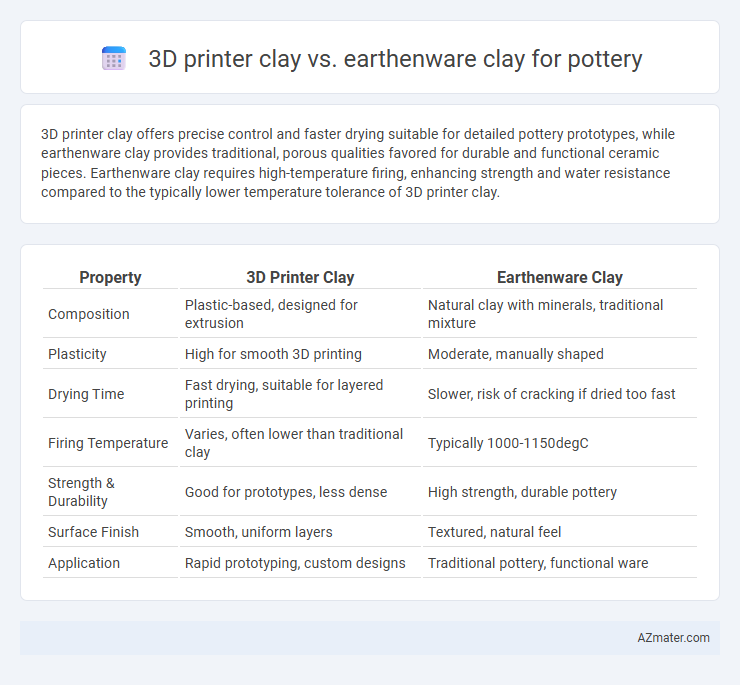
3D printer clay offers precise control and faster drying suitable for detailed pottery prototypes, while earthenware clay provides traditional, porous qualities favored for durable and functional ceramic pieces. Earthenware clay requires high-temperature firing, enhancing strength and water resistance compared to the typically lower temperature tolerance of 3D printer clay.
Table of Comparison
| Property | 3D Printer Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Plastic-based, designed for extrusion | Natural clay with minerals, traditional mixture |
| Plasticity | High for smooth 3D printing | Moderate, manually shaped |
| Drying Time | Fast drying, suitable for layered printing | Slower, risk of cracking if dried too fast |
| Firing Temperature | Varies, often lower than traditional clay | Typically 1000-1150degC |
| Strength & Durability | Good for prototypes, less dense | High strength, durable pottery |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, uniform layers | Textured, natural feel |
| Application | Rapid prototyping, custom designs | Traditional pottery, functional ware |
Introduction to 3D Printer Clay and Earthenware Clay
3D printer clay is a specialized, printable material designed for additive manufacturing, offering precise control over pottery shapes and intricate designs through digital modeling. Earthenware clay is a traditional, natural clay known for its porous texture and warm reddish-brown color, widely used in hand-built pottery and kiln firing processes. While 3D printer clay enables rapid prototyping with consistent material properties, earthenware clay emphasizes artisanal craftsmanship and textural variation in finished ceramic pieces.
Composition and Material Differences
3D printer clay typically consists of a synthetic polymer base combined with fine clay particles, enabling precise layer-by-layer deposition and faster drying times compared to traditional earthenware clay. Earthenware clay is primarily composed of natural minerals like kaolinite, quartz, and feldspar, which offer plasticity and durability when fired at lower temperatures. The synthetic additives in 3D printer clay enhance printability and consistency, while earthenware's natural composition supports traditional hand-building and wheel-throwing techniques with a longer firing process.
Workability and Handling Characteristics
3D printer clay offers precise control and consistency, allowing intricate designs and reduced material waste, but it often requires specialized equipment and careful handling to avoid drying and cracking issues. Earthenware clay provides a traditional tactile experience with excellent plasticity and moisture retention, making it easier to shape and manipulate by hand, though it may be less precise for fine details compared to 3D printed clay. Both materials differ significantly in workability, with 3D printer clay favoring automation and repeatability, while earthenware clay supports hands-on craftsmanship and organic forms.
Firing Temperatures and Processes
3D printer clay typically requires lower firing temperatures, around 1100degC to 1200degC, and is designed for precise layering, enabling intricate shapes with minimal shrinkage. Earthenware clay fires at lower temperatures, generally between 1000degC and 1150degC, resulting in a porous and more fragile ceramic ideal for decorative pottery but less durable than stoneware or porcelain. The firing process for earthenware often involves oxidation atmospheres, while 3D printed clays can be engineered for specific kiln environments, offering greater control over final texture and strength.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
3D printer clay offers exceptional design flexibility, enabling intricate and complex shapes that are difficult to achieve with traditional methods, thanks to precise layer-by-layer deposition. Earthenware clay, while versatile and widely used in pottery, is limited by manual shaping techniques, restricting the complexity of designs to the potter's skill level. The digital control inherent in 3D printing allows for repeatable, highly detailed patterns and geometries that expand creative possibilities beyond conventional earthenware craftsmanship.
Surface Finishes and Texture Outcomes
3D printer clay offers precise surface finishes with smooth, uniform textures ideal for detailed and intricate designs, while traditional earthenware clay provides a more organic, tactile surface with natural variations enhancing rustic aesthetics. Earthenware clay can achieve varied textures through hand-building techniques and firing processes, resulting in rich, earthy surface finishes that are difficult to replicate with 3D printing. The ability of 3D printer clay to produce consistent layers allows for innovative surface patterns, whereas earthenware clay's porous nature contributes to unique glaze applications and tactile depth.
Durability and Functional Properties
3D printer clay offers precise layering and uniform density, enhancing structural integrity and reducing the likelihood of cracks compared to traditional earthenware clay. Earthenware clay, while more porous and less durable, provides excellent thermal insulation and is well-suited for functional pottery like cooking vessels and flower pots. The durability of 3D printed clay objects typically surpasses earthenware due to controlled firing and composition, making it preferable for complex, high-strength applications.
Artistic Applications and Creative Possibilities
3D printer clay offers unparalleled precision and the ability to create complex, intricate designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional earthenware clay, expanding the scope of artistic applications in pottery. Earthenware clay provides a tactile, hands-on experience ideal for organic shapes and textures, supporting creative expression through molding and manual techniques. Combining both materials enables artists to push the boundaries of pottery by blending digital accuracy with handcrafted aesthetics, resulting in innovative and unique ceramic art pieces.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
3D printer clay significantly reduces material waste compared to traditional earthenware clay, optimizing resource use and minimizing environmental degradation. Earthenware clay extraction often leads to habitat disruption and soil erosion, whereas 3D printing technologies enable precise clay deposition, lowering energy consumption and carbon footprint. Sustainable pottery production increasingly favors 3D printer clay for its enhanced efficiency, recyclability, and potential integration with eco-friendly additives.
Cost and Accessibility for Pottery Makers
3D printer clay offers a cost-effective option for pottery makers due to lower material waste and faster production times compared to traditional earthenware clay, which often requires costly kiln firings and specialized tools. Accessibility increases with 3D printer clay as it can be sourced digitally and printed on-demand, eliminating the need for extensive studio space and physical clay suppliers. Earthenware clay remains widely available but involves higher upfront costs and maintenance of equipment, making it less affordable for beginners or small-scale artisans.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Earthenware clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com