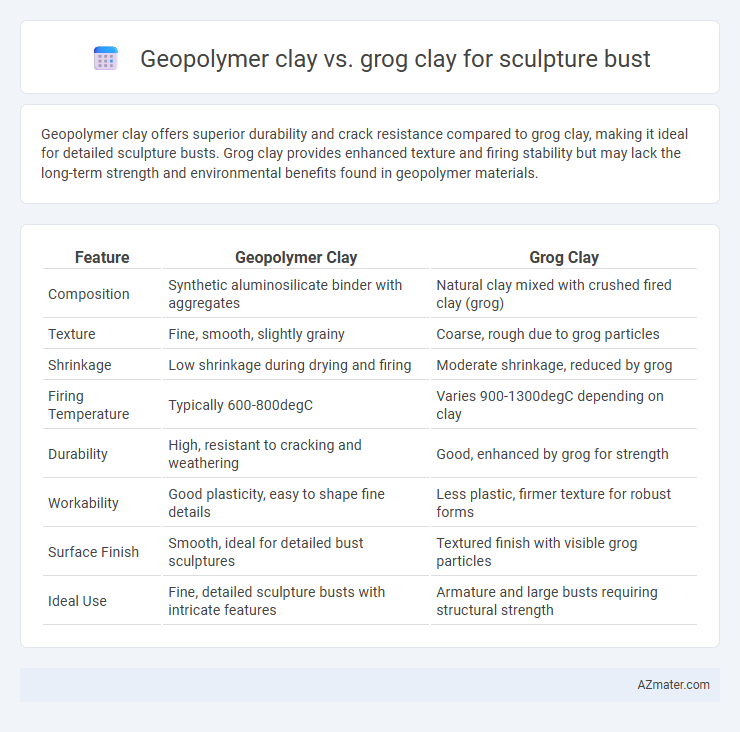
Geopolymer clay offers superior durability and crack resistance compared to grog clay, making it ideal for detailed sculpture busts. Grog clay provides enhanced texture and firing stability but may lack the long-term strength and environmental benefits found in geopolymer materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Geopolymer Clay | Grog Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Synthetic aluminosilicate binder with aggregates | Natural clay mixed with crushed fired clay (grog) |
| Texture | Fine, smooth, slightly grainy | Coarse, rough due to grog particles |
| Shrinkage | Low shrinkage during drying and firing | Moderate shrinkage, reduced by grog |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 600-800degC | Varies 900-1300degC depending on clay |
| Durability | High, resistant to cracking and weathering | Good, enhanced by grog for strength |
| Workability | Good plasticity, easy to shape fine details | Less plastic, firmer texture for robust forms |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, ideal for detailed bust sculptures | Textured finish with visible grog particles |
| Ideal Use | Fine, detailed sculpture busts with intricate features | Armature and large busts requiring structural strength |
Introduction to Geopolymer Clay and Grog Clay
Geopolymer clay is a synthetic, eco-friendly material composed primarily of aluminosilicate minerals activated by alkaline solutions, offering high strength and rapid curing ideal for detailed sculpture busts. Grog clay, on the other hand, incorporates pre-fired clay particles known as grog, enhancing texture and reducing shrinkage during firing, making it a traditional choice for durability and crack resistance in sculpting. Both materials provide distinct advantages: geopolymer clay excels in precision and environmental sustainability, while grog clay ensures structural integrity and tactile richness.
Composition and Material Properties
Geopolymer clay consists mainly of aluminosilicate precursors activated by alkaline solutions, resulting in a high-strength, heat-resistant material ideal for detailed sculpture busts. Grog clay contains pre-fired, ground ceramic particles (grog) mixed into the clay body, enhancing thermal shock resistance and reducing shrinkage during firing. The inorganic polymer network in geopolymer clay offers superior durability and lower porosity compared to grog clay's traditional ceramic matrix, influencing texture and finish in sculptural works.
Workability: Sculpting with Geopolymer vs Grog Clay
Geopolymer clay offers superior workability for sculpture busts due to its consistent texture and plasticity, allowing for finer detailing and smoother finishes. Grog clay, embedded with coarse grog particles, provides structural strength and reduces shrinkage but can be more challenging to sculpt intricate details because of its gritty texture. Artists often choose geopolymer clay for precision work, while grog clay is preferred for robust, textured effects and durability in larger busts.
Surface Texture and Detail Retention
Geopolymer clay offers a smooth, consistent surface texture that enhances fine detail retention, making it ideal for intricate sculpture busts. Grog clay contains granular particles that create a rougher texture, which can support structural strength but may limit the sharpness of detailed features. For artists prioritizing crisp surface detail and a polished finish, geopolymer clay is generally preferred over grog clay.
Drying and Shrinkage Differences
Geopolymer clay exhibits minimal shrinkage during drying due to its inorganic polymer matrix, reducing crack formation in sculpture busts compared to traditional grog clay. Grog clay contains pre-fired clay particles that improve drying strength but still experiences more notable shrinkage as water evaporates from the porous structure. Controlling drying speed is crucial for grog clay to mitigate cracking, whereas geopolymer clay allows for more uniform drying with less deformation risk.
Firing Methods and Temperature Requirements
Geopolymer clay typically cures at room temperature or requires low-temperature firing around 200-300degC, making it suitable for air-drying and minimal kiln use, while grog clay demands high-temperature firing between 1,000degC and 1,300degC to vitrify and achieve durability. Geopolymer's inorganic polymer matrix offers chemical resistance without traditional pyrometric cone reliance, contrasting with grog clay's reliance on thermal sintering and grog particles for shrinkage control and enhanced strength. Sculptors selecting materials must consider geopolymer clay's energy-efficient curing against grog clay's traditional kiln firing, which affects final texture, structural integrity, and longevity of sculptural busts.
Durability and Longevity in Sculpture Busts
Geopolymer clay offers exceptional durability and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for long-lasting sculpture busts. Grog clay, enhanced with fired clay particles, improves structural integrity and reduces shrinkage during firing, providing stable and crack-resistant sculptures. Both materials ensure longevity, but geopolymer clay generally surpasses grog clay in maintaining strength and weather resistance over extended periods.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer clay offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to grog clay due to its use of industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, reducing landfill waste and carbon emissions. Grog clay, while traditional and valued for its texture and firing properties, involves mining and high-temperature firing that contribute to resource depletion and greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing geopolymer clay promotes sustainability through energy-efficient processing and the reuse of industrial materials, making it a greener option for sculpture bust creation.
Cost Comparison and Accessibility
Geopolymer clay generally incurs higher initial costs due to specialized chemical components like aluminosilicate and activators, but it offers enhanced durability and low shrinkage, making it cost-effective for long-term use in sculpture busts. Grog clay, composed of natural clay mixed with fired clay particles, is more affordable and widely accessible through conventional art supply stores, appealing to artists seeking budget-friendly materials. While geopolymer clay availability may be limited to industrial suppliers or online retailers, grog clay benefits from extensive distribution and easier procurement for sculptors.
Artist Recommendations and Use Cases
Artists recommend geopolymer clay for sculpture busts due to its superior durability, resistance to cracking, and excellent fine detail retention, making it ideal for outdoor sculptures and long-term display. Grog clay is preferred by artists who prioritize texture and structural stability during firing, especially for larger busts requiring strong internal support and less shrinkage. Use cases for geopolymer clay involve archival-quality, weather-resistant pieces, while grog clay is commonly used in traditional ceramic busts and experimental textures where controlled firing processes are available.
Infographic: Geopolymer clay vs Grog clay for Sculpture bust
 azmater.com
azmater.com