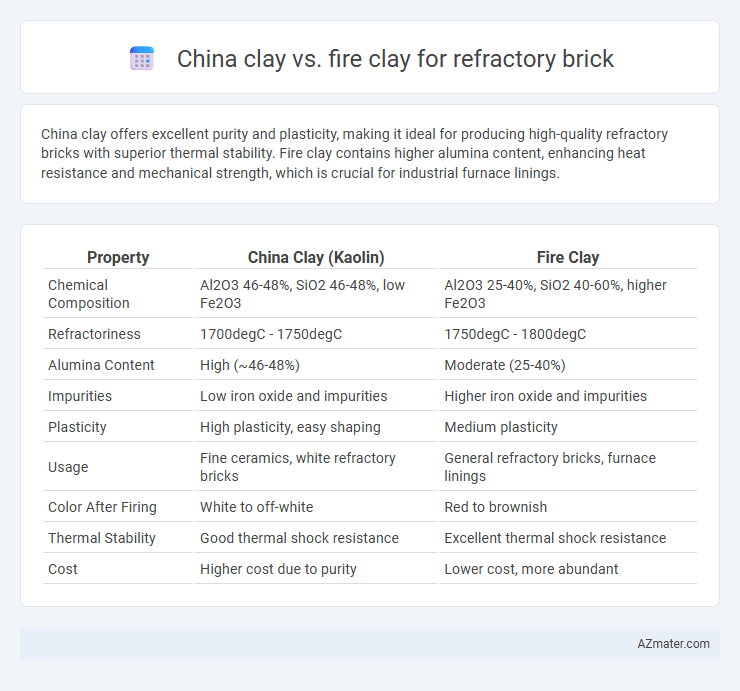
China clay offers excellent purity and plasticity, making it ideal for producing high-quality refractory bricks with superior thermal stability. Fire clay contains higher alumina content, enhancing heat resistance and mechanical strength, which is crucial for industrial furnace linings.
Table of Comparison
| Property | China Clay (Kaolin) | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Al2O3 46-48%, SiO2 46-48%, low Fe2O3 | Al2O3 25-40%, SiO2 40-60%, higher Fe2O3 |
| Refractoriness | 1700degC - 1750degC | 1750degC - 1800degC |
| Alumina Content | High (~46-48%) | Moderate (25-40%) |
| Impurities | Low iron oxide and impurities | Higher iron oxide and impurities |
| Plasticity | High plasticity, easy shaping | Medium plasticity |
| Usage | Fine ceramics, white refractory bricks | General refractory bricks, furnace linings |
| Color After Firing | White to off-white | Red to brownish |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal shock resistance | Excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to purity | Lower cost, more abundant |
Introduction to Refractory Bricks
Refractory bricks are critical components in high-temperature industrial applications, designed to withstand extreme heat and thermal cycling. China clay, characterized by high alumina content and fine particle size, offers excellent refractory properties with good plasticity and resistance to thermal shock. Fire clay contains higher silica and alumina proportions, providing enhanced durability and strength at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for lining furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces.
What is China Clay?
China clay, also known as kaolin, is a soft, white mineral composed primarily of kaolinite used extensively in refractory bricks for its high thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion. Fire clay is rich in alumina and silica, offering excellent heat resistance and strength, but China clay provides superior plasticity and workability during brick formation. The unique properties of China clay make it ideal for applications requiring precise molding and smooth surface finishes in refractory materials.
What is Fire Clay?
Fire clay, a highly refractory material composed mainly of kaolinite and other alumina silicates, withstands extreme temperatures up to 1580degC, making it ideal for manufacturing refractory bricks. Unlike China clay, which is purer and finer for ceramics, fire clay contains higher impurities such as quartz and mica, enhancing its thermal stability and mechanical strength under high heat. This composition allows fire clay bricks to endure thermal cycling and chemical corrosion in industrial furnaces, kilns, and boilers.
Chemical Composition Comparison
China clay (kaolin) primarily consists of silica (SiO2) around 46-51% and alumina (Al2O3) about 40-45%, with minimal iron oxide and other impurities, making it ideal for high-purity refractory bricks requiring good thermal stability. Fire clay contains higher alumina content, typically 25-40%, silica content ranging from 40-55%, and a greater amount of fluxing oxides like iron oxide (Fe2O3) and alkalis, which influence its refractoriness and melting point. The higher alumina and impurity levels in fire clay contribute to its enhanced mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance compared to the relatively purer and more stable china clay in refractory applications.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
China clay exhibits lower refractoriness and mechanical strength compared to fire clay, making it less suitable for high-temperature applications. Fire clay boasts superior thermal stability, higher compressive strength, and enhanced resistance to thermal shock, which ensures greater durability in refractory bricks. The dense microstructure of fire clay contributes to its robust performance under extreme conditions, outperforming the more porous China clay in physical resilience.
Temperature Resistance and Thermal Stability
China clay, composed primarily of kaolinite, offers moderate temperature resistance up to approximately 1,400degC, making it suitable for low to medium heat refractory bricks. Fire clay contains higher alumina content, enabling superior thermal stability and temperature resistance, typically enduring temperatures up to 1,600degC or more. The enhanced refractory properties of fire clay result from its ability to maintain structural integrity under rapid temperature fluctuations and prolonged high heat, outperforming China clay in high-temperature industrial applications.
Manufacturing Process Differences
China clay, also known as kaolin, undergoes a refining process involving washing, centrifuging, and drying to achieve high purity and fine particle size ideal for refractory bricks requiring smooth texture and insulating properties. Fire clay, sourced from sedimentary deposits containing higher alumina content, is processed mainly by crushing, drying, and partial calcination to enhance its heat resistance and durability in high-temperature refractory applications. The manufacturing difference lies in china clay's extensive purification for purity, while fire clay emphasizes thermal stability through mineralogical treatment.
Applications in the Refractory Industry
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, offers excellent plasticity and high alumina content, making it ideal for forming smooth, dense refractory bricks used in glass furnaces and ceramics kilns. Fire clay contains a higher amount of silica and alumina, providing superior thermal stability and resistance to spalling, which suits it for linings in high-temperature environments such as steelmaking furnaces and petrochemical reactors. Both types of clay are essential in the refractory industry, with china clay favored for fine finishing and fire clay chosen for heavy-duty, high-temperature applications.
Cost Analysis: China Clay vs Fire Clay
China clay generally offers a lower cost option compared to fire clay due to its abundant availability and simpler processing requirements, which reduces manufacturing expenses for refractory bricks. Fire clay bricks, while more expensive upfront, provide superior thermal resistance and durability, translating to longer service life and lower replacement costs in high-temperature industrial applications. When conducting a cost analysis, the initial investment for fire clay bricks is justified by their enhanced performance and reduced maintenance frequency over China clay bricks.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Refractory Brick
China clay offers high purity and flexibility, making it ideal for lightweight refractory bricks requiring excellent thermal insulation. Fire clay, with its high alumina content and durability, is preferred for heavy-duty refractory bricks that must withstand intense heat and mechanical stress. Selecting the right clay depends on the specific thermal performance, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance demands of your refractory application.
Infographic: China clay vs Fire clay for Refractory brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com