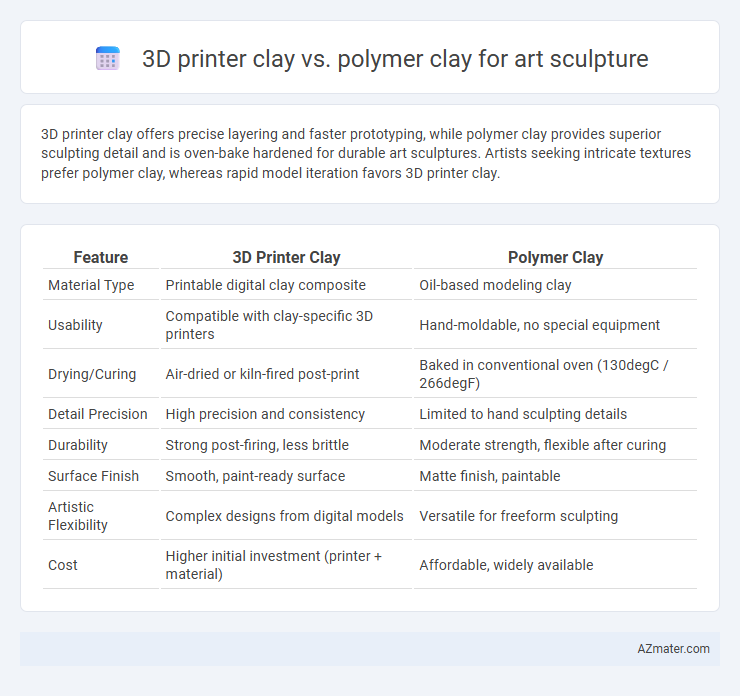
3D printer clay offers precise layering and faster prototyping, while polymer clay provides superior sculpting detail and is oven-bake hardened for durable art sculptures. Artists seeking intricate textures prefer polymer clay, whereas rapid model iteration favors 3D printer clay.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Polymer Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Printable digital clay composite | Oil-based modeling clay |
| Usability | Compatible with clay-specific 3D printers | Hand-moldable, no special equipment |
| Drying/Curing | Air-dried or kiln-fired post-print | Baked in conventional oven (130degC / 266degF) |
| Detail Precision | High precision and consistency | Limited to hand sculpting details |
| Durability | Strong post-firing, less brittle | Moderate strength, flexible after curing |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, paint-ready surface | Matte finish, paintable |
| Artistic Flexibility | Complex designs from digital models | Versatile for freeform sculpting |
| Cost | Higher initial investment (printer + material) | Affordable, widely available |
Introduction: 3D Printer Clay vs Polymer Clay in Sculpture
3D printer clay offers precise layering and customization advantages in sculpture, enabling complex shapes and detailed textures unattainable with traditional materials. Polymer clay, known for its pliability and ease of hand modeling, excels in creating smooth, organic forms with a wide range of colors and finishes. Sculptors often choose 3D printer clay for digital accuracy, while polymer clay remains favored for tactile artistry and manual craftmanship.
Material Composition and Properties
3D printer clay typically consists of ceramic-based materials combined with binders to enable precise layering and curing during the printing process, resulting in durable, heat-resistant sculptures after firing. Polymer clay is a synthetic modeling compound made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) particles suspended in a plasticizer, allowing for flexible, lightweight, and air-dry or oven-baked finished pieces. The distinct material compositions influence the properties, where 3D printer clay provides higher structural strength and detail fidelity, while polymer clay offers greater malleability and ease of use for hand-sculpting and intricate textures.
Workability: Shaping and Detailing
3D printer clay offers precise layering capabilities that enable intricate detailing and smooth surface finishes ideal for complex art sculptures. Polymer clay provides exceptional workability by allowing artists to easily mold, blend, and refine shapes manually, facilitating tactile adjustments and fine textures. While 3D printer clay excels in replicable, consistent forms, polymer clay is preferred for hands-on shaping and detailed embellishments.
Curing and Hardening Processes
3D printer clay typically cures through a layer-by-layer UV or heat curing process, allowing complex structures to harden quickly and retain fine details, suitable for precision art sculptures. Polymer clay requires manual baking in a conventional oven at temperatures between 265degF and 275degF (130degC to 135degC) for 15 to 30 minutes per quarter-inch of thickness, ensuring thorough hardening while maintaining flexibility for intricate sculpting. Both materials offer durable finishes, but 3D printer clay's curing process delivers faster, more controlled hardening compared to the time-intensive baking essential for polymer clay.
Texture and Surface Finish
3D printer clay offers a highly consistent texture and smooth surface finish due to precise layer deposition, ideal for detailed and intricate art sculptures. Polymer clay provides a more tactile, hand-molded feel with slight variations in texture that enhance the organic appearance of sculptural pieces. Surface finish of polymer clay can be customized with sanding, polishing, or painting, while 3D printer clay typically requires minimal post-processing for a clean, uniform look.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
3D printer clay offers unparalleled design flexibility, enabling artists to create highly complex and precise sculptures through digital modeling and layering techniques. Polymer clay allows for intricate hand-crafted details and organic textures but is limited by manual sculpting precision and shape complexity. Combining both materials can enhance artistic expression by leveraging 3D printing's structural complexity with polymer clay's tactile versatility.
Tools and Equipment Needed
3D printer clay requires specialized equipment such as a compatible 3D printer with precise extrusion capabilities and software for designing digital models, enabling intricate detailing and replication. Polymer clay demands basic tools including sculpting blades, rollers, and baking ovens to cure the material, making it accessible for hands-on artists without digital equipment. While 3D printer clay involves more technical setup, polymer clay offers versatile manual sculpting tools suited for traditional art forms.
Durability and Longevity
3D printer clay, often made from ceramic or resin-based materials, offers high durability and resistance to environmental factors, making it ideal for long-lasting art sculptures. Polymer clay provides flexibility and ease of use but is less durable over time, prone to cracking or fading when exposed to UV light and moisture. For sculptures requiring extended longevity, 3D printer clay delivers superior structural integrity and preservation compared to polymer clay.
Cost and Accessibility
3D printer clay offers a cost-effective solution by reducing material waste and enabling precise designs with minimal raw material, though initial investment in a 3D printer can be high. Polymer clay is more accessible for beginners and hobbyists with low upfront costs, widely available in art stores, and requires no specialized equipment. Overall, polymer clay remains the affordable choice for small-scale projects, while 3D printer clay suits artists seeking scalability and durability in complex sculptures.
Choosing the Right Clay for Artistic Vision
Choosing the right clay for artistic sculpture depends on the desired texture, durability, and detail precision, with 3D printer clay offering superior accuracy and ease of replication for intricate designs, while polymer clay excels in handcrafting flexibility and vibrant color options. 3D printer clay, compatible with advanced CAD software, enables artists to achieve complex geometries and consistent results, making it ideal for prototypes and detailed models. Polymer clay's malleability and ability to harden through baking provide a tactile experience suited for expressive, small-scale sculptures that require unique surface treatments and color blending.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Polymer clay for Art sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com