during production makes it an innovative choice for sustainable pottery compared to conventional earthen clay.
Cost Analysis and Accessibility
Nano-enhanced clay offers higher performance and durability in pottery but comes at a significantly higher cost due to advanced manufacturing processes and specialized materials. Earthen clay remains more accessible and affordable, widely sourced from natural deposits with minimal processing, making it the preferred choice for artisans and hobbyists. Cost analysis favors earthen clay for budget-conscious projects, while nano-enhanced clay suits premium products where enhanced strength justifies the expense.
Applications in Modern Pottery and Art
Nano-enhanced clay offers superior tensile strength and faster drying times, making it ideal for intricate, high-detail pottery and modern sculptural art. Earthen clay retains natural textures and traditional warmth, preferred for rustic pottery and large-scale ceramic artworks. Both materials expand creative possibilities, with nano-enhanced clay catering to contemporary precision and earthen clay supporting classic, tactile aesthetics.
Future Trends in Pottery Materials
Nano-enhanced clay integrates nanoparticles to improve plasticity, firing strength, and surface finish, offering greater durability and fine detailing compared to traditional earthen clay. Future trends in pottery materials emphasize sustainability and functional performance, with nanotechnology enabling faster drying times, reduced cracking, and enhanced thermal resistance. Innovation in these advanced clays promises new applications in both artistic pottery and industrial ceramics, fostering a shift toward smarter, more efficient production methods.
Infographic: Nano-enhanced clay vs Earthen clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com