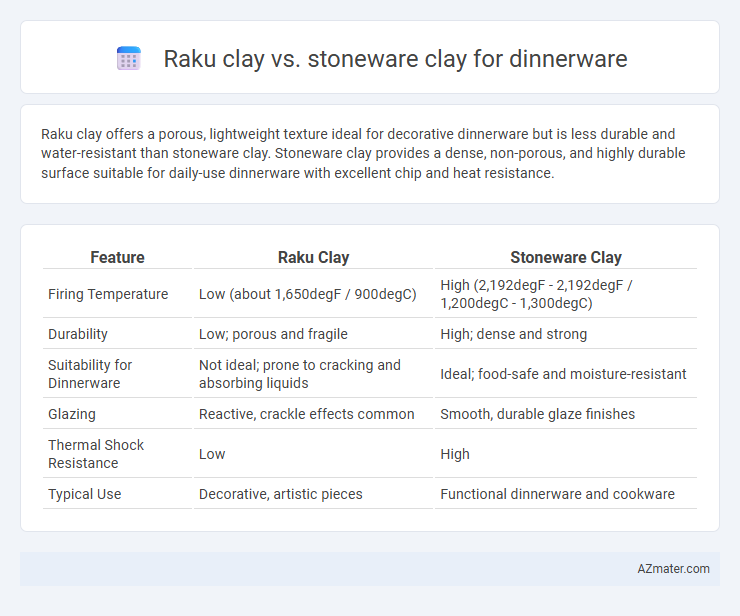
Raku clay offers a porous, lightweight texture ideal for decorative dinnerware but is less durable and water-resistant than stoneware clay. Stoneware clay provides a dense, non-porous, and highly durable surface suitable for daily-use dinnerware with excellent chip and heat resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raku Clay | Stoneware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Firing Temperature | Low (about 1,650degF / 900degC) | High (2,192degF - 2,192degF / 1,200degC - 1,300degC) |
| Durability | Low; porous and fragile | High; dense and strong |
| Suitability for Dinnerware | Not ideal; prone to cracking and absorbing liquids | Ideal; food-safe and moisture-resistant |
| Glazing | Reactive, crackle effects common | Smooth, durable glaze finishes |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low | High |
| Typical Use | Decorative, artistic pieces | Functional dinnerware and cookware |
Introduction: Raku Clay vs Stoneware Clay for Dinnerware
Raku clay offers a porous, lightweight texture ideal for decorative dinnerware but requires sealing due to its low vitrification and thermal shock resistance. Stoneware clay features a dense, durable composition with high vitrification, making it suitable for functional dinnerware that withstands regular use and dishwasher safety. Choosing between Raku and Stoneware depends on the balance between aesthetic appeal and practical durability in dinnerware applications.
Composition and Properties of Raku Clay
Raku clay is composed of grog and organic materials designed to withstand rapid thermal shock during the Raku firing process, making it more porous and less vitrified than stoneware clay. This porosity results in a lighter, more fragile dinnerware compared to the dense, vitrified, and durable nature of stoneware clay, which contains higher levels of alumina and silica. The unique composition of Raku clay allows it to crackle and cool quickly, offering distinctive surface textures but requiring sealing to ensure food safety and durability in everyday use.
Composition and Properties of Stoneware Clay
Stoneware clay features a dense, non-porous composition primarily made of kaolin, ball clay, and feldspar, making it highly durable and vitrified when fired at high temperatures between 1200degC and 1300degC. Its strength and resistance to chipping and thermal shock make stoneware ideal for everyday dinnerware, providing a sturdy and long-lasting option. Unlike raku clay, which is porous and fragile due to low firing temperatures, stoneware clay offers superior hardness and water resistance suitable for functional tableware.
Firing Temperatures: Raku vs Stoneware
Raku clay typically fires at lower temperatures between 1,650degF and 1,830degF (900degC to 1,000degC), resulting in a porous and more fragile surface suitable for decorative rather than functional dinnerware. Stoneware clay requires higher firing temperatures, usually between 2,100degF and 2,300degF (1,150degC to 1,260degC), creating a dense, vitrified, and durable body ideal for functional dinnerware such as plates and bowls. The higher firing temperature of stoneware ensures enhanced strength, heat resistance, and non-porosity, making it the preferred choice for everyday use.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Stoneware clay offers superior durability and strength compared to Raku clay, making it ideal for everyday dinnerware that withstands frequent use and washing. Raku clay is more porous and prone to cracking due to its low firing temperature and thermal shock sensitivity, which limits its practical use for functional dinnerware. Stoneware's dense vitrification process results in a non-porous, chip-resistant surface that maintains longevity and structural integrity under regular dining conditions.
Food Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Raku clay often contains materials that can release harmful substances when not properly sealed, making it less suitable for food-safe dinnerware compared to stoneware clay, which is vitrified at higher temperatures and is typically non-porous and food-safe. Stoneware clay's dense structure and glaze options reduce the risk of bacterial contamination and leaching of toxins, ensuring safer use in everyday dining. Food safety regulations favor stoneware dinnerware because it is less likely to harbor harmful chemicals or heavy metals, whereas raku pieces require careful sealing and are better suited for decorative purposes.
Glaze Options and Aesthetic Results
Raku clay offers unique glaze options that develop crackled, metallic, and smoky finishes due to rapid cooling in post-firing reduction, creating unpredictable and organic aesthetics ideal for artistic dinnerware. Stoneware clay supports a wider variety of glaze compositions, including high-fire and matte glazes, producing durable, food-safe, and consistent finishes suited for everyday use. The aesthetic results of Raku emphasize rustic, textured surfaces, while Stoneware yields smooth, refined, and functional dinnerware with greater color stability.
Resistance to Thermal Shock and Staining
Stoneware clay exhibits superior resistance to thermal shock compared to Raku clay, making it ideal for everyday dinnerware that undergoes rapid temperature changes from oven to table. The high vitrification level in stoneware creates a dense, non-porous surface that resists staining from food and liquids, preserving the dinnerware's appearance over time. Raku clay, while aesthetically unique due to its low-fired, crackled finish, is more porous and prone to staining, requiring sealing and careful handling to maintain durability.
Suitability for Daily Use and Maintenance
Stoneware clay offers superior durability and chip resistance, making it highly suitable for daily use dinnerware that withstands frequent washing and handling. Raku clay, while artistically unique due to its porous nature and crackled finish, requires more careful maintenance and is less practical for everyday meals because it can absorb liquids and stain easily. Regular sealing of Raku pieces is necessary to maintain their appearance and functionality, unlike stoneware, which is typically more low-maintenance and dishwasher safe.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Dinnerware Needs
Raku clay, known for its porous texture and distinctive crackle finish, is ideal for decorative dinnerware but less suitable for everyday use due to its susceptibility to thermal shock and moisture absorption. Stoneware clay offers greater durability, non-porous qualities, and resistance to chipping, making it the preferred choice for functional dinnerware that withstands frequent washing and high temperatures. Selecting the right clay depends on whether the priority is aesthetic appeal with delicate artistry or robust, practical dinnerware designed for everyday durability.
Infographic: Raku clay vs Stoneware clay for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com