Wild clay offers a naturally occurring blend of minerals with unique impurities that create rustic textures, while earthenware clay is a refined, porous material ideal for low-fire pottery and detailed shaping. Wild clay often requires more processing due to organic content, whereas earthenware clay provides consistent plasticity and vibrant glaze compatibility.
Table of Comparison
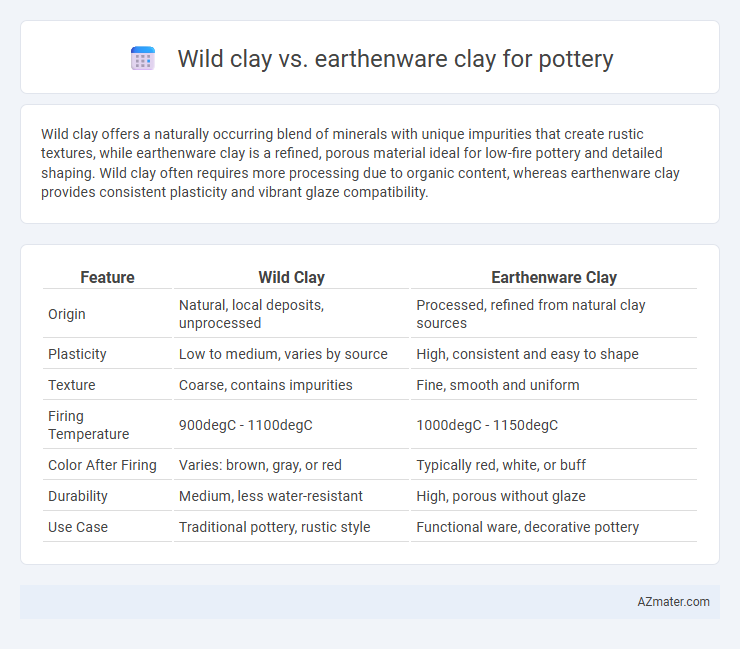
| Feature | Wild Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural, local deposits, unprocessed | Processed, refined from natural clay sources |
| Plasticity | Low to medium, varies by source | High, consistent and easy to shape |
| Texture | Coarse, contains impurities | Fine, smooth and uniform |
| Firing Temperature | 900degC - 1100degC | 1000degC - 1150degC |
| Color After Firing | Varies: brown, gray, or red | Typically red, white, or buff |
| Durability | Medium, less water-resistant | High, porous without glaze |
| Use Case | Traditional pottery, rustic style | Functional ware, decorative pottery |
Introduction to Pottery Clays
Wild clay, sourced directly from natural deposits, contains organic materials and impurities that affect its plasticity and firing temperature, making it ideal for rustic, textured pottery. Earthenware clay, refined and often commercially processed, offers consistency with lower firing temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, suitable for functional and decorative ceramics. Understanding the distinct properties of wild clay versus earthenware clay helps potters select the appropriate material based on desired texture, durability, and artistic finish.
What is Wild Clay?
Wild clay refers to naturally occurring clay collected directly from the environment, often containing a mix of minerals, organic matter, and impurities. Unlike processed earthenware clay, wild clay's texture and composition can vary significantly, affecting its plasticity, firing temperature, and durability. Potters value wild clay for its unique characteristics and traditional connection, though it may require additional purification for consistent pottery results.
What is Earthenware Clay?
Earthenware clay is a porous, low-fire clay typically fired between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, making it ideal for decorative pottery and functional ware like dishes and planters. It contains higher levels of iron and other minerals, which give it a distinct reddish or brownish color and a relatively coarse texture compared to wild clay. Unlike wild clay, earthenware clay is more refined and commercially processed, offering greater consistency and ease in shaping and glazing for pottery projects.
Key Differences: Wild Clay vs Earthenware Clay
Wild clay, sourced from natural, unrefined deposits, contains varied impurities and minerals that affect its plasticity and firing behavior, making it less predictable for pottery. Earthenware clay is a refined, softer material often enriched with added fluxes to lower firing temperatures and achieve consistent results in handmade and wheel-thrown pottery. The key differences lie in composition, workability, and firing requirements, influencing the texture, durability, and finish of the final ceramic piece.
Sourcing and Processing Wild Clay
Wild clay for pottery is typically sourced from natural deposits found in riverbanks, forests, or excavated soils, requiring minimal processing beyond cleaning and sieving to remove impurities such as stones and organic matter. In contrast, earthenware clay is often commercially refined and processed to ensure consistency in particle size, plasticity, and firing properties, involving steps like levigation and blending. Wild clay's natural composition can vary significantly, which may impact its workability and firing results, whereas earthenware clay offers more predictable performance due to standardized processing.
Commercial Preparation of Earthenware Clay
Commercial preparation of earthenware clay involves refining raw materials by removing impurities and blending them with specific additives to enhance plasticity and firing properties, ensuring consistency for mass production. Wild clay, in contrast, requires extensive processing to eliminate organic content and achieve similar homogeneity, often making it less commercially viable. Industrial earthenware clay typically undergoes controlled particle size distribution and mineral composition adjustments to optimize drying, shaping, and firing performance in pottery manufacturing.
Workability: Texture and Plasticity Comparison
Wild clay typically features a coarse texture with variable particle sizes, resulting in lower plasticity and increased difficulty in shaping, making it less ideal for detailed pottery work. Earthenware clay offers a smoother texture and higher plasticity, allowing for easier molding, finer detail, and better workability during wheel throwing or hand-building. The consistency and moisture retention in earthenware clay promote greater flexibility, which helps potters achieve precise forms and reduces cracking during drying and firing.
Firing Temperatures and Results
Wild clay typically requires higher firing temperatures, ranging between 1200degC to 1300degC, resulting in stronger, more durable pottery with a vitrified finish. Earthenware clay fires at lower temperatures, around 1000degC to 1150degC, producing a porous, less dense ceramic that is often glazed to achieve water resistance. Firing wild clay at earthenware temperatures usually results in underfired, fragile pieces, while firing earthenware clay at high stoneware temperatures can cause warping or melting.
Creative Potential and Aesthetic Outcomes
Wild clay offers a unique, organic texture and natural impurities that enhance the creative potential for artists seeking raw, earthy aesthetics in pottery. Earthenware clay provides smoother consistency and vibrant color options, allowing for refined detailing and bright glaze finishes that emphasize traditional craftsmanship. Both clays deliver distinct aesthetic outcomes, with wild clay favoring rustic, naturalistic styles and earthenware clay excelling in polished, colorful designs.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Wild clay, often sourced locally with minimal processing, generally has a lower environmental footprint compared to earthenware clay, which may involve extensive mining and transportation. Earthenware clay requires higher energy consumption during firing due to its lower firing temperature, contributing to greater carbon emissions. Sustainable pottery practices favor wild clay for its reduced resource extraction and energy efficiency, promoting eco-friendly ceramic production.
Infographic: Wild clay vs Earthenware clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com