Colored clay offers rich, natural hues ideal for rustic pottery, while porcelain clay provides a smooth, translucent finish preferred for fine, detailed ceramics. Porcelain's high firing temperature creates durable, vitrified pieces, whereas colored clay is more versatile for low-fire, decorative work.
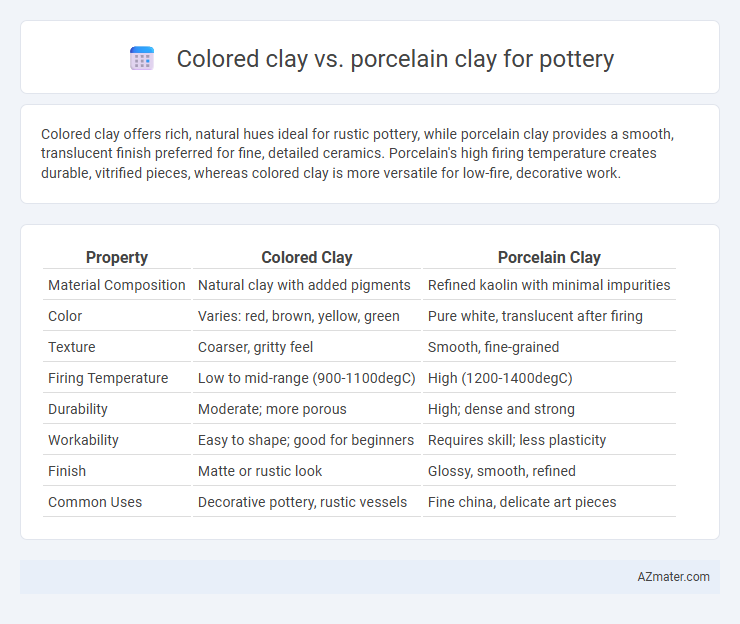
Table of Comparison
| Property | Colored Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural clay with added pigments | Refined kaolin with minimal impurities |
| Color | Varies: red, brown, yellow, green | Pure white, translucent after firing |
| Texture | Coarser, gritty feel | Smooth, fine-grained |
| Firing Temperature | Low to mid-range (900-1100degC) | High (1200-1400degC) |
| Durability | Moderate; more porous | High; dense and strong |
| Workability | Easy to shape; good for beginners | Requires skill; less plasticity |
| Finish | Matte or rustic look | Glossy, smooth, refined |
| Common Uses | Decorative pottery, rustic vessels | Fine china, delicate art pieces |
Introduction: Understanding Colored Clay and Porcelain Clay
Colored clay contains natural or added pigments that provide vibrant hues, offering artists diverse aesthetic possibilities without requiring additional glazing. Porcelain clay is a highly refined, white clay known for its smooth texture, translucency, and strength, ideal for delicate and precise pottery work. Both clays differ in plasticity, firing temperature, and finish, influencing their suitability for various ceramic techniques and artistic effects.
Key Differences Between Colored Clay and Porcelain Clay
Colored clay features natural or added pigments that provide a variety of hues and textures, making it ideal for artistic and decorative pottery. Porcelain clay is known for its fine, white, and smooth texture, offering high strength, translucency, and a delicate finish after firing. Key differences include porosity, firing temperature, and plasticity, with porcelain requiring higher firing temperatures and yielding a more vitrified, non-porous surface compared to colored clay.
Material Composition and Properties
Colored clay contains natural pigments and mineral additives that influence its plasticity and firing temperature, often resulting in a more textured and rustic finish. Porcelain clay is composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, offering high vitrification, translucency, and a smooth, glass-like surface after firing. The distinct material compositions affect their durability, with porcelain being more delicate but highly suitable for fine, detailed work, while colored clay offers versatility and richer, earthy tones.
Workability and Handling Techniques
Colored clay typically contains natural pigments and additives that enhance plasticity, making it easier to shape and ideal for hand-building techniques. Porcelain clay, known for its fine particle size and high kaolin content, offers a smooth, soft texture but requires precise moisture control to prevent cracking or warping during throwing and firing. While colored clay allows for more forgiving manipulation, porcelain demands advanced handling skills to maintain structural integrity and achieve its characteristic translucency.
Aesthetic Qualities: Appearance and Color Options
Colored clay offers a rich, natural palette with earthy tones and variegated textures that enhance the organic aesthetic of pottery pieces. Porcelain clay provides a smooth, pristine white surface ideal for glazing, allowing for bright, vibrant colors and fine detailed decoration. The choice between colored clay and porcelain depends on the desired visual impact, whether emphasizing raw, natural beauty or refined, glossy finishes.
Firing Temperature and Durability
Colored clay typically fires at lower temperatures ranging from 1,650degF to 2,100degF (900degC to 1,150degC), making it more suitable for earthenware pottery that is less dense and somewhat porous. Porcelain clay requires higher firing temperatures, usually between 2,300degF and 2,600degF (1,260degC to 1,430degC), resulting in a vitrified, non-porous, and highly durable ceramic product. The increased firing temperature of porcelain clay contributes to its superior strength, translucency, and resistance to chipping compared to colored clay pottery.
Common Uses and Applications in Pottery
Colored clay is widely used in pottery for decorative items, plaques, and functional ware that benefit from natural hues without the need for glazes, making it ideal for rustic and artistic styles. Porcelain clay, known for its fine, translucent qualities and strength after firing, is preferred in creating delicate, high-end tableware, figurines, and intricate sculptural pieces requiring a smooth, white finish. The choice depends on desired aesthetics and functionality: colored clay offers vibrant tones and texture, while porcelain ensures refined detail and durability for both artistic and practical pottery applications.
Cost Considerations and Accessibility
Colored clay typically costs less than porcelain clay due to the inclusion of natural pigments and minerals, making it a budget-friendly option for beginner potters. Porcelain clay, known for its fine texture and high firing temperature, tends to be more expensive and less accessible, often requiring specialized suppliers. Accessibility to colored clay is generally higher as it is widely available in art stores and online, whereas porcelain clay may be limited in distribution and demand more careful handling during the pottery process.
Suitability for Beginners vs Experienced Potters
Colored clay offers ease of use and immediate visual appeal, making it highly suitable for beginners who want to explore pottery without complex glazing processes. Porcelain clay, known for its fine texture and translucence, requires careful handling and firing techniques, appealing more to experienced potters seeking precision and high-quality finishes. Beginners benefit from the forgiving nature and vibrant outcomes of colored clay, while skilled artists leverage porcelain's versatility for delicate and refined creations.
Which Clay Should You Choose for Your Pottery Projects?
Colored clay offers natural pigmentation that eliminates the need for additional glazes, making it ideal for rustic, earthy pottery with immediate visual appeal, while porcelain clay is prized for its smooth, fine texture and translucent quality after firing, perfect for delicate, refined pieces requiring a high level of detail. Choose colored clay if you want vibrant, durable pottery with a more organic, tactile surface and less post-firing decoration. Opt for porcelain clay when you aim for elegant, lightweight pieces with a professional finish and the ability to showcase intricate designs through techniques like carving or glazing.
Infographic: Colored clay vs Porcelain clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com