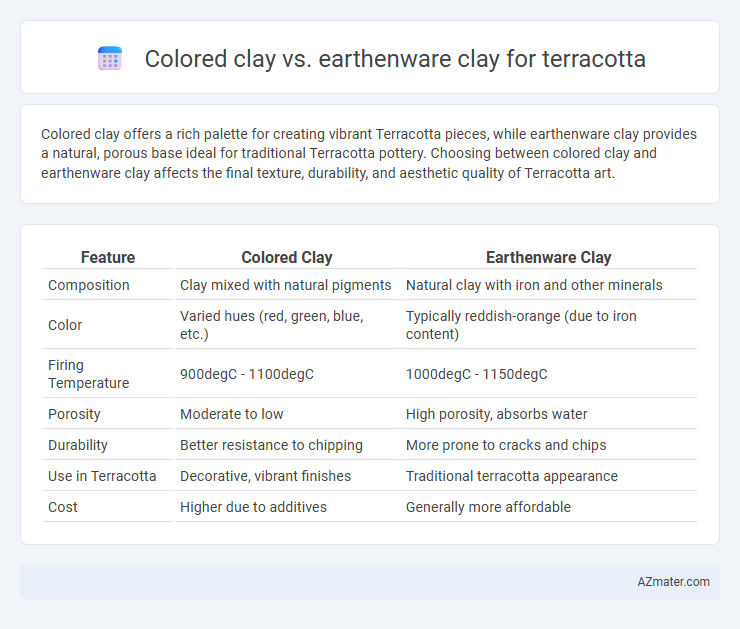
Colored clay offers a rich palette for creating vibrant Terracotta pieces, while earthenware clay provides a natural, porous base ideal for traditional Terracotta pottery. Choosing between colored clay and earthenware clay affects the final texture, durability, and aesthetic quality of Terracotta art.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Colored Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay mixed with natural pigments | Natural clay with iron and other minerals |
| Color | Varied hues (red, green, blue, etc.) | Typically reddish-orange (due to iron content) |
| Firing Temperature | 900degC - 1100degC | 1000degC - 1150degC |
| Porosity | Moderate to low | High porosity, absorbs water |
| Durability | Better resistance to chipping | More prone to cracks and chips |
| Use in Terracotta | Decorative, vibrant finishes | Traditional terracotta appearance |
| Cost | Higher due to additives | Generally more affordable |
Introduction: Understanding Colored Clay and Earthenware Clay
Colored clay, containing natural mineral pigments, offers a vibrant palette for creating unique terracotta pieces, enhancing aesthetic appeal with hues ranging from reds to greens. Earthenware clay, characterized by its porous texture and firing temperature between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, serves as the traditional base for terracotta, providing durability and workability. Understanding the mineral composition and firing properties of both clays is essential for achieving desired color intensity and structural integrity in terracotta art.
Composition Differences: Colored Clay vs Earthenware Clay
Colored clay for terracotta incorporates natural or synthetic mineral pigments, such as iron oxide, manganese, or copper compounds, altering its color profile while maintaining similar plasticity. Earthenware clay primarily consists of natural hydrated aluminosilicates with variable iron oxide content, typically yielding a reddish-brown hue after firing. The key composition difference lies in the intentional addition of colorants in colored clay, whereas earthenware clay relies on the mineral content naturally present within the clay body.
Color Variations and Pigments
Colored clay for terracotta offers a broader palette of hues directly integrated into the material, resulting in consistent color throughout the piece, while earthenware clay relies primarily on natural pigments and firing conditions to achieve its characteristic warm, reddish-brown tones. Colored clays often incorporate mineral oxides such as iron, cobalt, or manganese to deliver vibrant reds, blues, or blacks, providing more control over color intensity and variation. Earthenware clay's color variations depend largely on its mineral composition and the atmosphere of the kiln, leading to subtle shifts in shade and texture that highlight a more organic and earthy aesthetic.
Texture and Workability Comparison
Colored clay for terracotta offers a smoother texture with fine grains, enhancing detail and surface finish, while earthenware clay tends to be coarser and more porous, providing a rustic aesthetic. Workability is typically easier with colored clay due to its consistent plasticity, allowing for precise shaping and reduced cracking during drying. Earthenware clay, though slightly less plastic, exhibits good bonding properties and is preferred for traditional, thicker terracotta pieces.
Firing Temperatures and Methods
Colored clay for terracotta typically contains iron oxides and other mineral additives that influence its firing temperature, often ranging from 1000degC to 1150degC, resulting in vibrant hues after firing. Earthenware clay generally fires at lower temperatures between 950degC and 1100degC, producing a porous and slightly brittle ceramic body suitable for traditional terracotta uses. Firing methods for both clays include oxidation atmospheres in electric or gas kilns to achieve desired physical properties and color development.
Strength and Durability Factors
Colored clay for terracotta often contains added minerals and pigments that can enhance its compressive strength and resistance to wear compared to traditional earthenware clay. Earthenware clay, while naturally porous and softer, requires thorough firing at lower temperatures, which may result in less durability and increased susceptibility to chipping or cracking under stress. For applications demanding higher structural integrity and longevity, colored clay formulations typically offer superior strength and durability due to their modified composition and firing characteristics.
Porosity and Water Absorption
Colored clay for terracotta typically exhibits lower porosity and reduced water absorption compared to traditional earthenware clay, making it more resistant to moisture. Earthenware clay, known for its higher porosity, absorbs more water, which can affect the durability of terracotta products exposed to weather. Understanding the porosity differences between colored and earthenware clay is crucial for selecting the right material for functional or decorative terracotta applications.
Artistic Applications for Terracotta Creations
Colored clay offers vibrant hues directly in the material, enhancing artistic applications for terracotta creations by eliminating the need for external glazes and maintaining natural textures. Earthenware clay, with its porous nature and warm reddish-brown tones, provides a classic base ideal for detailed hand-building and surface carving in terracotta art. Both clays support intricate shaping and firing processes, but colored clay expands creative possibilities with built-in color variations essential for expressive terracotta sculptures and decorative pieces.
Cost and Availability of Each Clay Type
Colored clay for terracotta often incurs higher costs due to the inclusion of natural pigments and specialized processing, making it less readily available in standard art supply stores. Earthenware clay, commonly used in terracotta crafting, offers a more affordable option with widespread availability, as it is sourced from abundant natural materials and produced on a large scale. The price difference and accessibility make earthenware clay the preferred choice for budget-conscious artists and large-scale pottery production.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Terracotta Project
Colored clay offers vibrant hues that reduce the need for additional glazing, making it ideal for decorative terracotta projects requiring specific color palettes. Earthenware clay provides natural porosity and a warm, rustic texture perfect for traditional terracotta pottery and outdoor garden pieces. Selecting the right clay depends on the desired finish, durability, and functionality, with colored clays suited for artistic versatility and earthenware clay preferred for classic, breathable terracotta items.
Infographic: Colored clay vs Earthenware clay for Terracotta
 azmater.com
azmater.com