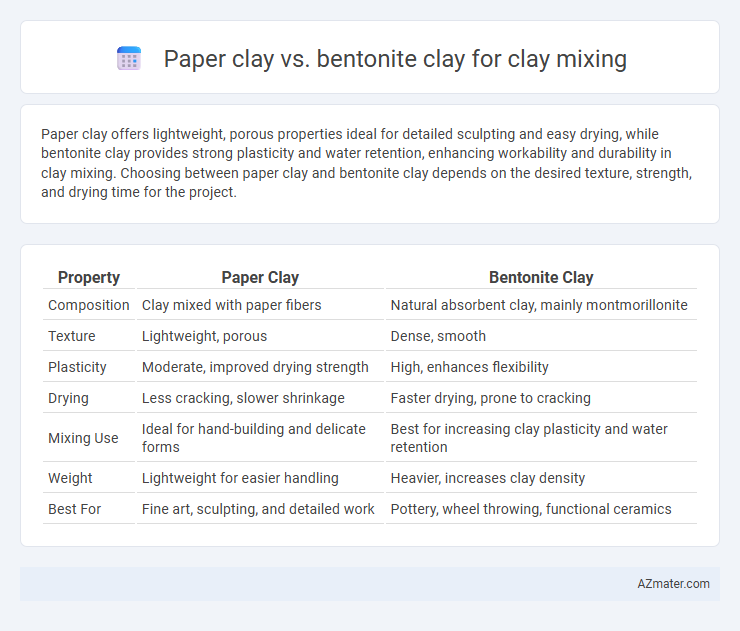
Paper clay offers lightweight, porous properties ideal for detailed sculpting and easy drying, while bentonite clay provides strong plasticity and water retention, enhancing workability and durability in clay mixing. Choosing between paper clay and bentonite clay depends on the desired texture, strength, and drying time for the project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Paper Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay mixed with paper fibers | Natural absorbent clay, mainly montmorillonite |
| Texture | Lightweight, porous | Dense, smooth |
| Plasticity | Moderate, improved drying strength | High, enhances flexibility |
| Drying | Less cracking, slower shrinkage | Faster drying, prone to cracking |
| Mixing Use | Ideal for hand-building and delicate forms | Best for increasing clay plasticity and water retention |
| Weight | Lightweight for easier handling | Heavier, increases clay density |
| Best For | Fine art, sculpting, and detailed work | Pottery, wheel throwing, functional ceramics |
Introduction to Clay Mixing: Paper Clay vs Bentonite Clay
Paper clay, composed of traditional clay blended with cellulose fiber, enhances drying strength and flexibility in ceramic projects, making it ideal for hand-building and sculptural work. Bentonite clay, derived from volcanic ash, offers superior plasticity and binding properties, improving the workability and cohesion of clay mixtures in wheel throwing and casting. Choosing between paper clay and bentonite clay depends on the desired texture, drying time, and structural requirements of the ceramic piece.
Composition and Origins of Paper Clay
Paper clay consists of traditional clay mixed with cellulose fibers sourced from recycled paper, enhancing its tensile strength and flexibility during drying and firing. Bentonite clay, derived from volcanic ash, is primarily composed of montmorillonite, known for its high plasticity and swelling properties. The cellulose content in paper clay reduces shrinkage and cracking, making it suitable for intricate sculpting, whereas bentonite's absorbent nature improves water retention and plasticity in clay mixing.
What is Bentonite Clay? Key Properties
Bentonite clay is a highly absorbent natural clay consisting primarily of montmorillonite, known for its exceptional swelling and water-retention capabilities. Key properties of bentonite clay include its fine particle size, plasticity, and ability to create strong bonds when mixed with water, making it ideal for enhancing the workability and durability of clay mixtures. Unlike paper clay, bentonite clay improves moisture retention and structural integrity, which benefits ceramic projects requiring increased strength and shrinkage control.
Workability and Texture Comparison
Paper clay offers enhanced workability due to its lightweight fiber content, making it easier to shape and less prone to cracking during drying compared to Bentonite clay, which is denser and more plastic but can become sticky and difficult to handle when overworked. Bentonite clay provides a smoother, more cohesive texture ideal for detailed sculpting, while paper clay's texture is more porous and flexible, allowing for better drying and rebonding between joins. The choice between the two depends on project requirements; paper clay excels in reduced shrinkage and repairability, whereas Bentonite clay delivers superior plasticity and surface finish.
Water Absorption and Plasticity Differences
Paper clay exhibits higher water absorption due to its cellulose fiber content, enhancing its ability to retain moisture and increase workability during the shaping process. Bentonite clay, rich in montmorillonite minerals, offers superior plasticity and swelling capacity, which improves moldability but can cause excessive stickiness if mixed with too much water. The distinct balance between water absorption in paper clay and plasticity in bentonite clay makes each suited for different ceramic and sculpting applications requiring varied moisture control and flexibility.
Strength and Durability in Finished Pieces
Paper clay enhances strength and durability in finished pieces by integrating cellulose fibers, which create a more flexible and resilient structure during drying and firing. Bentonite clay improves plasticity and adhesion but can lead to brittleness if overused, reducing long-term durability. Combining paper clay with bentonite optimizes the balance, resulting in stronger, more durable ceramic artworks.
Firing Temperatures and Shrinkage Rates
Paper clay typically fires at cone 04 to cone 06 (approximately 1828degF to 1945degF) with low shrinkage rates around 4-6%, making it ideal for hand-building and mixed clay bodies. Bentonite clay, with a firing temperature range of cone 06 to cone 10 (1828degF to 2345degF), exhibits higher shrinkage rates often exceeding 10%, which can affect the structural integrity during firing. Combining paper clay with bentonite reduces overall shrinkage and enhances workability while maintaining stable firing properties for various ceramic applications.
Common Applications in Ceramics and Sculpture
Paper clay enhances ceramic sculpture by adding tensile strength and reducing drying time, making it ideal for hand-building and delicate sculptural work. Bentonite clay improves plasticity and moisture retention, which benefits wheel-throwing and slab construction by increasing workability and minimizing cracking. Both clays are widely used in ceramics; paper clay is preferred for lightweight, intricate designs, while bentonite is favored for its robust binding properties in sturdy forms.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Paper clay incorporates recycled cellulose fibers, significantly reducing raw material extraction and promoting waste repurposing, resulting in a lower environmental footprint compared to bentonite clay. Bentonite clay mining often leads to habitat disruption and soil degradation, raising sustainability concerns, whereas paper clay supports circular economy principles by utilizing renewable resources. The biodegradability of paper clay also enhances its eco-friendliness, contrasting with bentonite's slower natural regeneration and energy-intensive processing.
Choosing the Right Clay: Factors to Consider
Paper clay enhances workability and drying flexibility by incorporating cellulose fibers, making it ideal for lightweight, sculptural projects and reducing cracking during firing. Bentonite clay offers high plasticity and binding properties, improving clay's cohesiveness and water retention, which is essential for wheel-throwing and hand-building techniques requiring strength. Consider project type, drying time, structural needs, and firing temperature compatibility when choosing between paper clay and bentonite clay for optimized clay mixing performance.
Infographic: Paper clay vs Bentonite clay for Clay mixing
 azmater.com
azmater.com