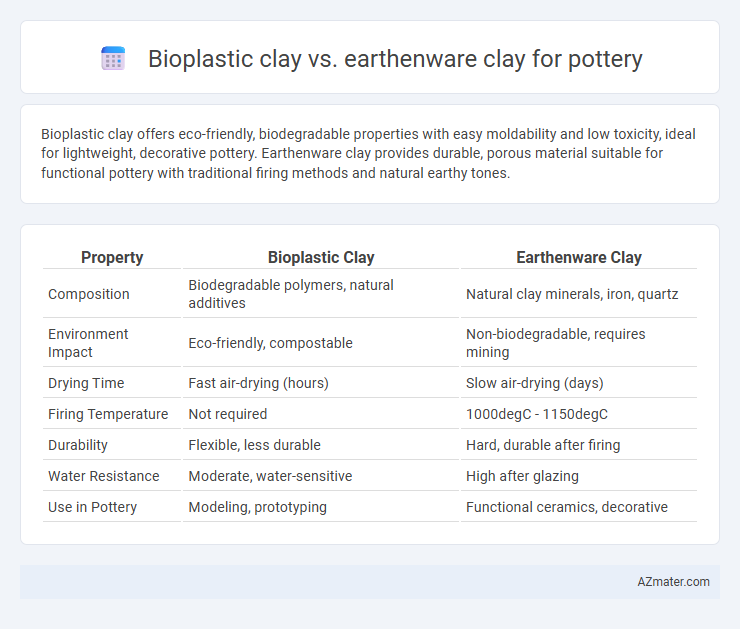
Bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly, biodegradable properties with easy moldability and low toxicity, ideal for lightweight, decorative pottery. Earthenware clay provides durable, porous material suitable for functional pottery with traditional firing methods and natural earthy tones.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioplastic Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Biodegradable polymers, natural additives | Natural clay minerals, iron, quartz |
| Environment Impact | Eco-friendly, compostable | Non-biodegradable, requires mining |
| Drying Time | Fast air-drying (hours) | Slow air-drying (days) |
| Firing Temperature | Not required | 1000degC - 1150degC |
| Durability | Flexible, less durable | Hard, durable after firing |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, water-sensitive | High after glazing |
| Use in Pottery | Modeling, prototyping | Functional ceramics, decorative |
Introduction to Bioplastic Clay and Earthenware Clay
Bioplastic clay, derived from renewable plant-based materials like cornstarch and cellulose, offers eco-friendly, non-toxic options ideal for lightweight, flexible pottery projects with low firing temperatures. Earthenware clay, a naturally occurring, porous clay fired at moderate temperatures (1,000-1,150degC), provides traditional durability and a rich, earthy finish suitable for functional ceramics and decorative pieces. Choosing between these clays depends on desired firing methods, environmental impact concerns, and final product characteristics in pottery.
Composition and Material Differences
Bioplastic clay is primarily composed of biodegradable polymers such as polylactic acid (PLA) combined with natural fibers, offering a lightweight and eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials. Earthenware clay consists mainly of natural minerals like kaolinite, quartz, and feldspar, with high iron content that gives it its characteristic reddish or brown color after firing. The key material difference lies in bioplastic clay's synthetic polymer base, which enhances flexibility and reduces drying time, whereas earthenware clay relies on mineral composition for hardness and porosity after kiln firing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioplastic clay is biodegradable and made from renewable resources such as cornstarch, significantly reducing plastic waste and greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional clays. Earthenware clay, though natural and abundant, requires high-temperature kiln firing that consumes considerable energy and emits carbon dioxide, impacting sustainability negatively. Choosing bioplastic clay supports eco-friendly pottery by minimizing environmental footprint while earthenware clay relies on traditional methods with higher resource intensity.
Workability and User Experience
Bioplastic clay offers superior workability due to its lightweight, non-toxic composition, making it ideal for detailed sculpting and easy shaping, especially for beginners and children. Earthenware clay, while heavier and more traditional, provides a tactile, authentic experience preferred by skilled potters who value its plasticity and ability to retain moisture for extended periods during shaping. User experience differs as bioplastic clay requires no firing, allowing immediate handling and repetitive use, whereas earthenware mandates kiln firing, adding a layer of complexity and craftsmanship to the pottery process.
Firing Temperatures and Techniques
Bioplastic clay typically requires no firing as it air-dries or cures at low temperatures, making it ideal for beginners and decorative pieces without kiln access. Earthenware clay demands kiln firing at approximately 1,000 to 1,150degC (1,832 to 2,102degF) to achieve durability and proper vitrification for functional pottery. The distinct firing techniques influence the final texture and strength, with earthenware offering more robustness and bioplastic clay providing flexibility and ease of use.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Bioplastic clay tends to be less durable and has lower structural strength compared to earthenware clay, which is known for its robustness and ability to withstand high firing temperatures. Earthenware clay's natural mineral composition provides greater resilience and resistance to cracking over time, making it ideal for functional pottery. The synthetic nature of bioplastic clay often results in a more flexible but less sturdy final product, limiting its use in items requiring long-term durability.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finishes
Bioplastic clay offers a smooth, uniform texture allowing for vibrant, consistent coloration and a glossy finish, ideal for detailed decorative pottery. Earthenware clay provides a natural, rustic appearance with porous surfaces that absorb glazes differently, resulting in unique, earthy tones and matte or semi-gloss finishes. The choice impacts the final aesthetic, with bioplastic clay favoring precision and polished looks, while earthenware clay embraces organic textures and traditional glaze effects.
Cost and Accessibility
Bioplastic clay generally costs more than earthenware clay due to its synthetic ingredients and eco-friendly properties, which may limit availability to specialized retailers or online stores. Earthenware clay is widely accessible and affordable, commonly found in art supply shops, making it a preferred choice for beginners and bulk projects. The cost-effectiveness and ease of procurement make earthenware clay the dominant option in pottery compared to the pricier, less accessible bioplastic clay.
Applications in Pottery and Sculpting
Bioplastic clay offers lightweight, non-toxic properties ideal for detailed sculpting and small decorative pottery pieces, especially in educational or hobbyist settings due to its easy air-drying process. Earthenware clay provides superior durability and traditional firing options, making it preferable for functional pottery like bowls and vases that require thermal resistance and glazing capabilities. Both materials cater to different artistic needs, with bioplastic clay suited for rapid prototyping and fine modeling, while earthenware excels in creating enduring, fired ceramic works.
Future Trends in Clay Materials for Pottery
Bioplastic clay offers a sustainable alternative to traditional earthenware clay, leveraging biodegradable polymers to reduce environmental impact in pottery. Future trends indicate increased innovation in hybrid clay materials combining bioplastics with natural minerals to enhance durability and workability. Advances in eco-friendly formulations aim to meet growing consumer demand for green ceramics without compromising artistic expression or functional quality.
Infographic: Bioplastic clay vs Earthenware clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com