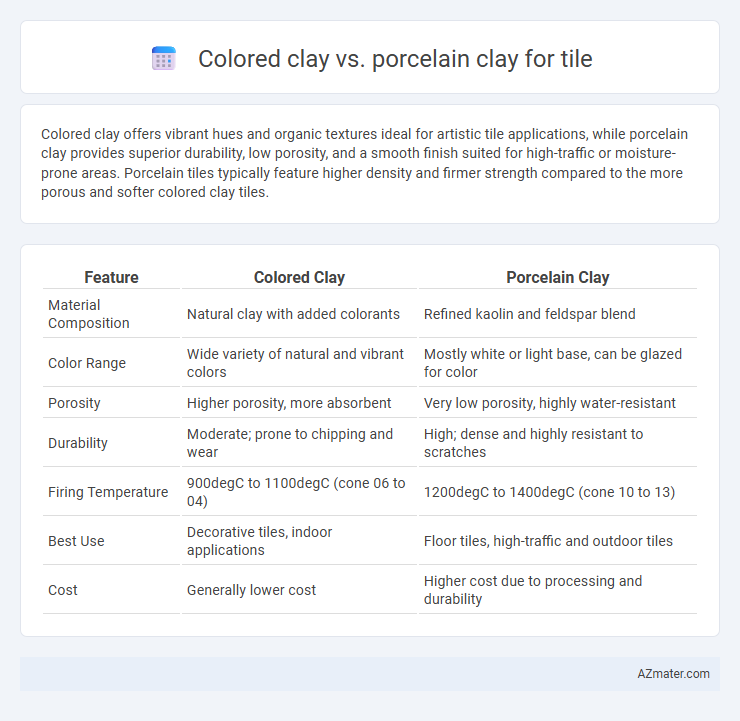
Colored clay offers vibrant hues and organic textures ideal for artistic tile applications, while porcelain clay provides superior durability, low porosity, and a smooth finish suited for high-traffic or moisture-prone areas. Porcelain tiles typically feature higher density and firmer strength compared to the more porous and softer colored clay tiles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Colored Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural clay with added colorants | Refined kaolin and feldspar blend |
| Color Range | Wide variety of natural and vibrant colors | Mostly white or light base, can be glazed for color |
| Porosity | Higher porosity, more absorbent | Very low porosity, highly water-resistant |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to chipping and wear | High; dense and highly resistant to scratches |
| Firing Temperature | 900degC to 1100degC (cone 06 to 04) | 1200degC to 1400degC (cone 10 to 13) |
| Best Use | Decorative tiles, indoor applications | Floor tiles, high-traffic and outdoor tiles |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to processing and durability |
Introduction to Tile Clay Types
Colored clay for tile offers natural pigmentation directly within the clay body, providing vibrant hues without the need for surface glazes, which enhances durability and colorfastness. Porcelain clay, characterized by its fine particle size and high kaolin content, results in tiles with exceptional density, strength, and low porosity, ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications. Selecting between colored clay and porcelain depends on desired aesthetic effects, firing temperature, and performance requirements in tile production.
What Is Colored Clay?
Colored clay is a natural clay mixed with various mineral oxides that impart distinct hues without the need for surface glazes, making it ideal for creating vibrant, durable tile bases. It offers enhanced coloration throughout the tile body, resulting in less wear visibility and increased longevity compared to traditional white porcelain clay. Unlike porcelain clay, which is prized for its strength and translucency but typically requires glazing for color, colored clay provides inherent aesthetic diversity combined with robust physical properties for tile manufacturing.
What Is Porcelain Clay?
Porcelain clay is a highly refined, kaolin-based material known for its dense, non-porous structure and exceptional durability, making it ideal for tile production that requires resistance to water and wear. Colored clay incorporates natural or synthetic pigments into various clay bodies, including porcelain, allowing for vibrant, decorative tiles with varying textures and finishes. Porcelain clay tiles exhibit superior hardness and a sleek, smooth surface compared to colored earthenware or stoneware clays, emphasizing longevity and minimal maintenance in high-traffic areas.
Composition and Material Differences
Colored clay for tiles typically contains natural pigments and iron oxides mixed with a high percentage of kaolin and ball clay, resulting in a more textured, earthy finish. Porcelain clay, characterized by a higher proportion of kaolin and quartz with minimal impurities, offers a denser, more vitrified body that is less porous and highly durable. The distinct mineral compositions influence firing temperature and strength, with porcelain requiring higher temperatures to achieve its characteristic hardness and translucency compared to colored clay.
Appearance and Design Possibilities
Colored clay offers rich, natural hues that integrate pigment directly into the material, creating earthy, tonal variations ideal for rustic or artisan tile designs. Porcelain clay provides a smooth, fine-grained surface allowing for precise detailing and a broad palette of glaze applications, perfect for modern or high-end decorative tiles. The choice between colored clay and porcelain clay directly impacts aesthetic versatility, with colored clay emphasizing organic textures and porcelain supporting sleek, intricate patterns.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Colored clay tiles offer moderate durability with some variations depending on the specific clay composition and firing temperature, making them suitable for decorative purposes but less ideal for high-traffic areas. Porcelain clay tiles, known for their high density and low porosity, provide superior strength and resistance to wear, chipping, and moisture, ensuring long-lasting performance in commercial and residential applications. The superior vitrification process in porcelain results in enhanced structural integrity, making these tiles a preferred choice where durability and strength are critical.
Porosity and Water Absorption
Porcelain clay exhibits significantly lower porosity and water absorption rates compared to colored clay, making it highly suitable for tile applications requiring durability and moisture resistance. The dense vitrification process of porcelain reduces pore spaces, achieving water absorption typically below 0.5%, whereas colored clay tiles can absorb upwards of 5%. This minimal porosity in porcelain tiles enhances their strength, stain resistance, and longevity, particularly in wet or outdoor environments.
Suitability for Different Applications
Colored clay offers robust natural pigments that enhance decorative tile designs and is ideal for rustic or artisanal applications where texture variations add character. Porcelain clay provides exceptional strength, low porosity, and fine particle size, making it best suited for high-traffic commercial flooring or outdoor environments requiring durability and low water absorption. Selecting between these clays depends on balancing aesthetic preferences with functional demands such as wear resistance and moisture exposure.
Cost and Accessibility
Colored clay tiles are generally more affordable due to the natural pigments integrated directly into the clay body, reducing additional processing costs, and they are widely accessible in most regions. Porcelain clay tiles tend to be more expensive because of their denser composition, higher firing temperatures, and refined manufacturing processes, which contribute to increased durability but limit accessibility to specialized suppliers. The cost difference also reflects the performance variations, with porcelain offering superior resistance to wear and moisture, often justifying the higher price in premium applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clay for Tiles
Colored clay offers vibrant hues and natural texture, making it ideal for decorative tiles with a rustic or artistic appeal. Porcelain clay provides superior strength, durability, and a smooth finish, perfect for high-traffic areas requiring long-lasting, water-resistant tiles. Selecting the right clay depends on the desired aesthetic, functional requirements, and installation environment, with porcelain excelling in performance and colored clay enhancing visual impact.
Infographic: Colored clay vs Porcelain clay for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com