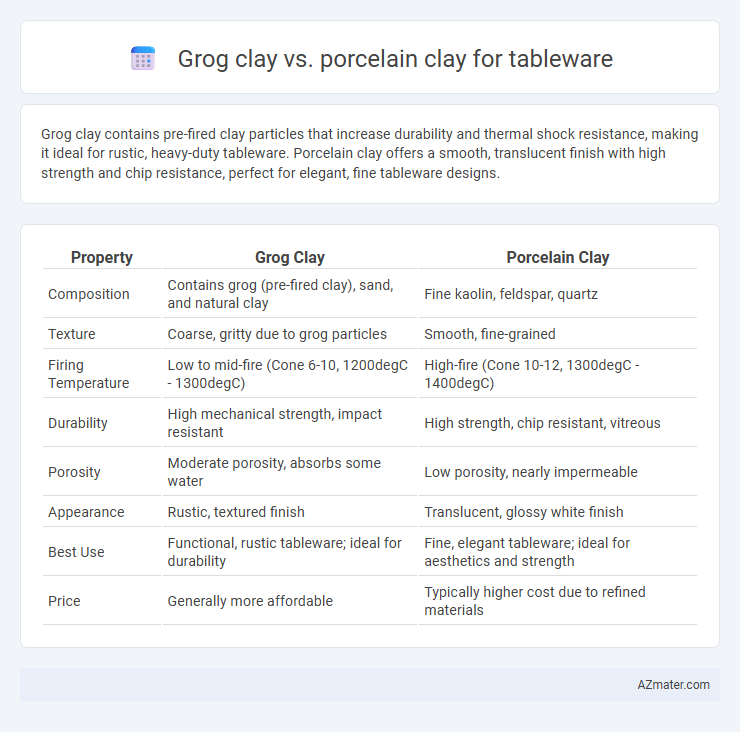
Grog clay contains pre-fired clay particles that increase durability and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for rustic, heavy-duty tableware. Porcelain clay offers a smooth, translucent finish with high strength and chip resistance, perfect for elegant, fine tableware designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Grog Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains grog (pre-fired clay), sand, and natural clay | Fine kaolin, feldspar, quartz |
| Texture | Coarse, gritty due to grog particles | Smooth, fine-grained |
| Firing Temperature | Low to mid-fire (Cone 6-10, 1200degC - 1300degC) | High-fire (Cone 10-12, 1300degC - 1400degC) |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, impact resistant | High strength, chip resistant, vitreous |
| Porosity | Moderate porosity, absorbs some water | Low porosity, nearly impermeable |
| Appearance | Rustic, textured finish | Translucent, glossy white finish |
| Best Use | Functional, rustic tableware; ideal for durability | Fine, elegant tableware; ideal for aesthetics and strength |
| Price | Generally more affordable | Typically higher cost due to refined materials |
Introduction to Grog Clay and Porcelain Clay
Grog clay contains pre-fired clay particles that improve structural strength and reduce shrinkage during firing, making it ideal for durable, heat-resistant tableware. Porcelain clay is composed of refined kaolin clay mixed with silica and feldspar, producing a smooth, translucent, and vitrified surface prized for elegant and delicate tableware pieces. The choice between grog and porcelain clay influences the texture, durability, and firing temperature suitable for different styles of ceramic tableware.
Composition and Material Properties
Grog clay contains coarse, pre-fired clay particles that enhance durability, reduce shrinkage, and improve thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty tableware. Porcelain clay, composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, offers a smooth texture, high translucency, and exceptional strength when fired at high temperatures, resulting in fine, delicate tableware. The inclusion of grog affects porosity and surface roughness, while porcelain's vitrification process yields a non-porous, glass-like finish suitable for elegant dining sets.
Workability and Ease of Shaping
Grog clay contains pre-fired clay particles that increase its plasticity and reduce shrinkage, making it easier to shape and less prone to cracking during drying and firing, ideal for sturdy tableware. Porcelain clay, known for its fine, smooth texture, requires more skill to work with due to its high plasticity and tendency to warp, but it yields delicate, translucent pieces favored for elegant tableware. The presence of grog enhances workability and structural strength, while porcelain's refinement offers superior aesthetic appeal but demands greater control during forming and drying.
Firing Temperatures and Methods
Grog clay contains crushed fired clay particles that improve thermal shock resistance, making it suitable for high-temperature firing between 1200degC and 1300degC in electric or gas kilns. Porcelain clay typically requires higher firing temperatures, ranging from 1200degC to 1400degC, and benefits from controlled ramping schedules in reduction or oxidation atmospheres to achieve its characteristic translucency and strength. The choice between grog clay and porcelain clay impacts firing methods, with grog clay offering greater durability during rapid temperature changes and porcelain demanding precise kiln control for optimal vitrification.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Grog clay incorporates pre-fired clay particles that enhance tableware's durability and resistance to thermal shock, making it less prone to cracking during firing or everyday use compared to porcelain clay. Porcelain clay, composed of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, offers a smooth, vitrified surface with high strength but is more brittle and susceptible to chipping under heavy impact. When prioritizing durability and strength, grog clay tableware generally outperforms porcelain in resisting mechanical stress, while porcelain excels in achieving a refined, delicate appearance with moderate strength.
Finishes and Aesthetic Qualities
Grog clay offers a textured, rustic finish with visible granules that enhance grip and create an earthy aesthetic ideal for casual, handmade tableware. Porcelain clay provides a smooth, translucent finish characterized by its fine, white appearance and delicate, refined surface, making it perfect for elegant and formal table settings. The choice between grog and porcelain influences the final look and tactile experience, with grog emphasizing durability and rustic charm, while porcelain delivers sleekness and sophistication.
Porosity and Food Safety Considerations
Porcelain clay boasts lower porosity compared to grog clay, making it less absorbent and more resistant to liquid penetration, which is crucial for maintaining hygiene in tableware. Its dense, vitrified structure reduces the risk of bacterial growth, enhancing food safety by preventing contaminants from seeping into the ceramic surface. Grog clay's higher porosity requires thorough glazing to achieve similar food-safe standards, whereas porcelain often provides inherent protection due to its compact molecular composition.
Cost and Accessibility
Grog clay typically costs less than porcelain clay, making it a more budget-friendly option for tableware production. It contains pre-fired clay particles that reduce shrinkage and improve workability, which can lower wastage and production time. Porcelain clay, although more expensive and less accessible due to its fine materials and specialized firing requirements, offers superior translucency and strength, making it ideal for high-end tableware.
Best Uses in Tableware Production
Grog clay enhances durability and heat resistance in tableware, making it ideal for creating robust, everyday use items like plates and bowls that withstand frequent handling and temperature changes. Porcelain clay, prized for its fine texture and translucency, is best suited for elegant, lightweight tableware designed for formal dining settings where aesthetics and smooth finishes are paramount. Choosing between grog and porcelain clays depends on the balance between functional strength and refined appearance desired in the finished tableware pieces.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Tableware
Grog clay offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for functional tableware that withstands frequent use and temperature changes. Porcelain clay provides a smooth, translucent finish with high strength and a refined aesthetic, perfect for elegant and delicate dinnerware. Selecting between grog clay and porcelain clay depends on the desired balance between ruggedness and visual appeal for your specific tableware needs.
Infographic: Grog clay vs Porcelain clay for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com