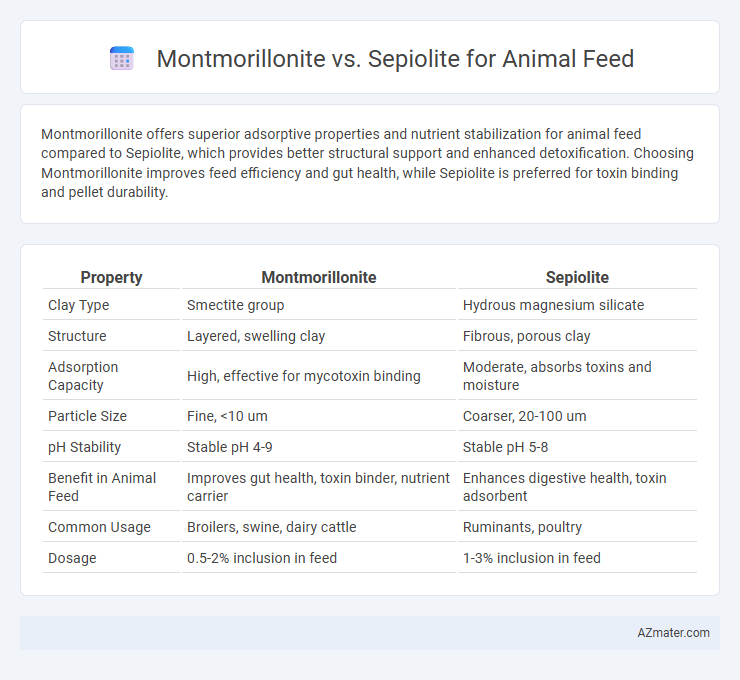
Montmorillonite offers superior adsorptive properties and nutrient stabilization for animal feed compared to Sepiolite, which provides better structural support and enhanced detoxification. Choosing Montmorillonite improves feed efficiency and gut health, while Sepiolite is preferred for toxin binding and pellet durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Montmorillonite | Sepiolite |
|---|---|---|
| Clay Type | Smectite group | Hydrous magnesium silicate |
| Structure | Layered, swelling clay | Fibrous, porous clay |
| Adsorption Capacity | High, effective for mycotoxin binding | Moderate, absorbs toxins and moisture |
| Particle Size | Fine, <10 um | Coarser, 20-100 um |
| pH Stability | Stable pH 4-9 | Stable pH 5-8 |
| Benefit in Animal Feed | Improves gut health, toxin binder, nutrient carrier | Enhances digestive health, toxin adsorbent |
| Common Usage | Broilers, swine, dairy cattle | Ruminants, poultry |
| Dosage | 0.5-2% inclusion in feed | 1-3% inclusion in feed |
Introduction to Montmorillonite and Sepiolite in Animal Feed
Montmorillonite and Sepiolite are clay minerals widely used in animal feed as natural binders and mycotoxin adsorbents, enhancing feed quality and safety. Montmorillonite, characterized by its high cation exchange capacity and swelling properties, improves nutrient absorption and intestinal health in livestock. Sepiolite's fibrous structure provides excellent moisture retention and toxin-binding capacity, supporting digestion and overall animal performance.
Chemical Composition and Structure: Montmorillonite vs Sepiolite
Montmorillonite and Sepiolite differ significantly in chemical composition and structure, affecting their suitability for animal feed applications. Montmorillonite is a swelling 2:1 clay mineral with a high cation exchange capacity due to its expandable layers of tetrahedral-octahedral-tetrahedral sheets, primarily composed of silica, alumina, and magnesium. Sepiolite is a fibrous 2:1 clay with a chain-like structure rich in magnesium silicate and lower swelling capacity, providing excellent adsorption properties and structural stability beneficial for toxin binding in animal nutrition.
Adsorption Capacity in Animal Nutrition
Montmorillonite exhibits high cation exchange capacity and superior adsorption properties, making it effective in binding toxins and enhancing nutrient retention in animal feed. Sepiolite, characterized by its fibrous structure and moderate adsorption capacity, is beneficial for reducing ammonia emissions and improving gut health in livestock. Both clays improve animal performance by adsorbing harmful substances, but Montmorillonite's greater surface area typically offers enhanced detoxification in animal nutrition.
