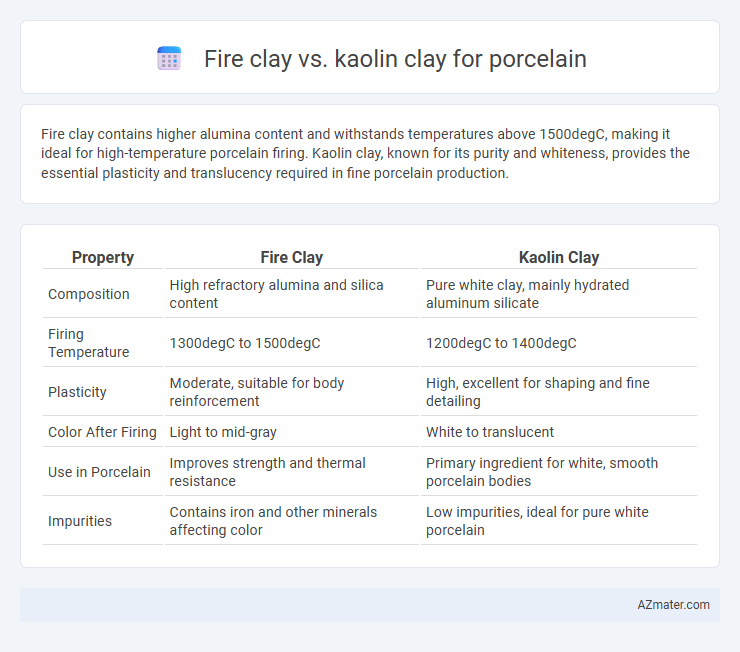
Fire clay contains higher alumina content and withstands temperatures above 1500degC, making it ideal for high-temperature porcelain firing. Kaolin clay, known for its purity and whiteness, provides the essential plasticity and translucency required in fine porcelain production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fire Clay | Kaolin Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High refractory alumina and silica content | Pure white clay, mainly hydrated aluminum silicate |
| Firing Temperature | 1300degC to 1500degC | 1200degC to 1400degC |
| Plasticity | Moderate, suitable for body reinforcement | High, excellent for shaping and fine detailing |
| Color After Firing | Light to mid-gray | White to translucent |
| Use in Porcelain | Improves strength and thermal resistance | Primary ingredient for white, smooth porcelain bodies |
| Impurities | Contains iron and other minerals affecting color | Low impurities, ideal for pure white porcelain |
Introduction to Fire Clay and Kaolin Clay
Fire clay, a refractory material rich in alumina and silica, withstands high temperatures and is commonly used as a foundational component in porcelain manufacturing to enhance thermal resistance and durability. Kaolin clay, known for its fine particle size and high purity of alumina and silica, imparts whiteness and plasticity to porcelain, enabling smooth shaping and a refined finished texture. Combining fire clay and kaolin clay optimizes porcelain's strength, translucency, and thermal stability, making the blend essential in high-quality ceramic production.
Chemical Composition Differences
Fire clay contains higher amounts of impurities such as iron oxide and quartz, contributing to its refractory properties and making it suitable for high-temperature applications in porcelain production. Kaolin clay is primarily composed of the mineral kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), which provides exceptional whiteness and plasticity essential for fine porcelain. The chemical difference lies in kaolin's higher purity with low levels of fluxing agents, whereas fire clay's complex mineral composition affects firing temperature and porcelain translucency.
Physical Properties Comparison
Fire clay exhibits higher refractory properties with a melting point above 1580degC, making it ideal for high-temperature porcelain firing, while kaolin clay has a lower melting point around 1400-1540degC, providing excellent plasticity and whiteness. Fire clay's coarse particle size offers enhanced thermal shock resistance and strength, whereas kaolin's fine particle size ensures smooth texture and translucency in finished porcelain. The mineral composition of fire clay, rich in alumina and silica, contrasts with kaolin's high kaolinite content, influencing the porcelain's durability and aesthetic qualities.
Porcelain Firing Temperatures
Fire clay and kaolin clay differ significantly in their firing temperatures when used in porcelain production. Fire clay typically vitrifies at higher firing temperatures, around 1300degC to 1400degC, enhancing thermal shock resistance and structural strength. Kaolin clay, essential for porcelain's whiteness and translucency, matures at slightly lower temperatures between 1200degC and 1350degC, contributing to the fine, smooth texture and delicate appearance characteristic of high-quality porcelain.
Plasticity and Workability in Porcelain
Fire clay offers higher plasticity and workability compared to kaolin clay, making it better suited for shaping intricate porcelain forms. Kaolin clay, while less plastic, provides exceptional whiteness and hardness after firing, contributing to the classic porcelain finish. Combining fire clay with kaolin enhances the overall workability without compromising the strength and translucency of the final porcelain product.
Impact on Porcelain Whiteness
Fire clay contains higher impurities and iron content, which can cause a slight gray or off-white tint in porcelain, reducing its overall whiteness. Kaolin clay, especially the pure white variety, is prized for its minimal iron content, contributing to the bright, translucent white finish characteristic of high-quality porcelain. Selecting kaolin for porcelain production significantly enhances whiteness and aesthetic appeal compared to fire clay.
Strength and Durability of Finished Porcelain
Fire clay contains a higher percentage of alumina, enhancing the strength and thermal shock resistance of porcelain products. Kaolin clay contributes to the smooth texture and whiteness but offers lower mechanical strength compared to fire clay. Porcelain blends with fire clay yield more durable and robust finished items, ideal for applications requiring high strength and longevity.
Applications in Porcelain Production
Fire clay exhibits high refractory properties and excellent thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for porcelain kiln furniture and high-temperature applications in porcelain production. Kaolin clay, rich in alumina and silica, provides whiteness, plasticity, and structural strength essential for forming fine porcelain bodies and achieving translucency. Combining fire clay and kaolin optimizes both durability and aesthetic qualities in porcelain manufacturing processes.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Fire clay is generally more affordable and widely available compared to kaolin clay, making it a cost-effective option for porcelain production. Kaolin clay, prized for its purity and whiteness, often commands a higher price and may be harder to source depending on geographic location. Manufacturers balance these factors by selecting fire clay for budget-sensitive projects while reserving kaolin for high-quality, fine porcelain due to its superior plasticity and whiteness.
Choosing the Best Clay for Porcelain Making
Fire clay and kaolin clay each offer distinct properties essential for porcelain making, with fire clay providing high plasticity and excellent thermal resistance, while kaolin clay is prized for its whiteness, purity, and translucency. The best choice depends on the desired porcelain characteristics; kaolin is ideal for fine, translucent porcelain due to its low impurity levels, whereas fire clay enhances durability and firing stability in stoneware or more robust porcelain types. Selecting the optimal clay involves considering composition, particle size, and firing temperature to achieve the balance of strength, aesthetics, and workability required for high-quality porcelain.
Infographic: Fire clay vs Kaolin clay for Porcelain
 azmater.com
azmater.com