Geopolymer clay offers superior thermal resistance and eco-friendly properties compared to traditional terracotta clay used for bricks. Terracotta clay bricks provide excellent durability and classic aesthetic appeal but have higher carbon emissions during firing.
Table of Comparison
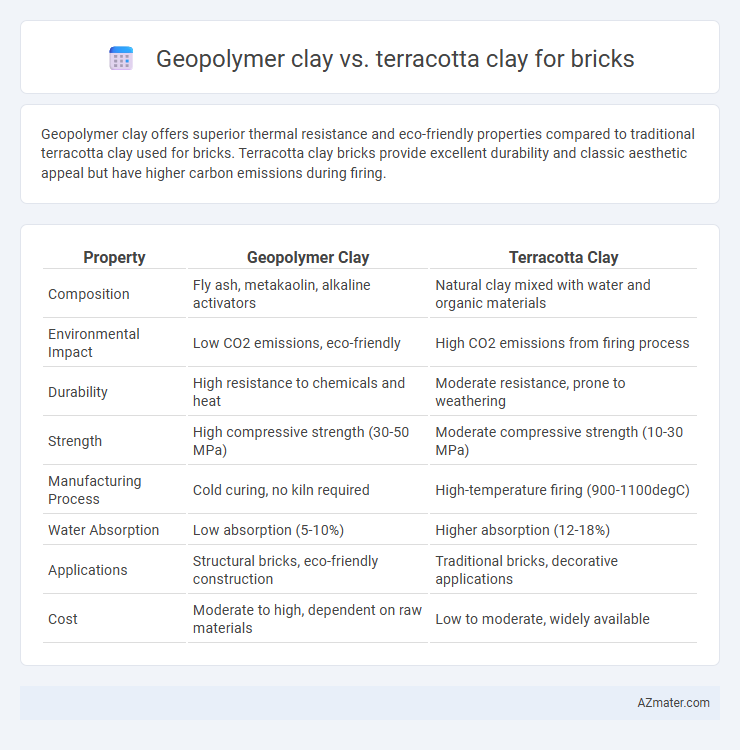
| Property | Geopolymer Clay | Terracotta Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fly ash, metakaolin, alkaline activators | Natural clay mixed with water and organic materials |
| Environmental Impact | Low CO2 emissions, eco-friendly | High CO2 emissions from firing process |
| Durability | High resistance to chemicals and heat | Moderate resistance, prone to weathering |
| Strength | High compressive strength (30-50 MPa) | Moderate compressive strength (10-30 MPa) |
| Manufacturing Process | Cold curing, no kiln required | High-temperature firing (900-1100degC) |
| Water Absorption | Low absorption (5-10%) | Higher absorption (12-18%) |
| Applications | Structural bricks, eco-friendly construction | Traditional bricks, decorative applications |
| Cost | Moderate to high, dependent on raw materials | Low to moderate, widely available |
Introduction to Geopolymer and Terracotta Clays
Geopolymer clay is an innovative material created from industrial byproducts such as fly ash and metakaolin, offering enhanced durability and eco-friendly properties for brick production. Terracotta clay, traditionally composed of natural earthen materials rich in iron oxide, is known for its porous texture and classic reddish-brown hue used in architectural and artistic applications. Both materials serve as essential components in brick making, with geopolymer clay emphasizing sustainability and advanced performance, while terracotta clay retains cultural heritage and aesthetic appeal.
Composition and Raw Materials
Geopolymer clay bricks are primarily composed of industrial byproducts such as fly ash or metakaolin combined with alkaline activators like sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate, enabling a chemical reaction that forms a durable, cementitious matrix. In contrast, terracotta clay bricks consist mainly of natural clay rich in alumina and silica, with varying amounts of iron oxide imparting the characteristic reddish-brown color after firing. The raw materials for geopolymer bricks emphasize sustainability and reduced carbon footprint by utilizing waste products, while terracotta relies on abundant natural earth materials extracted and shaped before kiln firing.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Geopolymer clay bricks utilize an alkali-activated binder derived from industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, which undergoes a low-temperature curing process, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to terracotta clay bricks. Terracotta clay bricks are traditionally manufactured through high-temperature kiln firing, often exceeding 1000degC, which consumes substantial energy and emits greenhouse gases. The geopolymer process offers a more sustainable manufacturing alternative by eliminating the need for extensive firing and utilizing waste materials, enhancing environmental efficiency in brick production.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Geopolymer clay bricks have a significantly lower environmental impact than terracotta clay bricks due to their reduced carbon emissions during production, as they require less energy-intensive firing processes. Terracotta clay bricks involve the extraction and high-temperature kilning of natural clay, leading to higher CO2 emissions and depletion of natural resources. The use of industrial by-products like fly ash in geopolymer clay contributes to waste recycling and decreases environmental degradation associated with traditional brick manufacturing.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Geopolymer clay bricks exhibit superior durability and compressive strength compared to traditional terracotta clay bricks due to their inorganic polymer matrix, which enhances resistance to chemical attacks and high temperatures. Studies reveal that geopolymer bricks achieve compressive strengths exceeding 50 MPa, surpassing typical terracotta bricks that range between 20-30 MPa. The enhanced microstructure of geopolymer clay significantly reduces porosity and water absorption, contributing to improved long-term performance in harsh environmental conditions.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Geopolymer clay bricks exhibit superior thermal insulation properties compared to traditional terracotta clay bricks due to their low thermal conductivity and dense microstructure, which significantly reduces heat transfer. Terracotta clay bricks, made from natural fired clay, offer moderate insulation but tend to absorb and retain heat, resulting in higher internal temperatures during hot weather. The enhanced thermal resistance of geopolymer clay makes it an energy-efficient choice for sustainable construction and temperature regulation in buildings.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Geopolymer clay bricks typically offer a cost advantage due to lower energy consumption and reduced raw material expenses compared to traditional terracotta clay bricks, which require high-temperature kiln firing. The economic benefits of geopolymer bricks include faster production cycles and less reliance on expensive natural clay deposits, leading to overall project savings. Terracotta bricks may present higher upfront costs but offer durability that can justify long-term investment in specific construction scenarios.
Applications in Construction
Geopolymer clay offers superior durability and fire resistance, making it ideal for structural bricks and load-bearing walls in modern construction. Terracotta clay bricks provide excellent thermal insulation and aesthetic appeal, commonly used in facades and decorative applications. Both materials enhance sustainability, but geopolymer bricks excel in eco-friendly construction due to lower carbon emissions during production.
Sustainability and Long-term Performance
Geopolymer clay bricks offer superior sustainability due to their lower carbon emissions and ability to incorporate industrial waste materials, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional terracotta clay bricks. These bricks demonstrate enhanced long-term performance with higher durability, resistance to chemical corrosion, and improved thermal stability, leading to extended service life and reduced maintenance. Terracotta clay bricks, while historically favored, often require higher energy for firing processes and show less resistance to weathering and mechanical stress over time.
Choosing the Right Clay for Bricks
Geopolymer clay offers enhanced durability and resistance to chemical corrosion compared to traditional terracotta clay, making it ideal for industrial or high-performance brick applications. Terracotta clay, rich in natural iron oxide, provides excellent thermal insulation and aesthetic warmth favored in residential and decorative bricks. Selecting the right clay depends on factors such as environmental exposure, structural requirements, and desired visual appeal to ensure optimal brick performance and longevity.
Infographic: Geopolymer clay vs Terracotta clay for Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com