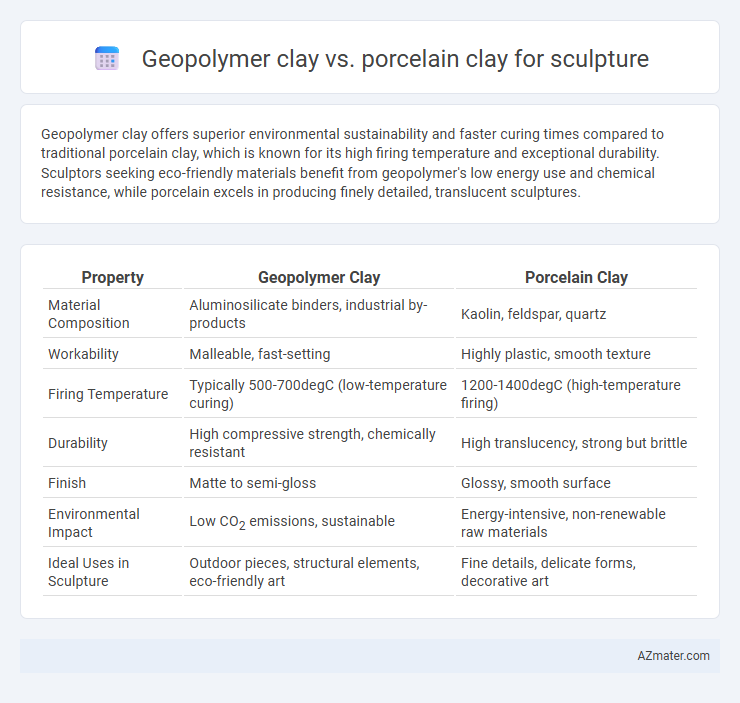
Geopolymer clay offers superior environmental sustainability and faster curing times compared to traditional porcelain clay, which is known for its high firing temperature and exceptional durability. Sculptors seeking eco-friendly materials benefit from geopolymer's low energy use and chemical resistance, while porcelain excels in producing finely detailed, translucent sculptures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Geopolymer Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Aluminosilicate binders, industrial by-products | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz |
| Workability | Malleable, fast-setting | Highly plastic, smooth texture |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 500-700degC (low-temperature curing) | 1200-1400degC (high-temperature firing) |
| Durability | High compressive strength, chemically resistant | High translucency, strong but brittle |
| Finish | Matte to semi-gloss | Glossy, smooth surface |
| Environmental Impact | Low CO2 emissions, sustainable | Energy-intensive, non-renewable raw materials |
| Ideal Uses in Sculpture | Outdoor pieces, structural elements, eco-friendly art | Fine details, delicate forms, decorative art |
Introduction to Geopolymer Clay and Porcelain Clay
Geopolymer clay is an eco-friendly, synthetic material composed of aluminosilicate minerals activated by alkaline solutions, offering rapid curing and high durability for sculptural applications. Porcelain clay, derived from kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, is prized for its fine texture, translucency, and ability to achieve detailed, smooth finishes after high-temperature firing. Both clays serve distinct artistic needs, with geopolymer clay excelling in structural strength and indoor/outdoor use, while porcelain clay remains favored for its classic aesthetic qualities and delicate precision in sculpture.
Composition Differences Between Geopolymer and Porcelain Clays
Geopolymer clay consists primarily of aluminosilicate materials activated by alkaline solutions, offering a synthetic, inorganic polymer matrix distinct from porcelain clay's natural kaolin, feldspar, and quartz blend. The aluminosilicate framework in geopolymer clay results in enhanced fire resistance and chemical durability compared to porcelain's vitrified, fine-grained structure. Porcelain clay's mineral composition enables translucency and high plasticity, whereas geopolymer clay's distinct chemical formulation provides greater structural stability and reduced shrinkage during firing.
Sculptural Workability and Handling Properties
Geopolymer clay offers superior sculptural workability due to its malleable texture and quick setting time, allowing artists to create detailed forms with ease and maintain structural integrity during the sculpting process. Porcelain clay, prized for its smoothness and fine grain, requires more precise handling as its plasticity is lower, making it less forgiving but ideal for intricate, delicate sculptures with high-definition surface finishes. Both materials demand different moisture control techniques; geopolymer clay needs consistent hydration to prevent cracking, while porcelain clay demands careful drying to avoid warping and ensure precise detail retention.
Drying and Firing Requirements
Geopolymer clay requires low-temperature curing, typically at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures around 70-90degC, eliminating the risk of cracking during drying and reducing energy consumption compared to traditional firing processes. Porcelain clay demands slow, even drying to prevent warping or cracking, followed by high-temperature firing in a kiln at temperatures between 1200-1400degC to achieve vitrification and durability. The drying and firing protocols for porcelain necessitate careful moisture control and prolonged kiln cycles, whereas geopolymer clay's curing process offers greater flexibility and faster turnaround times for sculptural works.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Geopolymer clay exhibits superior strength and durability compared to porcelain clay, owing to its inorganic polymer matrix that resists cracking and withstands extreme weather conditions. Porcelain clay, while offering a smooth finish and fine detail, tends to be more brittle and prone to chipping under mechanical stress or thermal shock. Sculptors seeking long-lasting outdoor sculptures often prefer geopolymer clay for its enhanced resilience and structural integrity.
Surface Texture and Detailing Capabilities
Geopolymer clay offers a slightly rougher surface texture ideal for rustic and organic finishes, while porcelain clay provides a smooth, fine-grained surface that excels in capturing intricate details with high precision. Porcelain's plasticity allows for delicate sculpting and sharp edges, making it preferred for detailed figurative work, whereas geopolymer clay's firmer composition supports robust textures and structural stability in larger sculptures. Both materials respond well to sgraffito and carving techniques, but porcelain typically yields cleaner, more refined details after firing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer clay significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing industrial byproducts such as fly ash and slag, decreasing reliance on virgin raw materials and lowering carbon emissions during production. Porcelain clay, composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and silica, requires extensive mining that contributes to habitat disruption and higher energy consumption in processing. The sustainability of geopolymer clay is enhanced by its lower firing temperatures and reduced waste generation, making it a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable sculpture practices.
Cost and Accessibility for Sculptors
Geopolymer clay offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional porcelain clay, with lower raw material expenses and no need for high-temperature firing, reducing overall sculpting costs. Porcelain clay, while prized for its fine texture and translucent qualities, tends to be more expensive due to sourcing and kiln requirements, making it less accessible for budget-conscious sculptors. Accessibility to geopolymer clay is expanding through commercial suppliers and DIY formulations, whereas porcelain clay availability may be limited to specialized art stores and ceramic studios.
Artistic Applications and Aesthetics
Geopolymer clay offers superior durability and faster curing times ideal for outdoor sculptures and modern artistic installations. Porcelain clay provides a refined, translucent finish prized for delicate, high-detail works with smooth textures and vibrant glaze potentials. Artists choose geopolymer for structural strength and weather resistance, while porcelain excels in creating elegant, timeless aesthetics with intricate detailing.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Sculpture Project
Geopolymer clay offers enhanced durability and environmental benefits with its non-toxic, lightweight, and fire-resistant properties, making it ideal for outdoor sculptures requiring weather resistance. Porcelain clay provides a smooth, fine texture and high plasticity that suits intricate, delicate indoor sculptures demanding precise detail and a refined finish. Selecting the right clay depends on the project's exposure conditions, desired texture, and structural requirements to achieve optimal longevity and aesthetic quality.
Infographic: Geopolymer clay vs Porcelain clay for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com