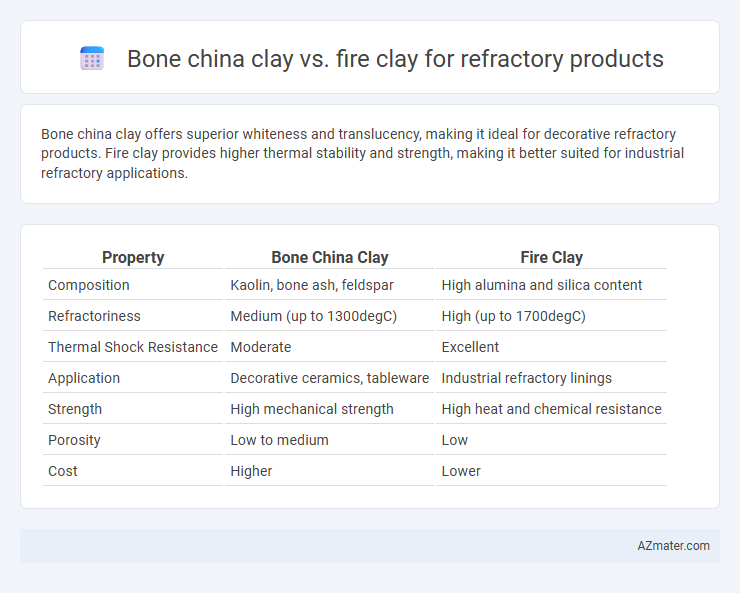
Bone china clay offers superior whiteness and translucency, making it ideal for decorative refractory products. Fire clay provides higher thermal stability and strength, making it better suited for industrial refractory applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bone China Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, bone ash, feldspar | High alumina and silica content |
| Refractoriness | Medium (up to 1300degC) | High (up to 1700degC) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Application | Decorative ceramics, tableware | Industrial refractory linings |
| Strength | High mechanical strength | High heat and chemical resistance |
| Porosity | Low to medium | Low |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Overview of Bone China Clay and Fire Clay
Bone china clay, primarily composed of kaolin and bone ash, is known for its exceptional whiteness, translucency, and fine particle size, making it ideal for producing delicate, high-quality ceramics with smooth finishes. Fire clay, characterized by its high alumina content and ability to withstand extreme temperatures, is widely used in refractory products for its superior thermal resistance and durability under intense heat conditions. Both clays serve distinct purposes: bone china clay enhances aesthetic properties in fine china production, while fire clay provides structural integrity and heat resistance in industrial refractory applications.
Chemical Composition Differences
Bone china clay primarily consists of kaolinite with significant amounts of calcium phosphate from bone ash, enhancing vitrification and translucency, while fire clay has higher alumina (Al2O3) content and lower fluxes, providing superior refractory properties and heat resistance. The calcium phosphate in bone china induces a lower melting point suitable for fine ceramics, whereas fire clay's composition includes silica (SiO2) and alumina in balanced proportions to withstand thermal shock and retain structural integrity at high temperatures. These chemical composition differences make bone china clay ideal for delicate ceramic ware, whereas fire clay is better suited for high-temperature refractory applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Bone china clay exhibits higher plasticity and finer particle texture compared to fire clay, enabling superior molding precision in refractory applications. Fire clay demonstrates greater thermal stability and higher refractoriness, making it more resistant to high temperatures above 1500degC. Density differences show bone china clay typically has lower porosity, resulting in better whiteware aesthetic but lower mechanical strength than the denser, more robust fire clay.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Tolerance
Bone china clay offers moderate thermal resistance with heat tolerance typically around 1200degC, making it suitable for decorative ceramic applications but less ideal for high-temperature refractory products. Fire clay, composed primarily of kaolin and alumina, provides superior thermal resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 1600degC, ensuring durability in industrial refractory uses such as furnace linings and kilns. The high alumina content in fire clay enhances its thermal shock resistance and heat tolerance compared to bone china clay, which lacks the robust refractory properties required for extreme heat environments.
Refractoriness: Performance Under High Temperatures
Bone china clay exhibits lower refractoriness compared to fire clay, making it less suitable for extreme high-temperature applications in refractory products. Fire clay demonstrates superior thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity and resistance to deformation at temperatures exceeding 1500degC. This enhanced refractoriness makes fire clay the preferred choice for industrial furnaces, kilns, and other high-heat environments requiring durable refractory materials.
Applications in Refractory Products
Bone china clay, known for its high purity and plasticity, is primarily used in the manufacture of fine ceramics and specialized refractory products requiring a smooth texture and high strength at moderate temperatures. Fire clay, characterized by its excellent heat resistance and durability, is widely utilized in refractory applications such as kiln linings, firebricks, and furnace parts that demand exposure to extreme temperatures and thermal shock. The superior refractory properties of fire clay make it indispensable in industrial furnaces, steel plants, and glass manufacturing, whereas bone china clay is favored in customized refractory products with aesthetic and functional requirements.
Durability and Longevity
Bone china clay, known for its fine particle size and high plasticity, offers superior translucency but lacks the high thermal resistance required for refractory applications. Fire clay contains a higher amount of alumina and silica, giving it exceptional durability and longevity under extreme heat and thermal cycling. The refractory product made with fire clay withstands prolonged high-temperature exposure and mechanical stress better than those made from bone china clay.
Cost and Availability
Bone china clay typically incurs higher costs due to its fine particle size and purity, making it less readily available compared to fire clay, which is abundant and more economical for refractory applications. Fire clay's widespread availability and natural resistance to high temperatures make it a cost-effective choice for industrial refractories. The economic advantage of fire clay is significant in large-scale production, whereas bone china clay is generally reserved for specialized, high-quality ceramic products.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bone china clay, composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and bone ash, offers a lower environmental footprint compared to fire clay due to its higher purity and reduced mining waste during processing. Fire clay, abundant and more robust, requires more intensive extraction and energy consumption, resulting in greater carbon emissions and landscape disruption. Sustainable practices favor bone china clay for refractory products when minimizing environmental degradation and resource depletion is a priority.
Choosing the Right Clay for Refractory Uses
Bone china clay offers high purity and a smooth texture, making it ideal for delicate refractory products requiring excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion. Fire clay excels in high-temperature durability and resistance to chemical corrosion, suitable for heavy-duty refractory linings exposed to intense heat and abrasive conditions. Selecting the right clay depends on specific application demands, balancing factors like temperature tolerance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength.
Infographic: Bone china clay vs Fire clay for Refractory product
 azmater.com
azmater.com