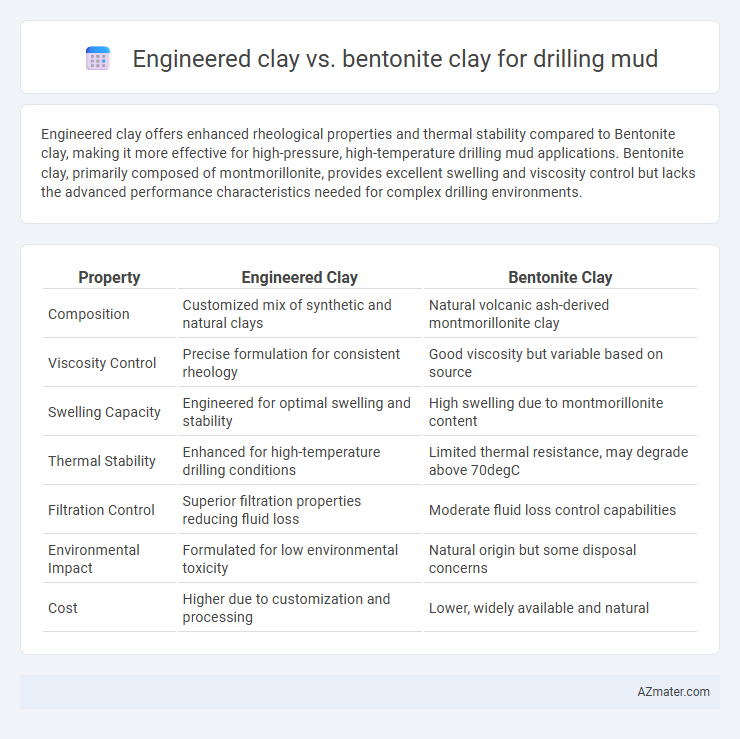
Engineered clay offers enhanced rheological properties and thermal stability compared to Bentonite clay, making it more effective for high-pressure, high-temperature drilling mud applications. Bentonite clay, primarily composed of montmorillonite, provides excellent swelling and viscosity control but lacks the advanced performance characteristics needed for complex drilling environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Engineered Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Customized mix of synthetic and natural clays | Natural volcanic ash-derived montmorillonite clay |
| Viscosity Control | Precise formulation for consistent rheology | Good viscosity but variable based on source |
| Swelling Capacity | Engineered for optimal swelling and stability | High swelling due to montmorillonite content |
| Thermal Stability | Enhanced for high-temperature drilling conditions | Limited thermal resistance, may degrade above 70degC |
| Filtration Control | Superior filtration properties reducing fluid loss | Moderate fluid loss control capabilities |
| Environmental Impact | Formulated for low environmental toxicity | Natural origin but some disposal concerns |
| Cost | Higher due to customization and processing | Lower, widely available and natural |
Introduction to Drilling Muds
Drilling muds are essential fluids in the drilling industry, designed to cool the drill bit, remove cuttings, and stabilize the borehole. Engineered clay, often formulated with specific additives, offers tailored rheological properties and enhanced thermal resistance compared to natural bentonite clay. Bentonite clay, primarily composed of montmorillonite, is highly valued for its excellent swelling and sealing capabilities but may require modification to meet complex drilling conditions.
Overview of Engineered Clay
Engineered clay is specifically designed to enhance drilling mud performance by improving viscosity, filtrate control, and thermal stability compared to natural clays like bentonite. It often incorporates synthetic additives or modified clay minerals tailored to withstand harsh drilling conditions and reduce formation damage. Engineered clay formulations provide superior suspension properties and optimize borehole stability during complex drilling operations.
Understanding Bentonite Clay
Bentonite clay, a highly absorbent and swelling type of engineered clay, is widely used in drilling mud due to its exceptional ability to form a viscous, thixotropic fluid that stabilizes boreholes and controls fluid loss. Unlike other engineered clays, bentonite contains montmorillonite, which enables it to expand up to 15 times its dry volume when hydrated, providing superior sealing and lubrication in drilling operations. Its unique mineral composition and rheological properties make bentonite indispensable for maintaining wellbore stability and enhancing the efficiency of drilling mud formulations.
Key Properties Comparison
Engineered clay exhibits enhanced viscosity and better thermal stability compared to Bentonite clay, making it ideal for high-temperature drilling operations. Bentonite clay, primarily composed of montmorillonite, provides superior swelling capacity and excellent water absorption, crucial for wellbore stability and fluid loss control. Both clays differ significantly in particle size distribution and chemical composition, impacting their rheological behavior and filtration properties in drilling mud formulations.
Performance in Drilling Operations
Engineered clay exhibits superior rheological properties and enhanced thermal stability compared to Bentonite clay, leading to improved hole cleaning and reduced fluid loss in drilling operations. Bentonite clay, primarily composed of montmorillonite, offers high swelling capacity and excellent viscosity, but often struggles under high-temperature and high-salinity conditions faced in deep wells. Optimizing drilling mud with engineered clay formulations results in increased drilling efficiency, better wellbore stability, and lower risk of stuck pipe incidents.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Engineered clay, often designed with tailored chemical properties, typically exhibits lower environmental risks compared to natural bentonite clay due to reduced heavy metal content and enhanced biodegradability. Bentonite clay, widely used for its excellent swelling and sealing properties in drilling mud, can pose environmental concerns such as groundwater contamination and soil degradation if not properly managed. Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) emphasize the importance of selecting clays with minimal toxicity and improved ecological compatibility to mitigate adverse effects on surrounding ecosystems during drilling operations.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Engineered clay offers consistent rheological properties and improved filter cake quality, reducing non-productive time in drilling operations compared to Bentonite clay. Bentonite clay, while generally lower upfront in cost, often requires higher additive usage to maintain mud performance under varying downhole conditions, increasing overall expenses. Cost efficiency analysis favors engineered clay for high-performance drilling due to reduced maintenance, enhanced wellbore stability, and minimized stuck pipe incidents, leading to lower total operational costs.
Compatibility with Drilling Fluids
Engineered clay offers enhanced compatibility with various drilling fluids due to its controlled particle size and chemical composition, allowing for tailored rheological properties and suspension stability. Bentonite clay, primarily composed of montmorillonite, provides excellent swelling capacity and fluid loss control but may react adversely with high salinity or calcium-rich fluids, affecting mud performance. Selecting the appropriate clay depends on the specific drilling fluid's chemistry and operational conditions to maintain optimal viscosity, lubrication, and filter cake quality.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Engineered clay and bentonite clay differ significantly in drilling mud applications, with engineered clays offering tailored rheological properties and enhanced thermal stability critical for deep well drilling. Case studies from offshore oil rigs highlight engineered clays' superior performance in maintaining hole stability and reducing fluid loss compared to conventional bentonite-based muds. Industry applications favor engineered clays in high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) environments due to their customizable formulations and greater compatibility with synthetic additives.
Choosing the Right Clay for Drilling Projects
Engineered clay offers predictable rheological properties and enhanced stability, making it ideal for complex drilling projects requiring precise fluid control. Bentonite clay, valued for its natural swelling capacity and high viscosity, is commonly used due to its cost-effectiveness and ability to form a robust filter cake. Selecting the right clay depends on factors like borehole conditions, required fluid properties, and budget constraints, with engineered clays providing customization and bentonite excelling in traditional mud formulations.
Infographic: Engineered clay vs Bentonite clay for Drilling mud
 azmater.com
azmater.com