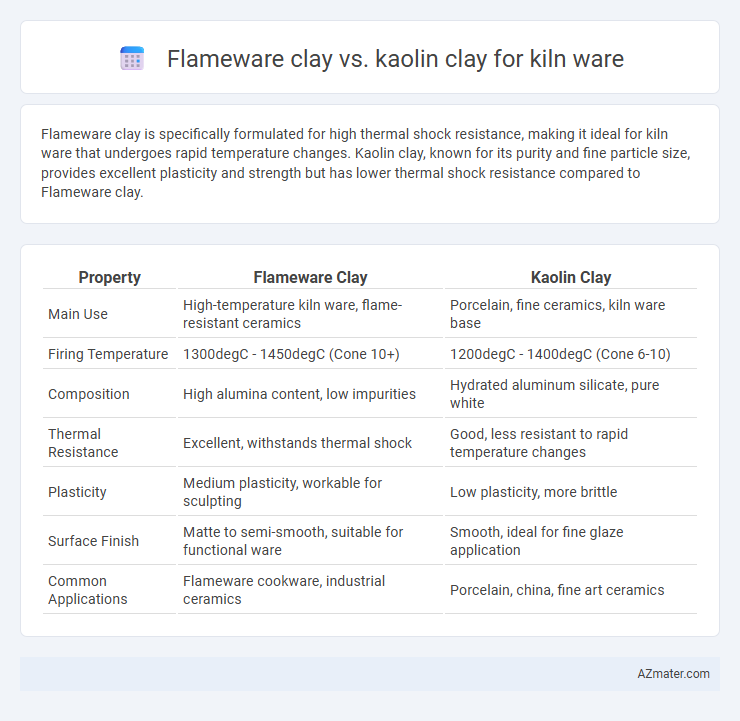
Flameware clay is specifically formulated for high thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for kiln ware that undergoes rapid temperature changes. Kaolin clay, known for its purity and fine particle size, provides excellent plasticity and strength but has lower thermal shock resistance compared to Flameware clay.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Flameware Clay | Kaolin Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Main Use | High-temperature kiln ware, flame-resistant ceramics | Porcelain, fine ceramics, kiln ware base |
| Firing Temperature | 1300degC - 1450degC (Cone 10+) | 1200degC - 1400degC (Cone 6-10) |
| Composition | High alumina content, low impurities | Hydrated aluminum silicate, pure white |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent, withstands thermal shock | Good, less resistant to rapid temperature changes |
| Plasticity | Medium plasticity, workable for sculpting | Low plasticity, more brittle |
| Surface Finish | Matte to semi-smooth, suitable for functional ware | Smooth, ideal for fine glaze application |
| Common Applications | Flameware cookware, industrial ceramics | Porcelain, china, fine art ceramics |
Introduction to Flameware and Kaolin Clays
Flameware clay is a specialized ceramic material designed for high-temperature kiln applications, valued for its excellent thermal shock resistance and durability during repeated firings. Kaolin clay, also known as china clay, is a primary ingredient in porcelain and ceramic production prized for its purity, fine particle size, and high refractory properties. Both clays serve essential roles in kiln ware, with Flameware optimized for functional and decorative heat-tolerant pieces, while Kaolin provides a strong, white, and smooth base ideal for precise ceramic forms.
Chemical Composition Differences
Flameware clay contains higher amounts of feldspar and silica, which provide greater thermal shock resistance and durability compared to Kaolin clay. Kaolin clay primarily consists of kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), offering purity and whiteness but lower vitrification temperatures, affecting strength under high heat. The chemical composition difference impacts their firing behavior: Flameware clay's fluxing agents allow for better shrinkage control and glaze adhesion in kiln ware applications.
Thermal Shock Resistance Comparison
Flameware clay exhibits superior thermal shock resistance compared to kaolin clay, making it ideal for kiln ware subjected to rapid temperature changes. This enhanced resistance stems from Flameware's grog and refractory component blend, which minimizes cracking during intense heating and cooling cycles. Kaolin clay, while purer and smoother, tends to have lower thermal shock tolerance, increasing the risk of fracture under thermal stress.
Strength and Durability in High-Temperature Firing
Flameware clay offers superior strength and durability for kiln ware due to its high alumina content, enabling it to withstand extreme high-temperature firing without warping or cracking. Kaolin clay, while valued for its purity and smooth texture, typically has lower thermal shock resistance compared to flameware, making it less ideal for intense kiln use. The enhanced refractory properties of flameware clay contribute to longer-lasting, more robust ceramic pieces in industrial and artistic high-temperature applications.
Workability and Forming Techniques
Flameware clay offers superior workability due to its smoother texture and higher plasticity, making it ideal for hand-building and intricate forming techniques in kiln ware. Kaolin clay, known for its purity and refractory properties, has a stiffer consistency, which can challenge sculpting but excels in wheel throwing and slip casting. Both clays respond differently to forming methods, with Flameware providing easier manipulation for detailed shapes and Kaolin delivering structural strength and durability during firing.
Compatibility with Glazes
Flameware clay exhibits high thermal shock resistance, making it compatible with most glazes without causing cracks or crazing during firing. Kaolin clay, known for its purity and refractory properties, provides a smooth surface ideal for glaze adhesion but may require careful matching of thermal expansion coefficients to avoid glaze defects. Choosing between Flameware and Kaolin clay depends on the desired kiln temperature and glaze formulation to ensure optimal glaze compatibility and durability.
Firing Temperature Ranges
Flameware clay typically fires within a temperature range of cone 05 to cone 06 (approximately 1828degF to 1945degF), making it suitable for low-fire kiln ware with durability and good thermal shock resistance. Kaolin clay, on the other hand, fires at much higher temperatures, between cone 9 and cone 12 (approximately 2300degF to 2345degF), producing highly vitrified, porcelain-like kiln ware with increased strength and translucency. The distinct firing temperature ranges of Flameware and Kaolin clays determine their appropriate applications in kiln ware, balancing thermal performance and finished product characteristics.
Common Applications in Kiln Ware
Flameware clay, known for its high plasticity and thermal shock resistance, is commonly used in creating functional kiln ware such as plates, bowls, and cookware that require durability and frequent temperature changes. Kaolin clay, prized for its purity and white firing properties, is primarily utilized in producing fine porcelain, sanitary ware, and electrical insulators due to its low shrinkage and high refractory quality. Both clays are essential in kiln ware but serve distinct roles based on the finished product's strength, appearance, and thermal performance requirements.
Pros and Cons: Flameware vs Kaolin Clay
Flameware clay offers excellent thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for kiln ware subjected to rapid temperature changes, but it can be less plastic and harder to shape compared to Kaolin clay. Kaolin clay provides superior smoothness, whiteness, and fine texture, which enhances detail in ceramic pieces, though it tends to be more brittle and less resistant to thermal shock than Flameware clay. Choosing between Flameware and Kaolin clay depends on prioritizing heat resilience for functional ware or surface quality for refined ornamental ceramics.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Kiln Projects
Flameware clay offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln projects such as flameware or flameproof pottery. Kaolin clay, known for its purity and smooth texture, excels in porcelain and delicate kiln-fired ceramics but is less resistant to thermal shock compared to Flameware. Selecting the right clay depends on your project's thermal requirements and desired finish, with Flameware preferred for functional, heat-resistant ware and Kaolin favored for fine, refined ceramics.
Infographic: Flameware clay vs Kaolin clay for Kiln ware
 azmater.com
azmater.com