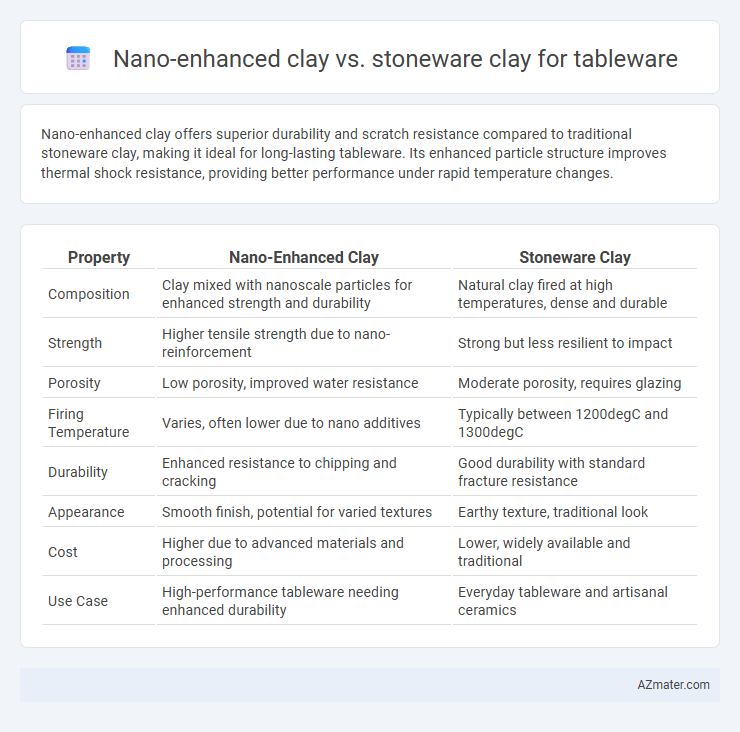
Nano-enhanced clay offers superior durability and scratch resistance compared to traditional stoneware clay, making it ideal for long-lasting tableware. Its enhanced particle structure improves thermal shock resistance, providing better performance under rapid temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano-Enhanced Clay | Stoneware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay mixed with nanoscale particles for enhanced strength and durability | Natural clay fired at high temperatures, dense and durable |
| Strength | Higher tensile strength due to nano-reinforcement | Strong but less resilient to impact |
| Porosity | Low porosity, improved water resistance | Moderate porosity, requires glazing |
| Firing Temperature | Varies, often lower due to nano additives | Typically between 1200degC and 1300degC |
| Durability | Enhanced resistance to chipping and cracking | Good durability with standard fracture resistance |
| Appearance | Smooth finish, potential for varied textures | Earthy texture, traditional look |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced materials and processing | Lower, widely available and traditional |
| Use Case | High-performance tableware needing enhanced durability | Everyday tableware and artisanal ceramics |
Introduction to Nano-Enhanced Clay and Stoneware Clay
Nano-enhanced clay incorporates nanoparticles to improve mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to cracking compared to traditional stoneware clay. Stoneware clay, known for its high-firing temperature and dense, vitreous body, provides excellent durability and a natural, earthy texture ideal for tableware. The inclusion of nanomaterials in nano-enhanced clay can enhance surface smoothness and reduce porosity, offering advanced performance over conventional stoneware in everyday use.
Composition and Structure Differences
Nano-enhanced clay incorporates nanoparticles such as silica or alumina, which refine the microstructure by filling microscopic pores and enhancing particle packing density, resulting in a denser and more homogeneous matrix. Stoneware clay primarily consists of natural feldspar, quartz, and kaolin minerals, forming a coarse-grained, vitrified structure with notable porosity after firing. These compositional and structural differences influence mechanical strength, thermal stability, and surface finish, with nano-enhanced clay offering superior durability and reduced water absorption compared to traditional stoneware clay.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Nano-enhanced clay utilizes nanomaterials to improve particle dispersion and reduce firing temperature, enabling faster sintering and enhanced mechanical strength compared to traditional Stoneware clay. The manufacturing process of nano-enhanced clay involves precise nanomaterial integration and high-shear mixing, resulting in uniform microstructure and improved durability. Stoneware clay typically undergoes longer kiln firing at higher temperatures, which increases energy consumption and production time relative to the more efficient nano-enhanced clay methods.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits significantly higher strength and durability compared to traditional stoneware clay, due to the incorporation of nanoparticles that improve the microstructure and reduce porosity. This enhancement results in tableware that resists chipping, cracking, and wear under frequent use, extending its lifespan substantially. Stoneware clay, while sturdy, lacks the reinforced matrix of nano-enhanced variants, making it more susceptible to mechanical stress and thermal shock over time.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Nano-enhanced clay demonstrates superior thermal resistance compared to traditional stoneware clay, allowing tableware to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. The incorporation of nanoparticles enhances the material's thermal shock tolerance and durability, resulting in longer-lasting, high-performance tableware. Stoneware clay, while robust, lacks the nano-level reinforcement necessary for optimal heat endurance and performance under extreme conditions.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Nano-enhanced clay incorporates nanoparticles to improve durability and reduce porosity, minimizing the risk of bacteria absorption and enhancing food safety for tableware. Stoneware clay is naturally dense and non-porous after firing, offering excellent resistance to water and food stains, ensuring safe contact with various foods. Both materials meet FDA and EU regulations for food compatibility, but nano-enhanced clay provides advanced protection against microscopic contaminants, making it highly suitable for hygienic tableware.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Versatility
Nano-enhanced clay offers superior surface smoothness and uniformity, resulting in a refined, almost glass-like finish that enhances the visual appeal of tableware. Stoneware clay provides a robust, rustic texture with natural earthy tones, delivering timeless aesthetic qualities suited for traditional or artisanal designs. The nano-enhancement allows for finer detailing and more intricate patterns, increasing design versatility compared to the more organic and coarse characteristics of stoneware clay.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nano-enhanced clay offers improved durability and reduced material usage in tableware production, resulting in lower resource consumption and waste compared to traditional stoneware clay. Stoneware clay, while naturally abundant and recyclable, demands higher firing temperatures that increase energy consumption and carbon emissions. Advancements in nano-technology in clay formulations contribute to more sustainable manufacturing processes by minimizing environmental footprints and extending product lifespan.
Cost Effectiveness and Market Availability
Nano-enhanced clay offers superior strength and durability at a higher production cost compared to traditional stoneware clay, impacting its cost-effectiveness for tableware. Stoneware clay remains widely available and economically viable for mass-market production, benefiting from established supply chains and manufacturing processes. Market availability of nano-enhanced clay is currently limited, constraining its adoption despite performance advantages in high-end or specialty tableware segments.
Future Trends in Tableware Materials
Nano-enhanced clay offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to thermal shock compared to traditional stoneware clay, making it ideal for modern tableware demands. Emerging trends highlight the integration of nanotechnology to create lightweight, scratch-resistant, and highly customizable designs, aligning with sustainability and performance goals. Future tableware materials will increasingly blend nano-enhanced composites to meet consumer preferences for long-lasting, eco-friendly, and aesthetically versatile products.
Infographic: Nano-enhanced clay vs Stoneware clay for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com