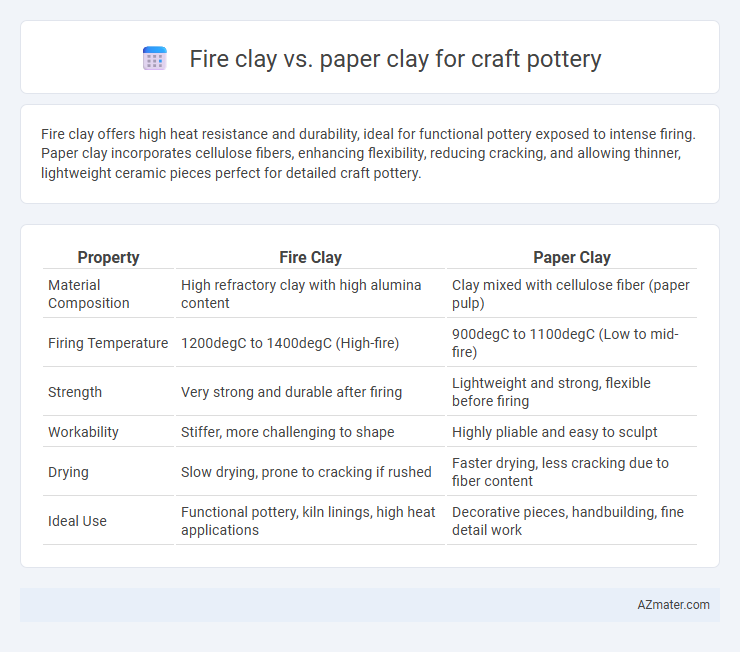
Fire clay offers high heat resistance and durability, ideal for functional pottery exposed to intense firing. Paper clay incorporates cellulose fibers, enhancing flexibility, reducing cracking, and allowing thinner, lightweight ceramic pieces perfect for detailed craft pottery.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fire Clay | Paper Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High refractory clay with high alumina content | Clay mixed with cellulose fiber (paper pulp) |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC to 1400degC (High-fire) | 900degC to 1100degC (Low to mid-fire) |
| Strength | Very strong and durable after firing | Lightweight and strong, flexible before firing |
| Workability | Stiffer, more challenging to shape | Highly pliable and easy to sculpt |
| Drying | Slow drying, prone to cracking if rushed | Faster drying, less cracking due to fiber content |
| Ideal Use | Functional pottery, kiln linings, high heat applications | Decorative pieces, handbuilding, fine detail work |
Understanding Fire Clay: Composition and Properties
Fire clay is a refractory material composed primarily of kaolinite, quartz, and mica, known for its high resistance to heat and thermal shock, making it ideal for craft pottery that requires firing at high temperatures. Its dense, non-refractory nature allows it to maintain structural integrity during kiln firing, resulting in durable, heat-resistant ceramic pieces. The inherent plasticity and fine particle size of fire clay contribute to excellent workability and smooth surface finishes in pottery applications.
What is Paper Clay? Key Ingredients and Characteristics
Paper clay is a type of ceramic material that incorporates paper fibers into traditional clay, enhancing its strength and flexibility. Key ingredients include kaolin or ball clay combined with cellulose fibers, improving workability and reducing drying time. Its characteristics allow for easier joining of dry and wet pieces, making it ideal for detailed craft pottery and sculptural work.
Workability: Comparing Fire Clay and Paper Clay
Fire clay offers a dense, refractory composition ideal for high-temperature durability but can be stiff and less pliable during shaping. Paper clay incorporates cellulose fibers, enhancing plasticity and flexibility, which improves workability by allowing thinner walls and easier joining of parts. The fiber content in paper clay reduces cracking risk during drying, making it more user-friendly for intricate or delicate pottery designs compared to the rigid texture of fire clay.
Strength and Durability: Which Clay Performs Better?
Fire clay offers superior strength and durability due to its high alumina content and resistance to high temperatures, making it ideal for functional pottery exposed to heat and wear. Paper clay incorporates cellulose fibers that enhance flexibility and reduce cracking during drying, but it is generally less durable when fired compared to fire clay. For long-lasting, strong pottery, fire clay performs better, while paper clay suits delicate or sculptural pieces requiring lighter workability.
Drying Time and Shrinkage Differences
Fire clay typically exhibits slower drying times due to its dense and refractory properties, resulting in reduced risk of cracks during drying. Paper clay, infused with cellulose fibers, dries faster and offers increased flexibility, allowing for easier manipulation and repair during the drying stage. Shrinkage rates are generally lower in paper clay because the organic fibers help control deformation, while fire clay shrinks more significantly as it loses moisture and densifies in the kiln.
Sculpting and Handbuilding Capabilities
Fire clay offers superior structural strength and high resistance to heat, making it ideal for sculpting detailed and durable pottery pieces that require firm support during firing. Paper clay incorporates cellulose fibers, enhancing flexibility and allowing artists to create thinner, more intricate handbuilt forms without cracking or collapsing. Both clays excel in handbuilding, but paper clay's lightweight, plastic texture is especially advantageous for delicate sculptural elements and multi-part assemblies.
Firing Temperatures and Kiln Considerations
Fire clay typically withstands higher firing temperatures up to cone 10 (approx. 2345degF or 1285degC), making it ideal for stoneware and porcelain crafts, whereas paper clay generally fires at lower temperatures, around cone 06 to 04 (about 1828degF to 1940degF or 998degC to 1060degC). Kiln considerations for fire clay include the need for higher fuel consumption and longer firing schedules due to its dense composition, while paper clay allows for faster firing cycles and lower energy use because of its porous, fibrous structure. Choosing between the two depends on the desired finished durability and the specific kiln's temperature range and atmosphere capabilities.
Surface Finishes and Glazing Options
Fire clay offers a dense, smooth surface ideal for holding glaze without excessive absorption, resulting in vibrant, glossy finishes and excellent color retention for craft pottery. Paper clay contains paper fibers that create a porous texture, allowing for unique matte or textured surface finishes but may require special glazing techniques to prevent peeling or cracking during firing. Both clays support various glaze types, but fire clay is preferred for intricate, high-gloss glazing, while paper clay suits creative, textured applications where surface interaction with glaze plays a distinct role.
Cost Analysis: Fire Clay vs. Paper Clay
Fire clay, a dense and durable material used in craft pottery, generally costs more due to its high refractory properties and less widespread availability. Paper clay incorporates cellulose fibers, reducing overall material weight and drying time, which often lowers costs associated with kiln firing and waste. Choosing paper clay can lead to cost savings in both raw material expenses and energy consumption during firing compared to fire clay.
Best Uses: Choosing the Right Clay for Your Pottery Project
Fire clay is ideal for high-temperature firing and creating durable, functional pottery such as cookware and kiln furniture due to its heat resistance and strength. Paper clay, enriched with cellulose fibers, offers enhanced workability and flexibility, making it perfect for delicate sculptural pieces and intricate hand-building projects. Selecting between fire clay and paper clay depends on the pottery's intended use--opt for fire clay for durability and heat exposure, while choosing paper clay for fine detail and lightweight versatility.
Infographic: Fire clay vs Paper clay for Craft pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com