3D printer clay offers rapid prototyping and customization capabilities for fine ceramics, while porcelain clay provides superior strength, translucency, and traditional aesthetic qualities essential for high-quality ceramic art. Choosing between them depends on balancing modern manufacturing speed with classic material properties.
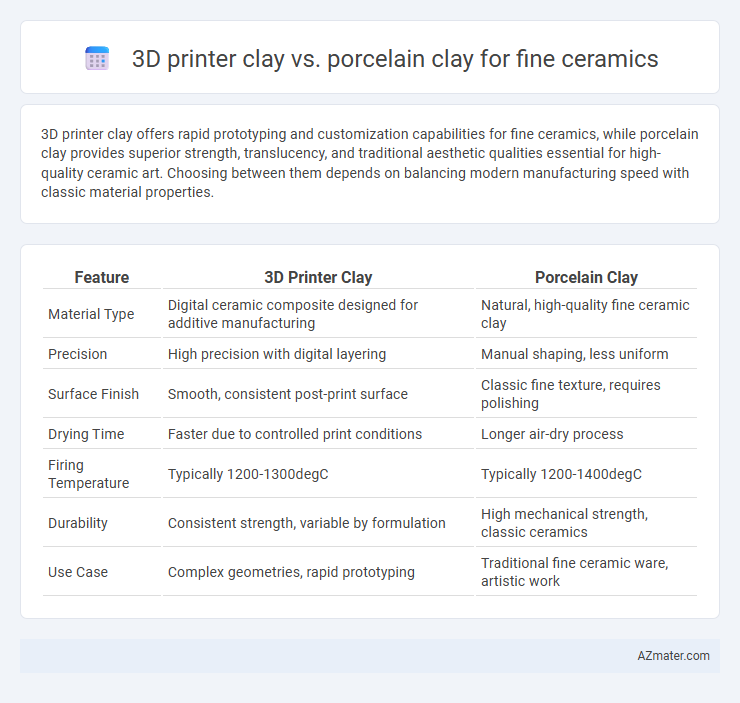
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Digital ceramic composite designed for additive manufacturing | Natural, high-quality fine ceramic clay |
| Precision | High precision with digital layering | Manual shaping, less uniform |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, consistent post-print surface | Classic fine texture, requires polishing |
| Drying Time | Faster due to controlled print conditions | Longer air-dry process |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 1200-1300degC | Typically 1200-1400degC |
| Durability | Consistent strength, variable by formulation | High mechanical strength, classic ceramics |
| Use Case | Complex geometries, rapid prototyping | Traditional fine ceramic ware, artistic work |
Introduction to 3D Printing in Fine Ceramics
3D printer clay offers precise control and the ability to create complex, detailed designs in fine ceramics, making it ideal for intricate art and prototype development. Porcelain clay, prized for its smooth texture and translucent finish, is traditionally used in fine ceramics but poses challenges in 3D printing due to its viscosity and firing properties. Advances in 3D printing technology now enable the fusion of these materials' strengths, enhancing production efficiency and creative possibilities in the fine ceramics industry.
Overview of 3D Printer Clay Materials
3D printer clay materials for fine ceramics primarily consist of specially formulated ceramic pastes or slips that combine fine clay particles with binders and plasticizers to ensure smooth extrusion and shape retention. Unlike traditional porcelain clay, these 3D printable clays are optimized for layer-by-layer deposition, offering controlled viscosity and drying properties essential for precision and structural integrity in additive manufacturing. Key components include kaolin, feldspar, and silica powders finely milled to enhance surface finish and strength while maintaining compatibility with common ceramic 3D printers.
What is Porcelain Clay?
Porcelain clay is a highly refined, white-firing ceramic material composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, known for its strength, translucency, and smooth texture. Unlike 3D printer clay, which is formulated for additive manufacturing with enhanced plasticity and drying properties, porcelain clay requires skilled handwork or traditional shaping techniques to achieve its delicate, fine ceramic qualities. Porcelain's unique vitrification process during firing results in a dense, non-porous surface ideal for high-end ceramics and fine art pieces.
Material Properties: 3D Printer Clay vs. Porcelain Clay
3D printer clay, designed for additive manufacturing, offers superior plasticity and layer adhesion, enabling precise and complex ceramic shapes with minimal drying shrinkage compared to traditional porcelain clay. Porcelain clay, characterized by its high kaolin content and vitrification ability, provides exceptional strength, translucency, and smooth surface finish after firing, but is less adaptable to intricate 3D printing processes due to its finer particle size and brittleness in unfired stages. The choice between 3D printer clay and porcelain clay hinges on balancing the need for geometric complexity and printing feasibility against the desired mechanical strength and aesthetic qualities in fine ceramic production.
Printability and Workflow Differences
3D printer clay offers superior printability with its optimized viscosity and faster drying times, making it ideal for intricate, rapid prototyping in fine ceramics. Porcelain clay, known for its delicate composition and higher shrinkage rate, requires slower, more careful handling and longer drying phases to avoid cracks and warping during firing. Workflow with 3D printer clay integrates smoothly with digital design tools, enabling precise layering, whereas porcelain demands traditional mold-making or slip casting for consistent results in fine ceramic artistry.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Qualities
3D printer clay offers a precise, uniform surface finish ideal for intricate fine ceramic designs, enhancing detailed textures and complex geometries. Porcelain clay, known for its smooth, translucent quality, provides superior aesthetic appeal with a natural, refined elegance often sought in traditional fine ceramics. While 3D printed clay excels in structural consistency, porcelain's glossy surface and warm tones deliver timeless beauty and a more tactile sensory experience.
Strength and Durability Comparison
3D printer clay optimized for fine ceramics typically exhibits enhanced uniformity and reduced porosity compared to traditional porcelain clay, resulting in higher tensile strength and improved structural integrity. Porcelain clay, while prized for its vitrification and translucency, tends to be more brittle and susceptible to chipping under mechanical stress. Advances in 3D printing formulations enable the creation of ceramic pieces with superior durability and consistent density, surpassing the conventional limitations of porcelain clay in strength retention and impact resistance.
Firing and Post-Processing Considerations
3D printer clay for fine ceramics typically requires lower firing temperatures compared to porcelain clay, which demands high-temperature firing around 1,200-1,400degC to achieve its characteristic vitrification and translucency. Post-processing for 3D printed clay involves careful drying to prevent cracking due to layer adhesion, while porcelain clay requires extended soaking during firing to develop its dense, glass-like finish. Porcelain's higher shrinkage rate necessitates precise control during both firing and finishing to maintain dimensional accuracy and surface smoothness.
Cost and Accessibility of Materials
3D printer clay generally offers lower cost and greater accessibility compared to porcelain clay, benefiting from mass-produced composite materials designed for ease of use in additive manufacturing. Porcelain clay, while prized for its fine texture and strength, incurs higher expense due to its refined kaolin content and limited availability in specialized ceramic supply stores. The affordability and widespread supply of 3D printer clay enable artists and designers to experiment with complex shapes without the significant investment typically required for high-quality porcelain materials.
Choosing the Best Clay for Fine Ceramic Projects
3D printer clay offers precise control and consistency, making it ideal for intricate fine ceramic projects and rapid prototyping. Porcelain clay provides superior translucency and a smooth finish, valued for high-quality, delicate ceramics with a traditional feel. Selecting the best clay depends on project demands: use 3D printer clay for detailed designs and efficiency, while porcelain clay suits refined, classic ceramic art.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Porcelain clay for Fine Ceramic
 azmater.com
azmater.com