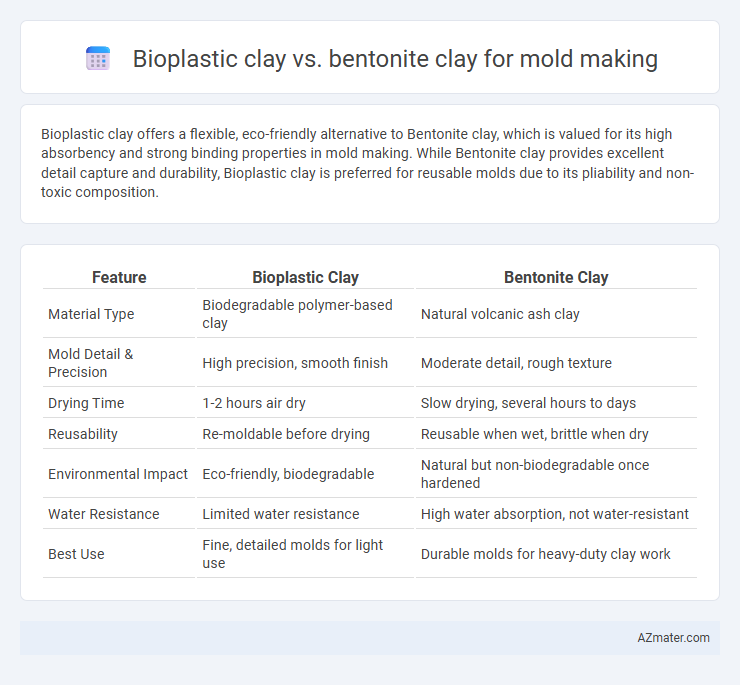
Bioplastic clay offers a flexible, eco-friendly alternative to Bentonite clay, which is valued for its high absorbency and strong binding properties in mold making. While Bentonite clay provides excellent detail capture and durability, Bioplastic clay is preferred for reusable molds due to its pliability and non-toxic composition.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioplastic Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable polymer-based clay | Natural volcanic ash clay |
| Mold Detail & Precision | High precision, smooth finish | Moderate detail, rough texture |
| Drying Time | 1-2 hours air dry | Slow drying, several hours to days |
| Reusability | Re-moldable before drying | Reusable when wet, brittle when dry |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Natural but non-biodegradable once hardened |
| Water Resistance | Limited water resistance | High water absorption, not water-resistant |
| Best Use | Fine, detailed molds for light use | Durable molds for heavy-duty clay work |
Introduction to Mold Making Clays
Mold making clays such as Bioplastic clay and Bentonite clay serve distinct purposes in crafting detailed molds. Bioplastic clay is prized for its eco-friendly composition and flexibility, making it ideal for creating reusable, non-toxic molds in artistic applications. Bentonite clay, valued for its superior absorbency and fine particle structure, excels in capturing intricate textures and forms, especially in industrial or heavy-duty mold making.
What is Bioplastic Clay?
Bioplastic clay is a biodegradable modeling material composed primarily of starches, natural polymers, and water, designed to be eco-friendly and non-toxic for mold making. Unlike Bentonite clay, which is a natural absorbent clay rich in montmorillonite used for its plasticity and water retention, bioplastic clay offers flexibility and easy cleanup without harsh chemicals. Its renewable composition makes bioplastic clay ideal for sustainable art projects and prototypes requiring lightweight, moldable substances.
What is Bentonite Clay?
Bentonite clay is a natural absorbent formed from aged volcanic ash, prized for its fine particles and excellent plasticity, making it suitable for creating detailed molds in various crafts. Unlike bioplastic clay, which is a synthetic, biodegradable modeling material, bentonite clay offers superior mold release properties and durability due to its unique swelling characteristics when hydrated. This swelling capability allows bentonite clay molds to capture intricate textures, making it a preferred choice for artists and sculptors seeking precision and flexibility in mold making.
Physical Properties Comparison
Bioplastic clay exhibits higher flexibility and lower density compared to Bentonite clay, allowing for easier manipulation and detailed mold creation. Bentonite clay offers superior plasticity and exceptional water absorption, making it ideal for molds requiring durability and moisture retention. The differing particle sizes and binding properties affect drying times, with Bentonite clay generally drying slower but resulting in more stable and rigid molds.
Environmental Impact: Bioplastic vs. Bentonite
Bioplastic clay offers a biodegradable alternative to conventional clays, reducing long-term environmental pollution through its compostable properties and renewable resources. Bentonite clay, while natural and abundant, requires intensive mining processes that can lead to habitat disruption and increased carbon emissions. Choosing bioplastic clay minimizes ecological footprint by leveraging sustainable materials and circular economy principles compared to the extraction and land degradation concerns associated with bentonite clay.
Mold Detail and Surface Quality
Bioplastic clay offers superior mold detail capture due to its fine particle consistency and flexibility, ensuring high-resolution surface textures and intricate designs are accurately replicated. Bentonite clay, while excellent for bulk mold stability, tends to have coarser particles that can slightly diminish surface finish sharpness and fine detail fidelity. For applications demanding crisp, detailed molds with smooth surface quality, bioplastic clay is generally preferred over bentonite clay.
Reusability and Longevity
Bioplastic clay offers superior reusability compared to bentonite clay because it softens when heated and hardens upon cooling, allowing multiple molding cycles without degradation. Bentonite clay, while effective for capturing fine details, tends to dry out and crack over time, limiting its longevity and reusability. For long-term mold making projects, bioplastic clay provides a more durable and reusable option, reducing material waste and maintaining consistent mold quality.
Cost Analysis: Bioplastic vs. Bentonite
Bioplastic clay typically costs significantly more than bentonite clay due to its synthetic composition and environmentally friendly properties, often ranging from $30 to $50 per pound compared to bentonite's $5 to $10 per pound. Bentonite clay's affordability makes it a preferred choice for large-scale mold making projects where budget constraints are critical. However, bioplastic clay offers long-term cost benefits by providing reusable and biodegradable molds, potentially reducing waste disposal expenses associated with bentonite clay.
Safety and Handling Considerations
Bioplastic clay offers a safer alternative for mold making due to its non-toxic composition, low dust generation, and ease of cleaning, making it ideal for indoor use and prolonged handling. Bentonite clay, while effective for mold creation, can pose respiratory risks from fine dust inhalation and requires careful handling with protective equipment such as masks and gloves to prevent skin irritation. Proper ventilation and adherence to safety guidelines are critical when working with bentonite clay to minimize health hazards.
Choosing the Right Clay for Mold Making
Bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly mold-making benefits with flexibility and non-toxic properties, making it ideal for detailed and reusable molds. Bentonite clay, known for its high plasticity and excellent water absorption, excels in creating strong, durable molds for ceramics and metal casting. Selecting the right clay depends on the mold's purpose: bioplastic clay suits lightweight, intricate designs, while bentonite clay is preferred for heavy-duty, heat-resistant molds.
Infographic: Bioplastic clay vs Bentonite clay for Mold making
 azmater.com
azmater.com