Mycotoxin Binding Efficiency: Comparative Analysis
Montmorillonite and sepiolite, both clay minerals, exhibit distinct mycotoxin binding efficiencies in animal feed, with montmorillonite demonstrating superior adsorption capacity for aflatoxins and ochratoxins due to its higher surface area and cation exchange capacity. Sepiolite shows selective affinity for specific mycotoxins like zearalenone and fumonisins, making it effective in multi-mycotoxin contamination scenarios where diverse toxin profiles are present. Comparative studies indicate that montmorillonite's structural properties enable broader spectrum mycotoxin mitigation, while sepiolite offers targeted binding with potential synergistic use for enhanced detoxification in livestock nutrition.
Impact on Animal Health and Performance
Montmorillonite enhances animal health by improving gut integrity and nutrient absorption due to its high cation exchange capacity and swelling properties, which can reduce toxin bioavailability and support immune function. Sepiolite, with its fibrous structure and strong adsorptive capacity, effectively binds mycotoxins and improves digestive efficiency, promoting better feed conversion ratios and overall performance. Both minerals contribute to animal wellbeing, but Montmorillonite is often favored for immune modulation, while Sepiolite excels in mycotoxin adsorption and gastrointestinal health maintenance.
Influence on Feed Digestibility and Nutrient Absorption
Montmorillonite improves feed digestibility by enhancing the absorption of nutrients through its high cation exchange capacity, promoting better gut health in animals. Sepiolite, with its fibrous structure, acts as an effective adsorbent and supports microbial activity in the digestive tract, aiding nutrient uptake and toxin binding. Comparative studies indicate Montmorillonite generally offers superior nutrient bioavailability, while Sepiolite provides benefits in mycotoxin adsorption and gut motility regulation.
Dosage Recommendations and Safety Considerations
Montmorillonite and Sepiolite are commonly used clay minerals in animal feed as binders and mycotoxin adsorbents, with typical dosages ranging from 0.5% to 2% of the total feed weight for Montmorillonite and 1% to 3% for Sepiolite. Montmorillonite exhibits high cation exchange capacity, enhancing nutrient absorption, but excessive dosages may impair mineral bioavailability, necessitating careful formulation to avoid deficiencies. Sepiolite's fibrous structure offers strong adsorptive properties with demonstrated safety profiles up to 3%, although long-term safety data warrants monitoring to prevent potential gastrointestinal impacts.
Cost-Effectiveness for Livestock Producers
Montmorillonite offers superior cost-effectiveness for livestock producers due to its high adsorption capacity and widespread availability, leading to lower overall feed additive expenses. Sepiolite, while beneficial for its unique fibrous structure and toxin-binding abilities, generally comes at a higher price point, impacting budget-intensive animal feed formulations. Choosing Montmorillonite can reduce feed costs without compromising the detoxification performance crucial for animal health and productivity.
Regulatory Status and Approvals Worldwide
Montmorillonite and Sepiolite are widely used clay minerals in animal feed, with Montmorillonite gaining broader regulatory approvals due to its recognized benefits in toxin binding and nutrient delivery. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) lists Montmorillonite under authorized feed additives, while Sepiolite's regulatory status is more limited but accepted in certain countries like Spain and Japan for specific applications. Global regulatory agencies, including the FDA and Chinese Ministry of Agriculture, generally recognize Montmorillonite as safe, whereas Sepiolite requires case-by-case evaluation depending on regional feed regulations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimum Clay for Animal Feed
Montmorillonite and Sepiolite each offer unique benefits for animal feed, with Montmorillonite excelling in moisture retention and toxin adsorption while Sepiolite provides superior adsorptive capacity and nutrient stabilization. Selecting the optimum clay depends on the specific dietary needs of the animals and the feed formulation goals, with Montmorillonite often favored for its mycotoxin-binding properties and Sepiolite for its high sorption efficiency and gut health support. A balanced evaluation of clay mineralogy, particle size, and cation exchange capacity ensures the best choice for enhancing animal nutrition and feed safety.
Infographic: Montmorillonite vs Sepiolite for Animal Feed
 azmater.com
azmater.com