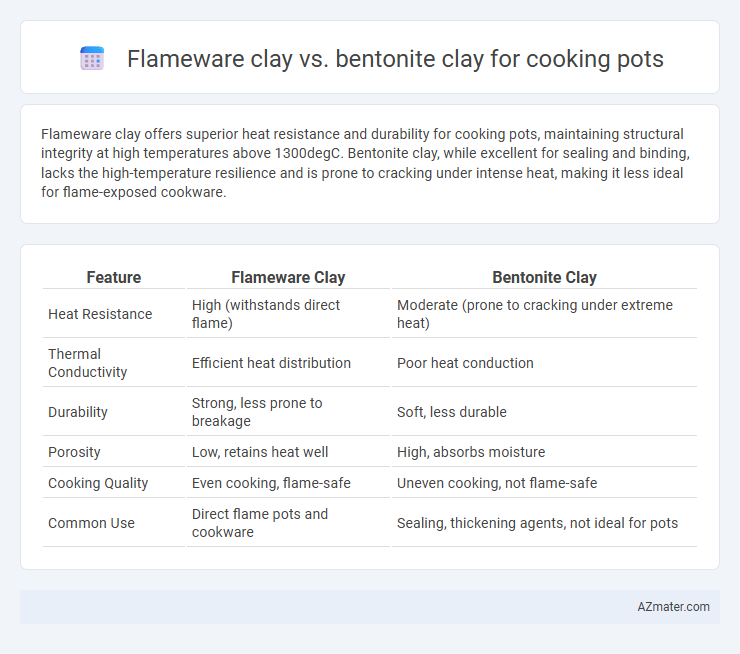
Flameware clay offers superior heat resistance and durability for cooking pots, maintaining structural integrity at high temperatures above 1300degC. Bentonite clay, while excellent for sealing and binding, lacks the high-temperature resilience and is prone to cracking under intense heat, making it less ideal for flame-exposed cookware.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flameware Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | High (withstands direct flame) | Moderate (prone to cracking under extreme heat) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Efficient heat distribution | Poor heat conduction |
| Durability | Strong, less prone to breakage | Soft, less durable |
| Porosity | Low, retains heat well | High, absorbs moisture |
| Cooking Quality | Even cooking, flame-safe | Uneven cooking, not flame-safe |
| Common Use | Direct flame pots and cookware | Sealing, thickening agents, not ideal for pots |
Introduction to Flameware Clay and Bentonite Clay
Flameware clay is a specially formulated ceramic material designed to withstand high temperatures, making it ideal for cooking pots that require thermal shock resistance and durability. Bentonite clay, derived from volcanic ash, is known for its excellent swelling properties and is often used as a natural binder or sealant, but it lacks the heat resistance necessary for direct use in cooking vessels. While Flameware clay ensures even heat distribution and longevity in cookware, Bentonite clay primarily serves supplementary roles in pottery and sealing rather than withstanding direct cooking temperatures.
Composition and Properties of Flameware Clay
Flameware clay is primarily composed of high alumina and kaolin, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and ideal for direct flame cooking, while bentonite clay consists mainly of montmorillonite, renowned for its swelling properties but less suited for high-temperature cookware. Flameware clay's dense microstructure and low porosity provide excellent durability and heat retention, allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. In contrast, bentonite's absorbent nature and lower firing temperature limit its use in flameware cooking pots.
Composition and Characteristics of Bentonite Clay
Bentonite clay, primarily composed of montmorillonite, is known for its exceptional swelling properties, high cation exchange capacity, and strong plasticity, making it highly absorbent and moldable. Unlike Flameware clay, which is formulated to withstand rapid thermal shocks and high temperatures due to its refractory minerals, Bentonite's natural composition provides superior binding and moisture retention but lower heat resistance. This makes Bentonite clay ideal for potting molds and coatings rather than direct exposure to intense heat in cooking pots.
Heat Resistance: Which Clay Handles Flames Better?
Flameware clay, specifically engineered for high-temperature applications, exhibits superior heat resistance compared to bentonite clay, making it ideal for direct flame cooking pots. Bentonite clay, while excellent for its plasticity and swelling properties, lacks the structural integrity to withstand prolonged exposure to intense heat without cracking. Therefore, flameware clay handles flames better by maintaining durability and thermal stability under extreme cooking conditions.
Durability and Longevity in Cooking Applications
Flameware clay offers exceptional durability and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for cooking pots subjected to high heat and rapid temperature changes. Bentonite clay, while useful for sealing and binding, lacks the structural strength and heat tolerance needed for prolonged cooking applications. Flameware's enhanced longevity ensures cookware maintains integrity and performance over extended use, outperforming bentonite-based alternatives in durability.
Safety and Health Considerations
Flameware clay, known for its high thermal resistance, is often favored for cooking pots due to its non-toxic and food-safe properties, minimizing the risk of harmful chemical leaching during cooking. Bentonite clay, while beneficial in cosmetic and industrial applications, may contain impurities or heavy metals that pose health concerns if used in cookware without proper processing and certification. Prioritizing flameware clay ensures safer cooking by preventing contamination and maintaining food integrity under high heat conditions.
Impact on Food Flavor and Aroma
Flameware clay imparts a subtle earthy aroma and retains natural mineral notes, enhancing the depth of food flavor during cooking. Bentonite clay, known for its high absorbency, may slightly alter the taste by drawing out certain flavors, which can result in a milder, less intense aroma. Choosing Flameware clay over Bentonite clay preserves the authentic, robust flavors of dishes, making it ideal for recipes prioritizing enhanced sensory appeal.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Flameware clay offers superior non-porous properties, making it easier to clean and maintain as it resists absorbing food odors and stains compared to Bentonite clay. Bentonite clay's porous nature requires more thorough cleaning to prevent residue buildup and potential bacterial growth, necessitating regular deep scrubbing and drying. Proper maintenance of Flameware clay often involves simple wiping or gentle washing, while Bentonite clay pots demand cautious drying to avoid cracking due to moisture retention.
Cost and Accessibility Comparison
Flameware clay typically costs more than bentonite clay due to its specialized formulation designed for high-heat cooking applications, making it less accessible for casual cooks. Bentonite clay is widely available and more affordable, commonly used in various industries including cooking pots, offering cost efficiency without compromising basic heat resistance. For budget-conscious consumers, bentonite clay provides greater accessibility in both retail and online markets, while flameware clay remains a premium option with limited availability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Clay for Cooking Pots
Flameware clay offers excellent heat retention and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking and baking applications. Bentonite clay provides superior thermal shock resistance and natural non-stick properties, which enhance cooking performance and ease of cleaning. When choosing the best clay for cooking pots, consider Flameware for robust, long-lasting cookware and Bentonite for versatile, user-friendly pots with enhanced thermal handling.
Infographic: Flameware clay vs Bentonite clay for Cooking pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com