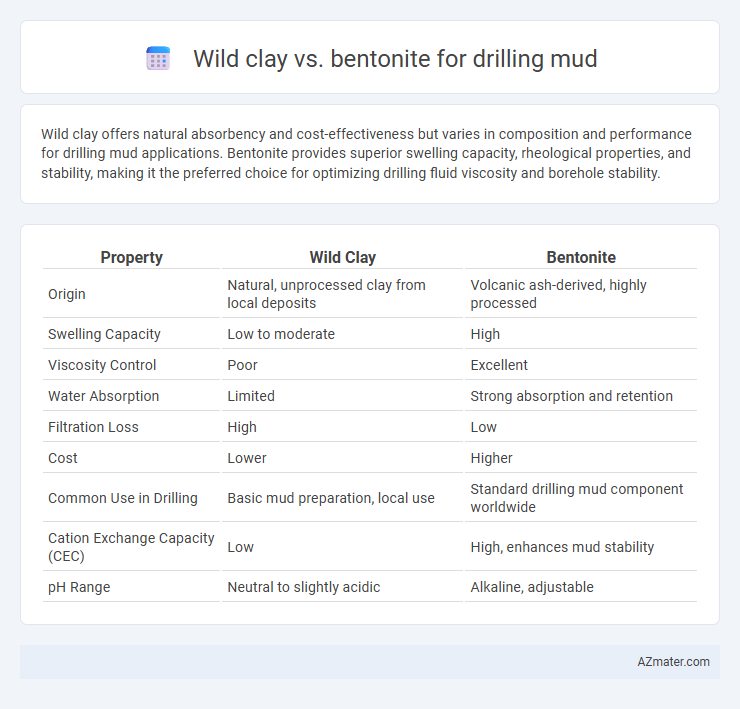
Wild clay offers natural absorbency and cost-effectiveness but varies in composition and performance for drilling mud applications. Bentonite provides superior swelling capacity, rheological properties, and stability, making it the preferred choice for optimizing drilling fluid viscosity and borehole stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Wild Clay | Bentonite |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural, unprocessed clay from local deposits | Volcanic ash-derived, highly processed |
| Swelling Capacity | Low to moderate | High |
| Viscosity Control | Poor | Excellent |
| Water Absorption | Limited | Strong absorption and retention |
| Filtration Loss | High | Low |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Use in Drilling | Basic mud preparation, local use | Standard drilling mud component worldwide |
| Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) | Low | High, enhances mud stability |
| pH Range | Neutral to slightly acidic | Alkaline, adjustable |
Introduction to Drilling Mud: Wild Clay and Bentonite
Wild clay and bentonite are essential components in drilling mud formulations used to lubricate and cool drilling equipment, stabilize boreholes, and carry drill cuttings to the surface. Bentonite, a highly absorbent aluminum phyllosilicate clay, offers superior swelling and thixotropic properties, enhancing viscosity and gel strength in drilling fluids. Wild clay, a naturally occurring heterogeneous mixture, provides cost-effective filtration and viscosity control but lacks the uniformity and performance consistency found in bentonite-based drilling muds.
Geological Origins and Composition
Wild clay, derived from surface deposits with minimal geological alteration, contains a heterogeneous mix of minerals including kaolinite, illite, and quartz, offering variable plasticity and swelling properties. Bentonite originates primarily from volcanic ash altered to montmorillonite-rich clay, characterized by exceptional swelling capacity and thixotropic behavior ideal for drilling mud applications. The high montmorillonite content in bentonite enhances its water absorption and viscosity, making it more effective than wild clay in stabilizing boreholes and suspending cuttings during drilling.
Physical Properties Comparison
Wild clay exhibits lower plasticity and higher permeability compared to bentonite, making it less effective in forming a stable filter cake during drilling operations. Bentonite's superior swelling capacity and higher viscosity contribute to better suspension of drill cuttings and enhanced borehole stabilization. Physical properties such as particle size, cation exchange capacity, and mineral composition critically influence the performance differences between wild clay and bentonite in drilling mud formulations.
Swelling Behavior and Plasticity
Wild clay exhibits lower swelling behavior compared to bentonite, making it less effective in sealing boreholes during drilling operations. Bentonite's high swelling capacity results from its montmorillonite content, which significantly enhances its plasticity and ability to create a stable, impermeable filter cake. This superior plasticity of bentonite improves drilling mud viscosity and suspension properties, ensuring better cuttings transport and borehole stability.
Rheological Performance in Drilling
Wild clay and bentonite differ significantly in rheological performance for drilling mud applications, with bentonite exhibiting superior viscosity and gel strength essential for efficient cuttings suspension and hole cleaning. Bentonite's high swelling capacity and fine particle size contribute to better shear thinning behavior and enhanced yield point, promoting improved flow properties under varying shear rates. Wild clay often shows lower plastic viscosity and inconsistent gel development, which can compromise drilling fluid stability and hinder optimal rheological control in challenging drilling environments.
Filtration Control Capabilities
Wild clay demonstrates moderate filtration control capabilities in drilling mud by providing an effective barrier to fluid loss and maintaining borehole stability. Bentonite outperforms wild clay due to its superior swelling properties and higher montmorillonite content, which enhance its ability to form a low-permeability filter cake that minimizes fluid invasion into the formation. This characteristic makes bentonite the preferred choice for drilling operations requiring stringent filtration control and optimal mud rheology.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wild clay and bentonite serve as primary components in drilling muds, with bentonite favored for its superior swelling properties and viscosity control. Bentonite mining raises environmental concerns due to habitat disruption and high water consumption, whereas wild clay extraction, being more localized and less intensive, offers a reduced ecological footprint. Sustainable drilling practices prioritize bentonite alternatives like wild clay to minimize land degradation and water resource depletion, aligning with stricter environmental regulations.
Cost Effectiveness and Local Availability
Wild clay offers significant cost savings due to its natural abundance and minimal processing requirements, making it an economically viable option for drilling mud in regions with easy access to deposit sites. Bentonite, while more expensive, provides superior swelling and viscosity properties essential for effective mud performance, but its cost-effectiveness depends on the proximity of supply sources and transportation expenses. Local availability of wild clay often reduces procurement and logistics costs, whereas bentonite's specialized beneficiation process and regional scarcity in some areas can increase overall operational expenses.
Challenges in Processing and Utilization
Wild clay presents challenges in drilling mud applications due to its inconsistent mineral composition and varying particle size, resulting in unpredictable rheological properties and poor suspension stability. Bentonite, primarily composed of montmorillonite, offers superior swelling capacity and viscosity control but requires precise purification and beneficiation to remove impurities that can reduce its effectiveness. Both materials demand tailored processing techniques to optimize their performance, with bentonite's processing complexity generally higher but yielding more reliable drilling mud characteristics.
Conclusion: Optimal Choice for Drilling Mud
Bentonite is the optimal choice for drilling mud due to its superior swelling capacity, viscosity control, and filtration properties compared to wild clay. Its high montmorillonite content enhances wellbore stability and lubrication, reducing drilling risks and equipment wear. While wild clay is cost-effective, bentonite's consistent quality and performance make it indispensable for efficient and safe drilling operations.
Infographic: Wild clay vs Bentonite for Drilling mud
 azmater.com
azmater.com