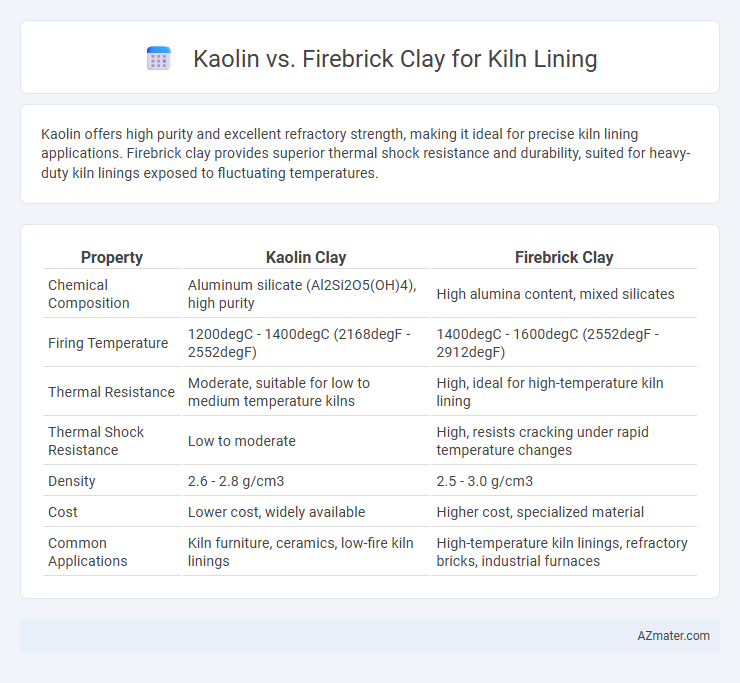
Kaolin offers high purity and excellent refractory strength, making it ideal for precise kiln lining applications. Firebrick clay provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability, suited for heavy-duty kiln linings exposed to fluctuating temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Kaolin Clay | Firebrick Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Aluminum silicate (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), high purity | High alumina content, mixed silicates |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC - 1400degC (2168degF - 2552degF) | 1400degC - 1600degC (2552degF - 2912degF) |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate, suitable for low to medium temperature kilns | High, ideal for high-temperature kiln lining |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low to moderate | High, resists cracking under rapid temperature changes |
| Density | 2.6 - 2.8 g/cm3 | 2.5 - 3.0 g/cm3 |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized material |
| Common Applications | Kiln furniture, ceramics, low-fire kiln linings | High-temperature kiln linings, refractory bricks, industrial furnaces |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Materials
Kiln lining materials like kaolin and firebrick clay are essential for thermal insulation and structural integrity in high-temperature environments. Kaolin, a pure white clay rich in alumina and silica, offers excellent refractory properties with low thermal expansion, making it ideal for precise temperature control. Firebrick clay contains higher levels of iron and other fluxes, providing durability and thermal shock resistance but with slightly lower insulation efficiency compared to kaolin.
What Is Kaolin Clay?
Kaolin clay is a pure, white-firing clay composed primarily of the mineral kaolinite, valued for its high refractory properties and fine particle size, making it ideal for kiln linings. It withstands high temperatures up to 1,750degC, offering durability and thermal stability in kiln construction compared to firebrick clay. Its low thermal expansion and excellent resistance to chemical attack enhance kiln longevity while maintaining consistent firing conditions.
What Is Firebrick Clay?
Firebrick clay is a high-temperature refractory material specifically formulated to withstand intense heat and thermal cycling in kiln linings. It features a dense, durable structure that resists thermal shock, making it ideal for protecting kiln interiors during firing processes. Compared to kaolin, firebrick clay offers superior insulation and longevity under extreme firing temperatures.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Kaolin, primarily composed of high-purity alumina (Al2O3) and silica (SiO2), offers excellent refractory properties due to its fine particle size and low impurity content, making it ideal for kiln lining requiring thermal stability and resistance to chemical attack. Firebrick clay typically contains a higher percentage of iron oxides (Fe2O3) and other fluxing agents, which lower its melting point and increase thermal conductivity but can reduce chemical resistance compared to kaolin. The chemical composition difference impacts durability; kaolin-based linings resist corrosion and spalling better in high-temperature, chemically aggressive environments, while firebrick clays provide robustness in high mechanical stress applications.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
Kaolin offers superior thermal stability with a high melting point around 1780degC, making it ideal for kiln linings that require excellent heat resistance and minimal thermal expansion. Firebrick clay, while durable and resistant to thermal shock, typically withstands temperatures up to 1600degC and is valued for its dense, insulating properties. Choosing between kaolin and firebrick clay depends on the kiln's operating temperature and the balance needed between thermal conductivity and mechanical strength.
Durability and Longevity
Kaolin clay offers exceptional purity and thermal stability, making it ideal for kiln linings that require high durability and resistance to thermal shock. Firebrick clay, known for its dense and robust composition, provides superior strength and long-lasting performance under intense, repetitive heating cycles. When comparing durability and longevity, firebrick clay typically outperforms kaolin by maintaining structural integrity over prolonged, high-temperature use, though kaolin excels in applications demanding high refractoriness and minimal contamination.
Installation and Workability
Kaolin offers superior workability for kiln lining due to its fine particle size and smooth texture, allowing for easier shaping and application during installation. Firebrick clay, while denser and more refractory, requires more skill to handle and shape properly, often necessitating pre-formed bricks or slabs for efficient kiln lining installation. The choice between kaolin and firebrick clay hinges on balancing ease of installation with heat resistance requirements in high-temperature kiln environments.
Cost Analysis: Kaolin vs Firebrick Clay
Kaolin generally costs more upfront compared to firebrick clay due to its higher purity and greater refractory qualities, which provide enhanced thermal resistance and longer lifespan in kiln lining applications. Firebrick clay offers a more budget-friendly option with sufficient durability for moderate kiln temperatures but may require more frequent replacement, increasing long-term expenses. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement intervals, shows kaolin as a potentially cost-effective investment for high-temperature, heavy-use kilns.
Best Applications for Each Clay Type
Kaolin kiln lining excels in high-temperature ceramic firings, offering excellent thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for porcelain and fine china production. Firebrick clay, known for its superior durability and heat retention, is best suited for heavy-duty kiln walls and industrial applications requiring prolonged high-heat exposure. Choosing kaolin benefits precision ceramics where purity and smoothness are critical, while firebrick clay provides robust structural integrity in demanding kiln operations.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Kiln Lining
Kaolin offers high purity and excellent refractory properties, making it ideal for kiln linings exposed to extreme temperatures and thermal shocks. Firebrick clay contains more alumina and silica, providing superior durability and resistance to wear in heavy-duty kiln environments. Selecting the right clay depends on balancing thermal insulation needs with mechanical strength requirements for optimal kiln performance.
Infographic: Kaolin vs Firebrick Clay for Kiln Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com