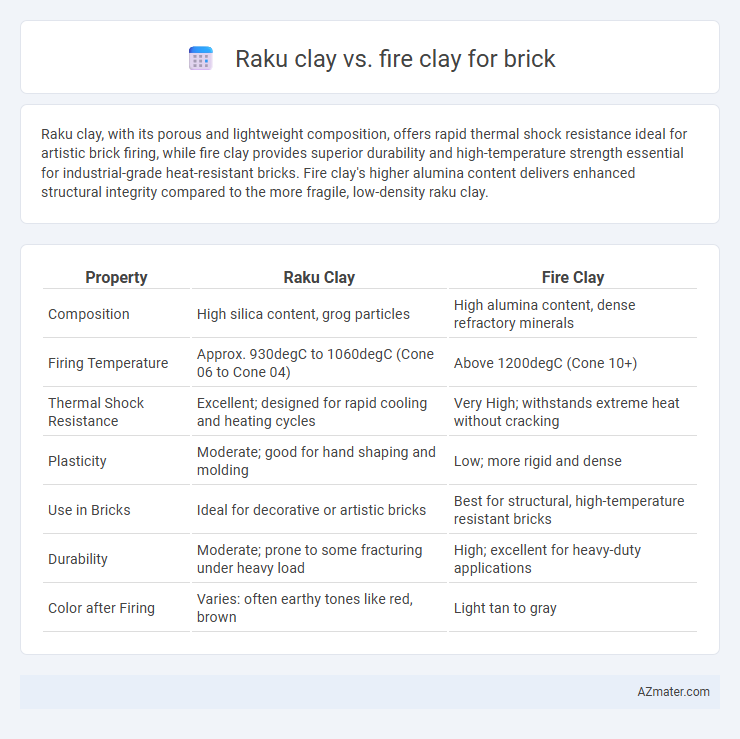
Raku clay, with its porous and lightweight composition, offers rapid thermal shock resistance ideal for artistic brick firing, while fire clay provides superior durability and high-temperature strength essential for industrial-grade heat-resistant bricks. Fire clay's higher alumina content delivers enhanced structural integrity compared to the more fragile, low-density raku clay.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Raku Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High silica content, grog particles | High alumina content, dense refractory minerals |
| Firing Temperature | Approx. 930degC to 1060degC (Cone 06 to Cone 04) | Above 1200degC (Cone 10+) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent; designed for rapid cooling and heating cycles | Very High; withstands extreme heat without cracking |
| Plasticity | Moderate; good for hand shaping and molding | Low; more rigid and dense |
| Use in Bricks | Ideal for decorative or artistic bricks | Best for structural, high-temperature resistant bricks |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to some fracturing under heavy load | High; excellent for heavy-duty applications |
| Color after Firing | Varies: often earthy tones like red, brown | Light tan to gray |
Introduction to Raku Clay and Fire Clay
Raku clay is a porous, low-firing ceramic material renowned for its unique thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for rapid heating and cooling processes in art and pottery. Fire clay, in contrast, is a highly refractory, dense material with a high alumina content, designed to withstand extreme temperatures up to 1750degC, typically used in industrial brick manufacturing for furnaces and kilns. The distinct physical properties of Raku and Fire clay influence their specific applications, with Raku clay favored in artistic ceramics and Fire clay preferred for heavy-duty, heat-resistant brick production.
Key Differences: Raku Clay vs Fire Clay
Raku clay is specifically formulated for rapid heating and cooling cycles in raku pottery, offering high thermal shock resistance but lower durability compared to fire clay. Fire clay, composed of refractory minerals, withstands extremely high temperatures and provides superior strength, making it ideal for industrial brick applications and kiln linings. The key difference lies in their thermal properties and structural integrity, with raku clay favored for artistic use and fire clay for heavy-duty, heat-resistant bricks.
Composition and Material Properties
Raku clay contains a higher concentration of kaolin and fluxes, enabling rapid thermal shock resistance and producing lightweight, porous bricks ideal for decorative applications. Fire clay, composed mainly of alumina and silica with minimal impurities, exhibits exceptional refractory properties, high melting points above 1500degC, and superior durability for structural brickworks in high-temperature environments. The distinct mineralogical composition of raku clay favors fast firing and aesthetic textures, whereas fire clay's material properties ensure robust performance under prolonged thermal stress.
Firing Temperatures and Techniques
Raku clay typically fires at low temperatures ranging between 1,650degF to 1,900degF (900degC to 1,040degC), designed for rapid cooling techniques that produce unique surface textures and crackles. Fire clay, in contrast, withstands much higher firing temperatures, up to 2,400degF (1,320degC), making it ideal for applications requiring high thermal resistance and durability in bricks. The firing technique for Raku involves immediate removal from the kiln followed by reduction in combustible materials, while fire clay bricks endure prolonged high-temperature firings for structural strength.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Raku clay exhibits lower durability and strength compared to fire clay, as it is primarily formulated for artistic pottery and rapid heating cycles rather than structural applications. Fire clay, characterized by its high alumina and silica content, offers superior refractory properties, making it highly resistant to heat, mechanical stress, and erosion in brick manufacturing. Consequently, fire clay bricks possess enhanced durability and strength, suitable for high-load and high-temperature environments, whereas raku clay bricks are more prone to cracking and wear under similar conditions.
Workability and Sculpting Qualities
Raku clay offers excellent workability and plasticity, making it ideal for intricate sculpting and detailed shapes due to its fine particle size and smooth texture. Fire clay, while denser and more refractory, is less pliable and better suited for structural bricks requiring high heat resistance rather than detailed sculptural work. Choosing between Raku and Fire clay depends on the balance between artistic flexibility and durability needed for the brick application.
Suitability for Brick Making
Raku clay, known for its porous and lightweight properties, is less suitable for traditional brick making due to its lower durability and susceptibility to cracking under high heat conditions. Fire clay, rich in alumina and silica, offers superior heat resistance and strength, making it ideal for manufacturing refractory bricks used in high-temperature industrial applications. The high plasticity and thermal stability of fire clay ensure bricks maintain structural integrity during firing and prolonged use in furnaces or kilns.
Cost and Availability
Raku clay is typically more expensive and less readily available than fire clay due to its specialized formulation and niche demand among ceramic artists. Fire clay, known for its high refractory properties and wide industrial use, is more abundant and cost-effective for brick making. The broader distribution network and larger production scale of fire clay contribute to its lower price and easier accessibility compared to Raku clay.
Environmental Impact
Raku clay typically has a lower environmental impact than fire clay due to its lower firing temperature, which reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions. Fire clay requires higher kiln temperatures, resulting in increased fuel use and greater ecological footprint during production. Choosing raku clay can support more sustainable brick manufacturing by minimizing resource use and greenhouse gas emissions.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Brick Project
Raku clay offers rapid firing and unique surface textures, ideal for artistic or decorative brick projects requiring quick turnaround and distinct aesthetics. Fire clay provides higher refractory properties and durability, making it the preferred choice for structural bricks subjected to intense heat and mechanical stress. Selecting between Raku and Fire clay depends on prioritizing either creative finish and speed or long-lasting, heat-resistant performance for your brick construction.
Infographic: Raku clay vs Fire clay for Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com