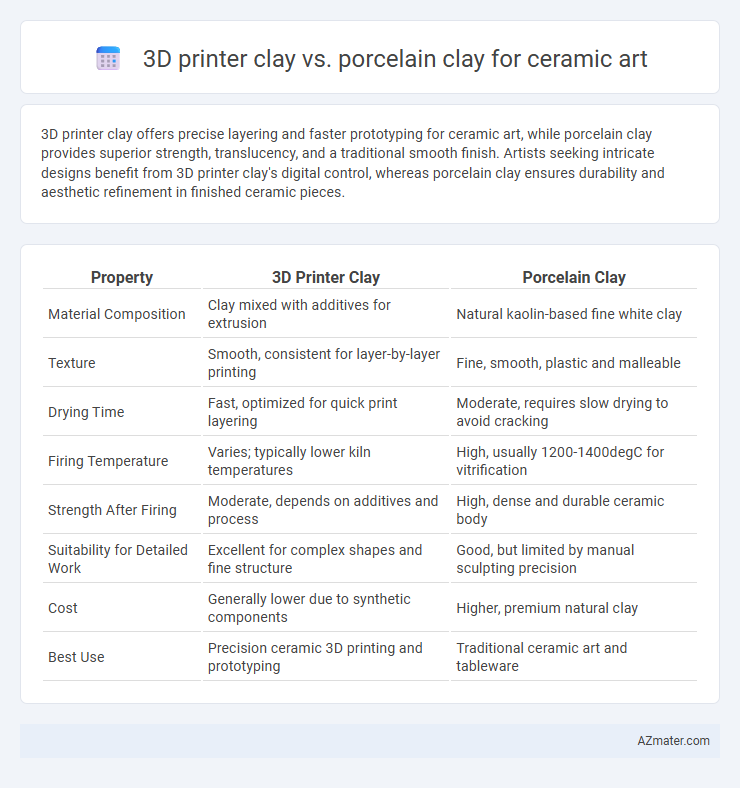
3D printer clay offers precise layering and faster prototyping for ceramic art, while porcelain clay provides superior strength, translucency, and a traditional smooth finish. Artists seeking intricate designs benefit from 3D printer clay's digital control, whereas porcelain clay ensures durability and aesthetic refinement in finished ceramic pieces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | 3D Printer Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay mixed with additives for extrusion | Natural kaolin-based fine white clay |
| Texture | Smooth, consistent for layer-by-layer printing | Fine, smooth, plastic and malleable |
| Drying Time | Fast, optimized for quick print layering | Moderate, requires slow drying to avoid cracking |
| Firing Temperature | Varies; typically lower kiln temperatures | High, usually 1200-1400degC for vitrification |
| Strength After Firing | Moderate, depends on additives and process | High, dense and durable ceramic body |
| Suitability for Detailed Work | Excellent for complex shapes and fine structure | Good, but limited by manual sculpting precision |
| Cost | Generally lower due to synthetic components | Higher, premium natural clay |
| Best Use | Precision ceramic 3D printing and prototyping | Traditional ceramic art and tableware |
Introduction to 3D Printing in Ceramic Art
3D printing in ceramic art revolutionizes traditional crafting by enabling precise and complex designs unattainable with manual methods. 3D printer clay, formulated for extrusion through printer nozzles, offers fine particle sizes and optimal plasticity for layer-by-layer building, contrasting with porcelain clay's dense, vitrified structure ideal for hand shaping and firing. Selecting appropriate clay impacts the final texture, strength, and detail resolution, influencing the artistic and functional qualities of ceramic pieces created via additive manufacturing.
What Is 3D Printer Clay?
3D printer clay is a specially formulated material designed for additive manufacturing processes, allowing precise layering to create intricate ceramic objects directly from digital models. Unlike traditional porcelain clay, it contains additives that improve flowability and reduce shrinkage during drying and firing, making it ideal for complex shapes and rapid prototyping in ceramic art. This innovative clay enables artists and designers to achieve high-detail ceramics with consistent structural integrity, expanding creative possibilities beyond conventional hand-building techniques.
