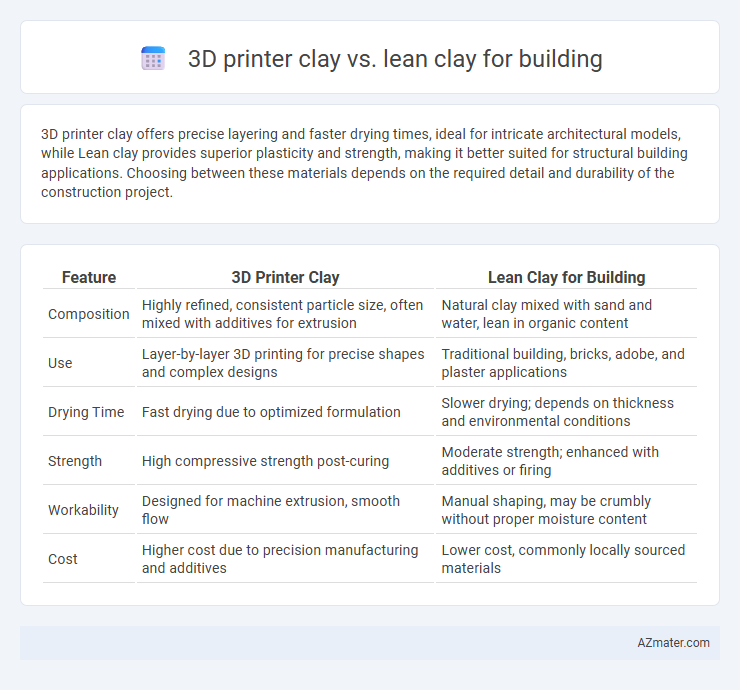
3D printer clay offers precise layering and faster drying times, ideal for intricate architectural models, while Lean clay provides superior plasticity and strength, making it better suited for structural building applications. Choosing between these materials depends on the required detail and durability of the construction project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Lean Clay for Building |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Highly refined, consistent particle size, often mixed with additives for extrusion | Natural clay mixed with sand and water, lean in organic content |
| Use | Layer-by-layer 3D printing for precise shapes and complex designs | Traditional building, bricks, adobe, and plaster applications |
| Drying Time | Fast drying due to optimized formulation | Slower drying; depends on thickness and environmental conditions |
| Strength | High compressive strength post-curing | Moderate strength; enhanced with additives or firing |
| Workability | Designed for machine extrusion, smooth flow | Manual shaping, may be crumbly without proper moisture content |
| Cost | Higher cost due to precision manufacturing and additives | Lower cost, commonly locally sourced materials |
Introduction to 3D Printer Clay and Lean Clay
3D printer clay is a specialized material designed for additive manufacturing, offering precise layer-by-layer construction ideal for complex architectural models and prototypes. Lean clay, traditionally used in construction, is a more uniform mixture with reduced water and impurities, providing enhanced workability and strength for structural applications. Both materials serve distinct roles, where 3D printer clay excels in digital fabrication processes and lean clay supports conventional building techniques.
Composition Differences: 3D Printer Clay vs Lean Clay
3D printer clay typically consists of a carefully balanced mixture of fine particulate clays, binders, and water to ensure optimal flow and extrusion properties in additive manufacturing processes. Lean clay, by contrast, contains a higher proportion of coarse sand and inert materials, resulting in reduced plasticity and greater strength for traditional building applications. The key compositional difference lies in the particle size distribution and binder content, where 3D printer clay prioritizes homogeneity and smoothness for precise layering, while lean clay emphasizes structural stability and workability for manual construction.
Workability and Forming Techniques
3D printer clay offers superior workability with a smooth, consistent texture ideal for automated extrusion and precise layer-by-layer forming techniques, enabling complex architectural details and rapid prototyping. Lean clay, with its lower plasticity and higher sand content, requires careful manual manipulation and traditional forming methods such as molding or hand sculpting, which can limit intricate design capabilities. The choice between these clays depends on the required detail level and production speed, where 3D printer clay excels in digital fabrication and lean clay suits conventional construction processes.
Structural Integrity and Durability Comparison
3D printer clay offers precise layering and uniform material distribution, enhancing structural integrity through controlled deposition, which reduces internal defects compared to traditional lean clay used in building. Lean clay, with its natural composition and variability, may show lower durability due to potential inconsistencies and higher porosity, impacting long-term stability under environmental stress. While 3D printer clay enables customized reinforcement and optimized density, lean clay benefits from proven performance in conventional construction but requires additional stabilization techniques to improve strength and weather resistance.
Drying and Shrinkage Rates
3D printer clay typically exhibits faster drying times due to its fine particle size and additives designed for controlled moisture evaporation, enabling quicker building cycles compared to traditional lean clay. Lean clay, composed mainly of natural clay with minimal additives, tends to have slower drying rates and higher shrinkage due to greater moisture content and less uniform particle distribution. The shrinkage rate of 3D printer clay is generally lower and more predictable, reducing the risk of cracking and deformation during drying, which is crucial for precision in construction applications.
Suitability for Construction Applications
3D printer clay offers precise extrusion and rapid setting times, making it ideal for intricate architectural models and small-scale construction prototypes. Lean clay, characterized by its low plasticity and higher sand content, provides enhanced stability and durability, better suited for traditional load-bearing walls and large structural elements. Choosing between 3D printer clay and lean clay depends on the project's scale, desired mechanical strength, and construction speed requirements.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
3D printer clay offers precise material usage, reducing waste and energy consumption compared to traditional Lean clay, which often requires more raw materials and prolonged drying times. Lean clay production involves higher water usage and emits more greenhouse gases due to manual processing, while 3D printing technology optimizes resource efficiency and minimizes carbon footprint through automated layering and reduced kiln firing. Sustainable construction benefits from 3D printer clay by enabling recyclable or biodegradable composite options that lower long-term environmental impact compared to conventional Lean clay bricks or blocks.
Cost Analysis: 3D Printer Clay vs Lean Clay
3D printer clay typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized equipment and technology requirements but offers precision and reduced labor expenses in large-scale building projects. Lean clay, composed mainly of natural clay with lower plasticity and minimal additives, presents a more affordable material cost but may increase overall expenses through longer drying times and manual labor. Evaluating total cost efficiency hinges on project scale, desired structural integrity, and the balance between material price and operational overheads.
Compatibility with Modern Building Technologies
3D printer clay is specifically formulated for compatibility with additive manufacturing technologies, offering precise extrusion and rapid drying suitable for automated building processes. Lean clay, traditional in composition with higher moisture and less refinement, often requires adaptation to integrate with modern digital construction methods. The enhanced rheological properties of 3D printer clay enable seamless integration with robotic arms and automated layering systems, making it more effective for smart construction environments compared to conventional lean clay.
Future Trends in Clay-Based Construction Methods
3D printer clay offers precise layering capabilities and material efficiency, making it ideal for automated, large-scale building applications, while lean clay provides traditional strength and durability with lower plasticity levels suited for foundational work. Future trends in clay-based construction emphasize sustainable materials with enhanced mechanical properties through nanomaterial additives and real-time sensor integration for structural health monitoring. Innovations in bio-based clays and adaptive printing techniques are set to revolutionize eco-friendly urban development by reducing carbon footprints and construction waste.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Lean clay for Building
 azmater.com
azmater.com