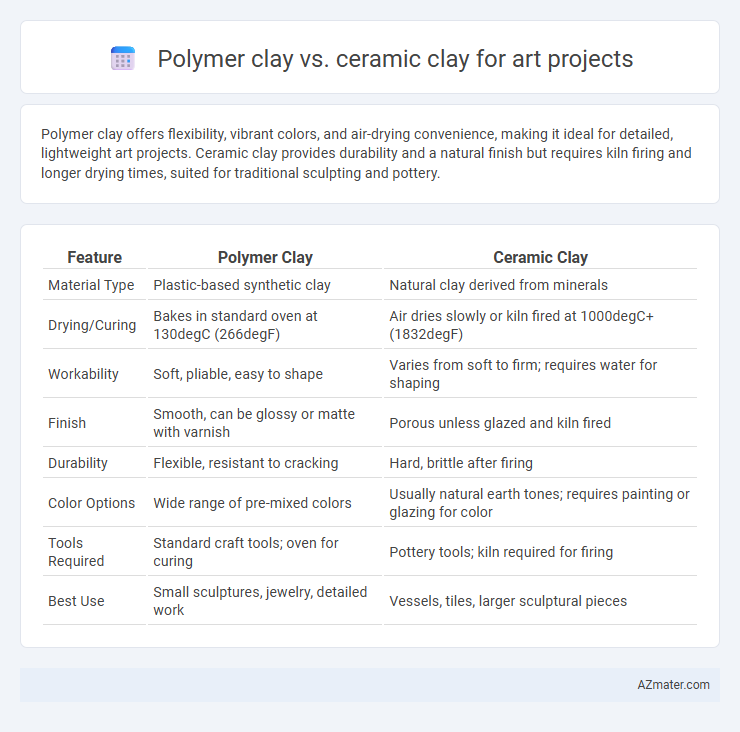
Polymer clay offers flexibility, vibrant colors, and air-drying convenience, making it ideal for detailed, lightweight art projects. Ceramic clay provides durability and a natural finish but requires kiln firing and longer drying times, suited for traditional sculpting and pottery.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polymer Clay | Ceramic Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Plastic-based synthetic clay | Natural clay derived from minerals |
| Drying/Curing | Bakes in standard oven at 130degC (266degF) | Air dries slowly or kiln fired at 1000degC+ (1832degF) |
| Workability | Soft, pliable, easy to shape | Varies from soft to firm; requires water for shaping |
| Finish | Smooth, can be glossy or matte with varnish | Porous unless glazed and kiln fired |
| Durability | Flexible, resistant to cracking | Hard, brittle after firing |
| Color Options | Wide range of pre-mixed colors | Usually natural earth tones; requires painting or glazing for color |
| Tools Required | Standard craft tools; oven for curing | Pottery tools; kiln required for firing |
| Best Use | Small sculptures, jewelry, detailed work | Vessels, tiles, larger sculptural pieces |
Introduction: Understanding Polymer Clay and Ceramic Clay
Polymer clay is a versatile, synthetic modeling material composed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) that cures in a home oven at low temperatures, making it ideal for detailed and colorful art projects. Ceramic clay, derived from natural minerals like kaolin and ball clay, requires high-temperature kiln firing to harden, resulting in durable, functional, and often glazed artworks. Artists choose polymer clay for ease of use and vibrant colors, while ceramic clay is favored for traditional pottery techniques and heat-resistant sculptures.
Composition and Material Differences
Polymer clay is a synthetic modeling material made primarily of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) combined with plasticizers, giving it flexibility and the ability to cure at low temperatures, typically between 265degF to 275degF (130degC to 135degC). Ceramic clay consists of natural minerals including kaolin, ball clay, feldspar, and quartz, requiring high-temperature kiln firing at around 1830degF (1000degC) or more to harden and develop durability. The plasticity and curing process distinguish polymer clay's pliable, non-porous finish from ceramic clay's porous, brittle structure after vitrification.
Working Properties: Flexibility and Malleability
Polymer clay offers superior flexibility and malleability, allowing artists to easily shape and manipulate intricate designs without cracking or drying out quickly. Ceramic clay, while more rigid and less forgiving, requires careful moisture control to maintain its workability but provides a stronger final structure after firing. Choosing between polymer and ceramic clay depends on the project's need for ease of sculpting versus durability and finish quality.
Baking and Curing Processes Compared
Polymer clay requires baking at a low temperature, typically around 265degF to 275degF for 15-30 minutes per quarter inch of thickness, allowing it to harden without cracking. Ceramic clay undergoes a more complex curing process involving a bisque firing at high temperatures (around 1,800degF) followed by glaze firing, which vitrifies the clay and creates a durable, glass-like surface. The lower temperature baking of polymer clay offers convenience and quicker results, while ceramic clay's kiln firing provides superior strength and heat resistance essential for functional ware.
Durability and Longevity of Finished Pieces
Polymer clay offers moderate durability, resistant to cracking and chipping, making it suitable for lightweight art projects with long-lasting color retention. Ceramic clay, when properly fired in a kiln, provides superior strength and longevity, with finished pieces often lasting centuries due to vitrification and glaze application. For art projects requiring durable, weather-resistant sculptures, ceramic clay ensures enhanced resilience over polymer alternatives.
Color Range and Finish Options
Polymer clay offers an extensive color range with vibrant, easily blendable hues, ideal for detailed and multicolored art projects, while ceramic clay typically comes in natural earthy tones that can be painted or glazed after firing. Polymer clay finishes are versatile, allowing for smooth, matte, or glossy textures without additional treatments, whereas ceramic clay requires glazing and firing to achieve a durable, glossy, or textured surface finish. The choice between polymer and ceramic clay depends on the desired color flexibility and finish durability specific to the art project's requirements.
Tools and Equipment Required
Polymer clay requires basic sculpting tools such as blades, needles, rollers, and rubber shapers, along with an oven for curing at low to moderate temperatures (usually around 265degF to 300degF). Ceramic clay demands additional equipment including a pottery wheel for shaping, various carving tools, sponges, wire cutters, and access to a kiln capable of reaching temperatures above 1,800degF for firing and vitrification. While polymer clay tools are often affordable and portable, ceramic projects necessitate specialized, heat-resistant tools and a dedicated workspace for drying and firing processes.
Cost and Accessibility for Artists
Polymer clay offers a cost-effective option for artists due to its lower price per pound and widespread availability in craft stores and online, making it accessible for beginners and hobbyists. Ceramic clay tends to be more expensive, especially when accounting for the need for specialized equipment like kilns, which may limit accessibility for artists without studio space or resources. The versatility of polymer clay in terms of storage and minimal setup costs appeals to budget-conscious creators compared to the higher initial investment and maintenance required for ceramic clay projects.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Polymer clay is a synthetic material that cures at low temperatures and emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to ceramic clay, which requires high-temperature firing that can release harmful fumes. Ceramic clay often involves energy-intensive kiln use, contributing to a larger carbon footprint, whereas polymer clay's curing process is more energy-efficient. Both materials require proper ventilation, but polymer clay generally poses fewer respiratory risks and creates less environmental waste when used in small-scale art projects.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Art Project
Polymer clay offers vibrant colors and flexible shaping, ideal for detailed and miniature art projects, while ceramic clay provides durability and a natural texture suitable for sculptures and pottery. Consider the project's purpose, whether you need oven-baked polymer clay or kiln-fired ceramic clay for longevity and finish. Selecting the right clay depends on drying methods, desired finish, and the complexity of the design to ensure optimal results.
Infographic: Polymer clay vs Ceramic clay for Art project
 azmater.com
azmater.com