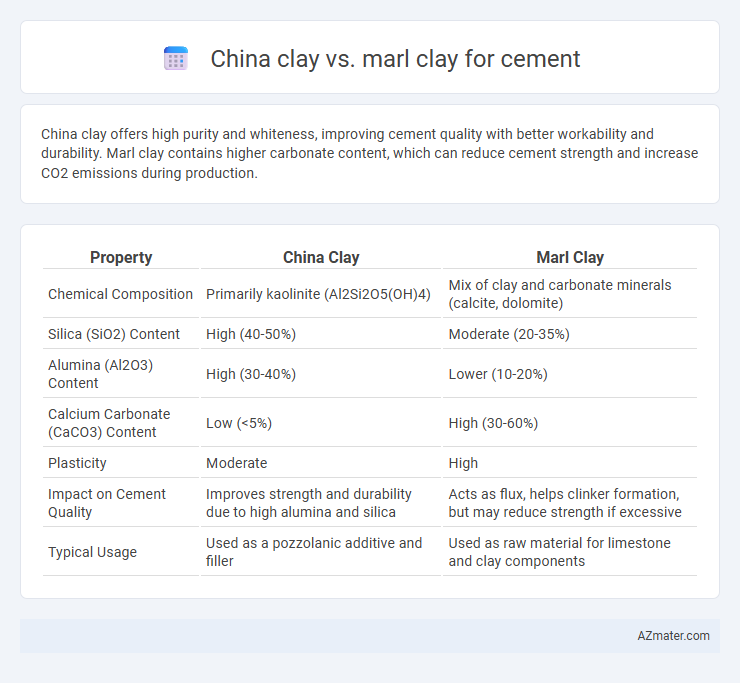
China clay offers high purity and whiteness, improving cement quality with better workability and durability. Marl clay contains higher carbonate content, which can reduce cement strength and increase CO2 emissions during production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | China Clay | Marl Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Primarily kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) | Mix of clay and carbonate minerals (calcite, dolomite) |
| Silica (SiO2) Content | High (40-50%) | Moderate (20-35%) |
| Alumina (Al2O3) Content | High (30-40%) | Lower (10-20%) |
| Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) Content | Low (<5%) | High (30-60%) |
| Plasticity | Moderate | High |
| Impact on Cement Quality | Improves strength and durability due to high alumina and silica | Acts as flux, helps clinker formation, but may reduce strength if excessive |
| Typical Usage | Used as a pozzolanic additive and filler | Used as raw material for limestone and clay components |
Introduction to China Clay and Marl Clay
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, is a fine, soft white clay essential for producing high-quality ceramics and as a subtle additive in cement to enhance workability and strength. Marl clay, containing a combination of clay and calcium carbonate, offers a naturally balanced source of silica and lime advantageous in cement manufacturing, improving the setting time and durability. Both clays contribute distinct chemical properties crucial for optimizing the performance and cost-efficiency of cement formulations.
Geological Origins and Composition
China clay, primarily kaolinite, originates from the weathering of granite and other acidic igneous rocks, characterized by a high silica and low iron content, making it ideal for producing white cement. Marl clay forms from sedimentary deposits rich in calcium carbonate and clay minerals, typically found in marine environments, contributing to cement's lime and alumina components. The distinctly different geological origins impact their mineral compositions, affecting cement properties such as color, strength, and setting time.
Chemical Properties Comparison
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), contains high levels of silica and alumina with low iron oxide and alkaline content, making it ideal for cement's chemical stability and whiteness. Marl clay, a mixture of clay and calcium carbonate (CaCO3), exhibits higher calcium and magnesium oxides, influencing cement's setting time and early strength development due to increased lime content. The lower silica and alumina in marl clay compared to China clay affects the pozzolanic activity, impacting long-term cement durability and sulfate resistance.
Physical Characteristics and Texture
China clay, also known as kaolin, exhibits a fine, smooth texture with high plasticity and whiteness, making it ideal for enhancing cement's workability and brightness. Marl clay contains a mix of clay and carbonate minerals, presenting a coarser texture with lower plasticity and higher calcium content, which can influence the setting time and strength development of cement. The physical characteristics of China clay contribute to better particle dispersion and hydration, whereas marl clay offers a more variable chemical composition affecting cement durability.
Role in Cement Manufacturing
China clay, or kaolin, enhances cement manufacturing by improving the plasticity and workability of the raw mix, contributing to better grindability and preventing clinker overheating. Marl clay, rich in calcium carbonate and clay minerals, acts as a natural fluxing agent, reducing the fuel consumption during clinker formation and aiding in the formation of essential clinker phases such as alite and belite. Both clays optimize the chemical composition of the raw material blend, ensuring consistent quality and strength in the final cement product.
Impact on Cement Quality and Strength
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, enhances cement quality by improving workability and reducing water demand, which contributes to higher early strength development. Marl clay contains significant amounts of calcium carbonate, which can act as a fluxing agent during clinker formation, potentially increasing cement strength but may also introduce variability in setting times. The distinct mineralogical properties of China clay and Marl clay influence cement hydration processes, ultimately affecting durability and mechanical performance.
Availability and Economic Considerations
China clay, also known as kaolin, is abundant in several regions of China and the United States, making it readily available but often more expensive due to refining processes. Marl clay, commonly found in Europe, especially the UK, is more widely accessible and typically less costly, as it requires minimal processing for cement production. Economic considerations favor marl clay for large-scale cement manufacturing due to lower extraction and processing costs, while china clay's higher purity can justify its use in specialized applications despite its higher price.
Environmental Implications
China clay offers lower carbon emissions during cement production due to its higher purity and lower calcination temperature compared to marl clay, which contains more impurities and requires more energy-intensive processing. The extraction of marl clay often leads to greater landscape disruption and higher water usage, increasing its environmental footprint relative to china clay. Utilizing china clay in cement manufacturing supports improved sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing resource consumption.
Industry Preferences and Applications
China clay, also known as kaolin, is valued in the cement industry for its high purity and whiteness, enhancing the quality and color of cement products. Marl clay, containing a mixture of clay and calcium carbonate, is preferred for its cost-effectiveness and contribution to the cement's strength and durability. Industry preferences lean toward china clay when superior finish and whiteness are required, whereas marl clay is favored in large-scale production for its availability and functional benefits in cement hydration.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clay for Cement
Selecting the appropriate clay for cement production hinges on the chemical and physical properties of China clay and Marl clay. China clay offers high purity with minimal impurities, resulting in consistent quality and improved strength in cement, whereas Marl clay tends to contain higher amounts of calcium carbonate and variable silica content that can affect cement setting and durability. For optimal cement performance, China clay is preferred when precise chemical composition and enhanced strength are critical, while Marl clay may be suitable for cost-sensitive applications where slight variability is acceptable.
Infographic: China clay vs Marl clay for Cement
 azmater.com
azmater.com