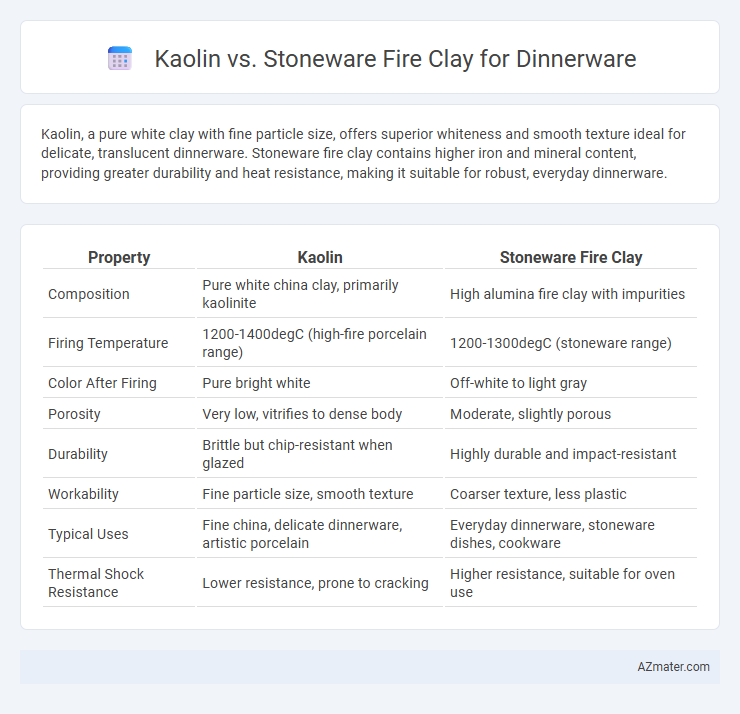
Kaolin, a pure white clay with fine particle size, offers superior whiteness and smooth texture ideal for delicate, translucent dinnerware. Stoneware fire clay contains higher iron and mineral content, providing greater durability and heat resistance, making it suitable for robust, everyday dinnerware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Kaolin | Stoneware Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure white china clay, primarily kaolinite | High alumina fire clay with impurities |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1400degC (high-fire porcelain range) | 1200-1300degC (stoneware range) |
| Color After Firing | Pure bright white | Off-white to light gray |
| Porosity | Very low, vitrifies to dense body | Moderate, slightly porous |
| Durability | Brittle but chip-resistant when glazed | Highly durable and impact-resistant |
| Workability | Fine particle size, smooth texture | Coarser texture, less plastic |
| Typical Uses | Fine china, delicate dinnerware, artistic porcelain | Everyday dinnerware, stoneware dishes, cookware |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Lower resistance, prone to cracking | Higher resistance, suitable for oven use |
Introduction to Kaolin and Stoneware Fire Clay
Kaolin is a pure, white clay primarily composed of the mineral kaolinite, known for its fine particle size, high plasticity, and excellent whiteness, making it ideal for delicate and refined dinnerware. Stoneware fire clay contains a mix of natural minerals like quartz and feldspar, providing high durability, heat resistance, and a rustic, earthy texture favored in robust, everyday dinnerware. Both materials play distinct roles in ceramics, with kaolin offering smoothness and translucency, while stoneware fire clay emphasizes strength and thermal shock resistance.
Composition Differences Between Kaolin and Stoneware Fire Clay
Kaolin is a pure, white clay primarily composed of the mineral kaolinite, known for its fine particle size and low iron content, which results in a high degree of whiteness and translucency in dinnerware. Stoneware fire clay contains a mix of kaolinite, quartz, and feldspar, with higher levels of iron and other impurities, giving it a coarser texture, greater durability, and a more natural, earthy appearance. These compositional differences influence firing temperatures and the final strength, porosity, and aesthetic qualities of the dinnerware produced from each clay type.
Physical Properties and Workability
Kaolin offers a fine particle size and high plasticity, resulting in smooth, white dinnerware with excellent strength and translucency after firing. Stoneware fire clay contains coarser particles and higher refractory content, providing greater thermal shock resistance and durability but less whiteness and smoothness. Workability is easier with kaolin due to its high plasticity, whereas fire clay requires more careful handling to avoid brittleness during shaping and drying.
Firing Temperatures and Behavior
Kaolin typically fires at higher temperatures around cone 10 (2381degF/1305degC), resulting in a white, translucent, and vitreous body ideal for fine dinnerware. Stoneware fire clay matures at slightly lower temperatures near cone 5-6 (2167-2232degF/1186-1222degC), producing a more durable and less translucent ceramic with excellent thermal shock resistance. Kaolin's high-fired vitrification contrasts with fire clay's robust mid-range firing behavior, influencing their suitability for different dinnerware styles and uses.
Color and Texture Outcomes
Kaolin porcelain offers a smooth, bright white surface ideal for vibrant, consistent color glazing, making dinnerware visually striking and elegant. Stoneware fire clay delivers a naturally earthy, speckled texture with warm, muted tones, resulting in rustic and organic dinnerware aesthetics. The choice between kaolin's refined finish and fire clay's robust texture directly influences the visual depth and tactile experience of the final product.
Strength and Durability in Dinnerware Applications
Kaolin provides a fine, white, and smooth texture ideal for elegant dinnerware but tends to be less durable under heavy use compared to stoneware fire clay. Stoneware fire clay, composed of high refractory minerals, offers superior strength and resistance to chipping, making it highly suitable for everyday dinnerware subjected to frequent handling and thermal stress. Its dense, non-porous structure enhances long-term durability, ensuring longevity in both commercial and home dining environments.
Glaze Compatibility and Finish
Kaolin offers excellent glaze compatibility for dinnerware due to its smooth texture and high purity, resulting in a bright, glossy finish that enhances aesthetic appeal. Stoneware fire clay, being denser and more robust, provides superior durability but requires careful glaze formulation to prevent defects such as crazing or blistering. Both materials allow for diverse finishes, but kaolin's fine particle size promotes a more uniform glaze application, making it ideal for delicate and intricate dinnerware designs.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
Kaolin, known for its pure white color and fine texture, is generally more expensive and less accessible than stoneware fire clay, which is abundant and affordable. Stoneware fire clay offers cost-effective durability suitable for everyday dinnerware, making it popular among budget-conscious buyers. Accessibility of kaolin is limited due to its specialized mining locations, whereas stoneware fire clay is widely available from multiple regional sources.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Kaolin dinnerware is favored for its high purity and low environmental footprint due to its refined natural clay content and energy-efficient firing processes, resulting in less waste and lower carbon emissions. Stoneware fire clay, although durable and robust, often requires higher firing temperatures, leading to increased energy consumption and a larger carbon footprint. Choosing kaolin-based dinnerware supports sustainability by promoting resource efficiency and reducing ecological impact throughout production and disposal.
Choosing the Right Clay for Dinnerware Production
Selecting the right clay for dinnerware production depends largely on the desired durability and finish; kaolin offers a pure, white, and smooth texture ideal for fine, translucent porcelain dinnerware, while stoneware fire clay is known for its coarse texture and high resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for robust, everyday use. Kaolin's high alumina content results in a refined, non-porous finish that withstands acidic foods, whereas fire clay's grit and iron content contribute to its strength and earthy aesthetic but may affect the color and glaze outcome. Considering factors like firing temperature, wear resistance, and visual appeal helps manufacturers determine whether kaolin or stoneware fire clay aligns best with both functional and stylistic requirements of dinnerware production.
Infographic: Kaolin vs Stoneware Fire Clay for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com