Polymer clay offers lightweight, moldable properties suitable for decorative bricks, while fire clay provides high heat resistance and durability essential for structural and refractory brick applications. Fire clay's thermal stability and strength make it ideal for kiln linings and industrial furnaces, contrasting with polymer clay's limited heat tolerance.
Table of Comparison
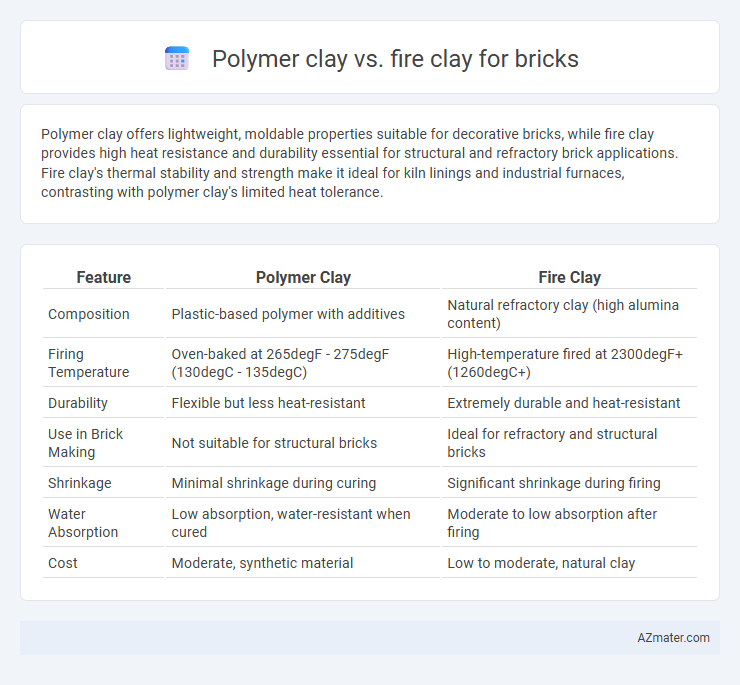
| Feature | Polymer Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Plastic-based polymer with additives | Natural refractory clay (high alumina content) |
| Firing Temperature | Oven-baked at 265degF - 275degF (130degC - 135degC) | High-temperature fired at 2300degF+ (1260degC+) |
| Durability | Flexible but less heat-resistant | Extremely durable and heat-resistant |
| Use in Brick Making | Not suitable for structural bricks | Ideal for refractory and structural bricks |
| Shrinkage | Minimal shrinkage during curing | Significant shrinkage during firing |
| Water Absorption | Low absorption, water-resistant when cured | Moderate to low absorption after firing |
| Cost | Moderate, synthetic material | Low to moderate, natural clay |
Introduction to Polymer Clay and Fire Clay
Polymer clay is a versatile, synthetic modeling material composed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) that hardens when baked at low temperatures, making it ideal for detailed crafting and decorative brick applications. Fire clay, a naturally occurring refractory material rich in alumina and silica, is traditionally used in brick manufacturing due to its high-temperature resistance and durability in kiln firing. The distinct chemical compositions and curing processes of polymer clay and fire clay define their suitability for different brick production techniques and end-use environments.
Composition and Material Properties
Polymer clay is a synthetic material composed mainly of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) combined with plasticizers, offering flexibility, ease of shaping, and low firing temperatures, which generally result in a lightweight, non-structural brick. Fire clay consists of natural, refractory clays rich in alumina and silica, enabling high-temperature resistance, durability, and structural integrity ideal for load-bearing and heat-exposed bricks. The primary differences lie in polymer clay's organic polymer base suited for decorative applications versus fire clay's inorganic mineral composition designed for thermal resistance and strength.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Polymer clay bricks are manufactured using synthetic polymers combined with plasticizers, cured through heat or UV light without traditional firing, enabling lower temperature processes and faster production cycles. Fire clay bricks, composed primarily of kaolin and other refractory clays, undergo a high-temperature firing process above 1200degC that imparts superior heat resistance and durability through mineral transformations. The distinct manufacturing approaches result in polymer clay bricks suited for decorative, lightweight applications, while fire clay bricks excel in structural and high-temperature environments due to their robust vitrification.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Fire clay bricks exhibit superior durability and strength compared to polymer clay bricks due to their high resistance to heat, pressure, and chemical corrosion, making them ideal for industrial and structural applications. Polymer clay bricks, while versatile and lightweight, lack the same level of compressive strength and thermal resistance, reducing their suitability for heavy load-bearing or high-temperature environments. The inherent mineral composition of fire clay contributes to its long-lasting performance, whereas polymer clay's organic components limit its structural resilience.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Performance
Fire clay exhibits superior heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1,500degC, making it ideal for refractory bricks used in furnaces and kilns. Polymer clay, on the other hand, typically withstands lower temperatures around 130degC and is more suitable for decorative or craft applications rather than structural thermal performance. The thermal conductivity of fire clay bricks is optimized for insulation and heat retention, whereas polymer clay lacks the necessary thermal stability for high-temperature environments.
Cost Analysis: Polymer vs Fire Clay Bricks
Polymer clay bricks generally incur a higher initial cost due to the specialized synthetic materials and manufacturing processes involved, whereas fire clay bricks tend to be more cost-effective, benefiting from abundant natural deposits and traditional production methods. Over time, fire clay bricks often present better economic value because of their durability and excellent thermal resistance, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses. For projects with budget constraints, fire clay bricks provide a more affordable solution without compromising structural integrity, while polymer clay bricks remain a premium option for niche applications requiring specific properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymer clay bricks are synthetic and typically derived from petroleum-based compounds, contributing to higher carbon emissions and environmental pollution during production compared to fire clay bricks, which are natural and primarily composed of kaolin and other clay minerals sourced from the earth. Fire clay bricks offer greater sustainability due to their natural composition, energy-efficient firing processes, and longer lifecycle with excellent resistance to weathering and wear. The recyclability and biodegradability of fire clay bricks further reduce their ecological footprint, making them a more eco-friendly choice in sustainable construction.
Installation and Workability
Polymer clay offers superior workability due to its lightweight and flexible nature, allowing easier molding and quicker installation in intricate brick designs. Fire clay, being denser and requiring high-temperature firing, demands more precise handling and extended curing times, making installation more labor-intensive. The choice between polymer clay and fire clay hinges on the project's complexity, with polymer clay favoring rapid, detailed work and fire clay suited for durable, heat-resistant brick structures.
Typical Applications in Construction
Polymer clay is primarily used for decorative and artistic brick applications due to its flexibility and ease of molding, making it ideal for custom facade elements and intricate architectural details. Fire clay bricks are essential in high-temperature construction environments such as kilns, furnaces, and fireplaces, offering exceptional thermal resistance and structural integrity. While polymer clay suits aesthetic and lightweight purposes, fire clay bricks dominate in industrial and heavy-duty construction where durability under heat stress is critical.
Which Clay is Best for Brick: Conclusion and Recommendations
Fire clay is generally best for bricks due to its high refractory properties, ability to withstand extreme temperatures, and durability in kiln firing. Polymer clay, while versatile for craft and sculptural projects, lacks the heat resistance and structural strength required for functional brick-making. For construction-grade bricks, selecting fire clay ensures optimal performance and longevity under thermal stress.
Infographic: Polymer clay vs Fire clay for Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com