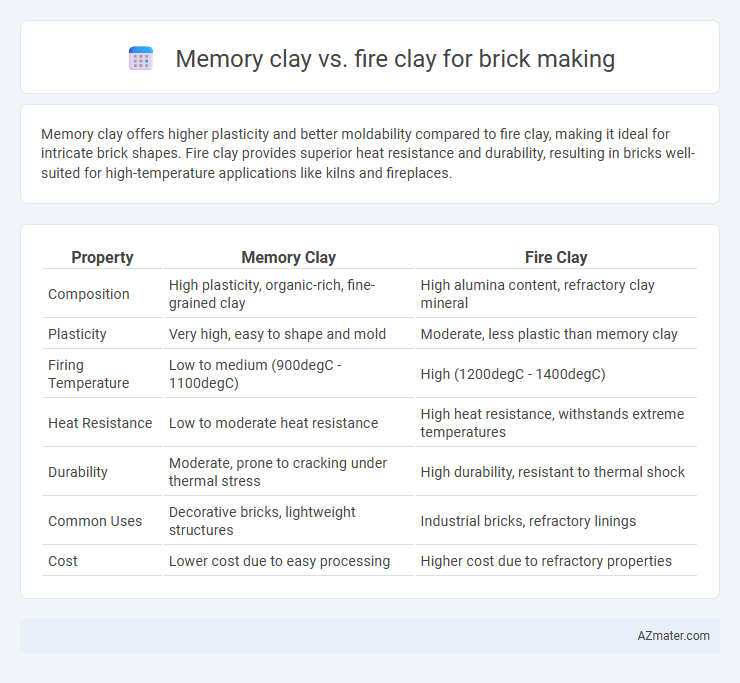
Memory clay offers higher plasticity and better moldability compared to fire clay, making it ideal for intricate brick shapes. Fire clay provides superior heat resistance and durability, resulting in bricks well-suited for high-temperature applications like kilns and fireplaces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Memory Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High plasticity, organic-rich, fine-grained clay | High alumina content, refractory clay mineral |
| Plasticity | Very high, easy to shape and mold | Moderate, less plastic than memory clay |
| Firing Temperature | Low to medium (900degC - 1100degC) | High (1200degC - 1400degC) |
| Heat Resistance | Low to moderate heat resistance | High heat resistance, withstands extreme temperatures |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking under thermal stress | High durability, resistant to thermal shock |
| Common Uses | Decorative bricks, lightweight structures | Industrial bricks, refractory linings |
| Cost | Lower cost due to easy processing | Higher cost due to refractory properties |
Introduction to Memory Clay and Fire Clay
Memory clay, known for its fine particle size and plasticity, allows for easy shaping and smooth finishes in brick making, while fire clay contains high alumina content, providing excellent heat resistance and durability. Fire clay bricks endure high temperatures without deformation, making them ideal for furnaces and kilns, whereas memory clay bricks are prized for intricate designs and aesthetic appeal. Both clays serve distinct purposes, with fire clay focusing on thermal stability and memory clay emphasizing formability and surface texture.
Key Differences Between Memory Clay and Fire Clay
Memory clay exhibits high plasticity and excellent molding capabilities, making it ideal for detailed brick shapes, while fire clay contains higher alumina content, providing superior heat resistance and durability in refractory bricks. Memory clay typically retains shape well under pressure but is less resistant to high temperatures compared to fire clay, which withstands thermal stress and erosion in kiln linings. The key differences lie in their chemical composition--memory clay's higher kaolinite content enhances workability, whereas fire clay's elevated silica and alumina levels contribute to its refractoriness and strength.
Physical Properties of Memory Clay vs Fire Clay
Memory clay exhibits higher plasticity and better workability compared to fire clay, which tends to have a more rigid texture due to its higher refractory mineral content. Fire clay possesses greater heat resistance and structural integrity at high temperatures, thanks to its elevated alumina and silica levels, making it ideal for bricks subjected to intense thermal conditions. The density of memory clay is generally lower than that of fire clay, impacting the thermal conductivity and strength of the final brick product.
Workability and Molding Performance
Memory clay offers superior workability due to its fine particle size and plasticity, enabling easier shaping and molding into intricate brick forms. Fire clay, while highly refractory with strong heat resistance, tends to be denser and less plastic, which can result in stiffer workability and more challenges during molding. The choice between memory clay and fire clay directly impacts molding performance, with memory clay preferred for detailed brick designs and fire clay favored for heavy-duty, heat-resistant bricks despite its comparatively reduced molding ease.
Firing Temperatures: Memory Clay vs Fire Clay
Memory clay typically fires at lower temperatures ranging from 1,000degC to 1,150degC, making it suitable for decorative bricks and ceramics that require less intense heat treatment. Fire clay, known for its high alumina content, withstands firing temperatures between 1,200degC and 1,400degC, producing bricks that exhibit superior strength and thermal resistance. The higher firing temperature of fire clay ensures enhanced durability and heat retention, essential for industrial furnaces and refractory applications.
Durability and Strength in Final Bricks
Fire clay bricks exhibit exceptional durability and high compressive strength due to their high alumina and silica content, making them ideal for high-temperature applications and structural use. Memory clay, while less common in brick making, tends to have lower mechanical strength and may lack the thermal resistance required for long-term durability in demanding environments. Choosing fire clay over memory clay results in bricks with superior hardness, resistance to chemical corrosion, and longer lifespan under stress.
Cost Comparison: Memory Clay and Fire Clay
Memory clay typically costs less than fire clay due to its abundant local availability and lower processing requirements, making it a budget-friendly option for brick manufacturing. Fire clay, known for its high refractory properties and durability, commands a higher price driven by more intensive mining and refining processes. The cost difference influences project budgets, with memory clay favored in cost-sensitive applications and fire clay chosen for high-performance bricks needing superior heat resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Memory clay bricks offer improved environmental benefits due to their lower energy consumption during manufacturing and reduced carbon emissions compared to traditional fire clay bricks. Fire clay requires high-temperature firing, leading to increased fossil fuel use and greater greenhouse gas output, whereas memory clay can often be cured at lower temperatures or air-dried, minimizing ecological footprint. Sustainable brick production increasingly favors memory clay for its resource efficiency, waste reduction, and potential for recycling, aligning with green building standards and eco-friendly construction practices.
Applications in Modern Brick Making
Memory clay, known for its high plasticity and fine particle size, is primarily utilized in precision molding and specialty brick production requiring detailed shapes. Fire clay, with its exceptional heat resistance and refractory properties, is widely used in manufacturing firebricks for kilns, furnaces, and other high-temperature industrial applications. Modern brick making leverages fire clay's durability in high-thermal environments, while memory clay is favored for aesthetic bricks and intricate architectural designs.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Brick Project
Memory clay offers excellent plasticity and workability, making it ideal for shaping bricks with precise dimensions and smooth textures. Fire clay, with its high refractory properties and resistance to heat, is preferred for bricks used in high-temperature environments like kilns or fireplaces. Selecting the right clay depends on the intended use of the bricks, where memory clay suits aesthetic and structural applications, while fire clay ensures durability under intense heat conditions.
Infographic: Memory clay vs Fire clay for Brick making
 azmater.com
azmater.com