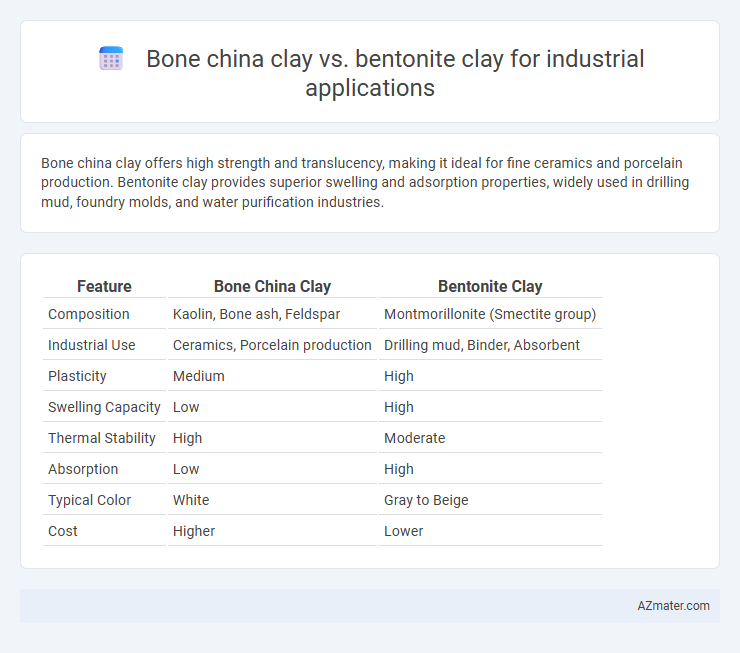
Bone china clay offers high strength and translucency, making it ideal for fine ceramics and porcelain production. Bentonite clay provides superior swelling and adsorption properties, widely used in drilling mud, foundry molds, and water purification industries.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bone China Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, Bone ash, Feldspar | Montmorillonite (Smectite group) |
| Industrial Use | Ceramics, Porcelain production | Drilling mud, Binder, Absorbent |
| Plasticity | Medium | High |
| Swelling Capacity | Low | High |
| Thermal Stability | High | Moderate |
| Absorption | Low | High |
| Typical Color | White | Gray to Beige |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Bone China Clay and Bentonite Clay
Bone china clay, prized for its high whiteness, translucency, and strength, is primarily utilized in ceramic and porcelain manufacturing, offering superior plasticity and fine particle distribution. Bentonite clay, characterized by its swelling properties and high cation-exchange capacity, excels in applications such as drilling mud, binder in foundry sands, and as an absorbent in industrial wastewater treatment. Industrial efficiency hinges on selecting bone china clay for aesthetic and structural ceramic needs, while bentonite clay is favored for its rheological control and adsorption capabilities.
Chemical Composition and Mineral Structure
Bone china clay primarily consists of kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), calcium phosphate from bone ash, and quartz, giving it a unique mineral structure that combines alumina and phosphate-based compounds ideal for high-strength ceramics and fine china production. Bentonite clay is mainly composed of montmorillonite, a type of smectite clay mineral with a layered structure rich in sodium and calcium ions, providing excellent swelling, adsorption, and sealing properties used extensively in drilling muds, foundry molds, and waste containment. The chemical composition differences--phosphate-rich bone china clay versus ion-exchange-heavy montmorillonite in bentonite--determine their distinct industrial uses based on mechanical strength versus rheological and absorptive behavior.
Physical Properties Comparison
Bone china clay exhibits high plasticity, fine particle size, and low impurity content, making it ideal for producing translucent, durable ceramics. Bentonite clay features exceptional swelling capacity, high cation exchange capacity, and strong thixotropic behavior, advantageous for drilling muds and sealing applications. The superior water absorption and binding properties of bentonite contrast with bone china clay's rigidity and thermal stability, influencing their distinct industrial uses.
Sourcing and Availability
Bone china clay, primarily sourced from kaolin-rich regions like China and the UK, offers consistent high purity essential for fine ceramic and electrical insulator manufacturing. Bentonite clay, abundant in the United States, India, and Greece, provides widespread availability due to large-scale mining operations supporting drilling, foundry, and agriculture industries. The differing geological availability significantly impacts supply chain stability and cost efficiency in industrial applications.
Processing Techniques for Industrial Use
Bone china clay, known for its high purity and fine particle size, requires controlled calcination and precise blending with feldspar and silica to achieve optimal whiteness and strength in industrial ceramics. Bentonite clay, prized for its swelling properties and plasticity, undergoes refining processes including drying, grinding, and activation with sodium hydroxide to enhance its binding and sealing capabilities in drilling fluids and foundry molds. Both clays demand tailored processing techniques to maximize their distinct physical and chemical properties for industrial applications.
Performance in Ceramic and Porcelain Industries
Bone china clay exhibits superior plasticity and whiteness, enhancing the strength and translucency of ceramic and porcelain products. Bentonite clay offers excellent binding and swelling properties, improving the workability and durability of ceramic bodies during shaping and firing. Performance differences make bone china clay preferable for fine, high-quality porcelain, while bentonite is favored for structural reinforcement in industrial ceramic formulations.
Role in Filtration and Absorption Applications
Bone china clay offers high absorbency and fine particle size, making it effective for precise filtration in industrial applications such as wastewater treatment and pharmaceuticals. Bentonite clay excels in adsorption due to its expansive structure and high cation exchange capacity, which enhances removal of heavy metals, oils, and other contaminants in environmental cleanup and chemical processing. Both clays serve crucial filtration and absorption roles, with bone china clay providing superior filtration clarity and bentonite delivering robust contaminant adsorption.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Viability
Bone china clay offers high translucency and strength, making it ideal for premium ceramics but often comes at a higher cost due to raw material and processing expenses. Bentonite clay provides excellent binding and swelling properties, widely used in drilling and foundry industries, with lower overall costs enhancing its economic viability for large-scale industrial applications. Evaluating cost-effectiveness, Bentonite clay generally presents a more affordable and versatile option for industries prioritizing budget without compromising functional performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bone china clay, primarily consisting of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, is less environmentally disruptive due to its specific mineral composition and lower energy-intensive firing processes in industrial applications. Bentonite clay, rich in montmorillonite, has a higher water absorption capacity, making it valuable for sealing and waste containment but often requires more intensive mining that can lead to habitat disruption and soil erosion. Sustainability considerations favor bone china clay for industries prioritizing reduced carbon footprints, while bentonite's role in environmental remediation supports its use in sustainable waste management systems.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Industrial Needs
Bone china clay offers superior whiteness, plasticity, and strength, making it ideal for fine ceramics and high-quality porcelain production in industrial applications. Bentonite clay provides excellent swelling properties, high absorbency, and strong binding capabilities, suitable for drilling mud, foundry sands, and sealing applications. Selecting the right clay depends on desired characteristics such as durability, absorbency, and plasticity required for specific industrial processes.
Infographic: Bone china clay vs Bentonite clay for Industrial application
 azmater.com
azmater.com