Understanding Porcelain Clay in Ceramics
Porcelain clay in ceramics is characterized by its fine particle size, high plasticity, and delicate translucency, making it ideal for detailed and refined ceramic art. Unlike 3D printer clay, which is formulated for rapid layering and structural stability during printing, porcelain requires precise control over moisture and firing temperatures to achieve its signature smooth, vitrified surface. Mastering porcelain clay involves understanding its sensitivity to shrinkage and warping, ensuring artists can create durable, elegant pieces with a clean, polished finish.
Material Composition: 3D Printer Clay vs Porcelain Clay
3D printer clay is typically composed of synthetic polymers combined with fine clay particles, designed for extrusion and layering in additive manufacturing processes, providing flexibility and fast drying times. Porcelain clay consists primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, resulting in a fine-grained, highly plastic material that vitrifies at high temperatures to produce a smooth, translucent finish. The distinct material compositions influence their workability, firing temperatures, and final surface qualities in ceramic art.
Workability and Handling Differences
3D printer clay offers superior workability with precise layering and minimal shrinkage, allowing intricate designs and faster prototyping in ceramic art. Porcelain clay, being inherently more fluid and delicate, requires skilled handling to maintain its smooth texture and prevent cracking during shaping and firing. Unlike 3D printer clay, porcelain demands careful moisture control and traditional handcraft techniques, which can impact the final product's structural integrity and aesthetic finesse.
Firing and Sintering Processes Compared
3D printer clay designed for ceramic art typically contains additives that allow for lower firing temperatures and faster sintering, making it compatible with standard ceramic kilns, whereas porcelain clay requires higher firing temperatures around 1200-1400degC to achieve vitrification and strength. The firing process for 3D-printed clay often includes careful controlled drying to prevent warping and cracking due to layer-by-layer construction, unlike porcelain, which benefits from its dense and particle-aligned structure. Sintering in porcelain clay results in a highly dense, translucent finish due to its fine particle size and composition, while 3D printer clay sintering may produce slightly more porous textures depending on the specific formulation and printer technology used.
Texture and Surface Quality Results
3D printer clay offers a more consistent and smooth texture ideal for detailed ceramic art, allowing precise control over surface quality with minimal post-processing. Porcelain clay, renowned for its fine-grained, translucent texture, delivers a delicate, high-quality surface finish that enhances the tactile and aesthetic appeal of ceramic pieces. While 3D printer clay excels in uniformity and repeatability, porcelain clay provides superior natural elegance and subtle surface variations valued in traditional ceramic art.
Durability and Strength Analysis
3D printer clay typically offers less durability and strength compared to porcelain clay due to its lower density and higher porosity, which can lead to increased fragility in finished ceramic art pieces. Porcelain clay is known for its high strength and resistance to chipping and cracking, attributed to its fine particle size and vitrification during firing at high temperatures (around 1200-1400degC). While 3D printer clay allows for precise shaping and rapid prototyping, porcelain clay remains superior for creating long-lasting and structurally robust ceramic artworks.
Artistic Possibilities and Limitations
3D printer clay offers unparalleled precision and the ability to create complex, intricate designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional methods, expanding artistic possibilities in ceramic art. Porcelain clay, known for its smooth texture and translucency after firing, allows artists to produce elegant, refined pieces but demands skilled handcrafting techniques and can be less forgiving in structural complexity. The limitations of 3D printer clay include potential fragility and surface finish issues, while porcelain clay's challenges lie in its shrinkage and tendency to warp during firing, impacting the artist's creative freedom.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Ceramic Art Project
Choosing the right clay for your ceramic art project depends on the desired texture, firing temperature, and detail precision. 3D printer clay offers excellent control for creating intricate designs and rapid prototyping, while porcelain clay provides a smooth, fine-grained finish ideal for high-quality, durable ceramic pieces. Consider the aesthetic goals and functional requirements to select between the innovative versatility of 3D printer clay and the traditional elegance of porcelain clay.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Porcelain clay for Ceramic art
 azmater.com
azmater.com