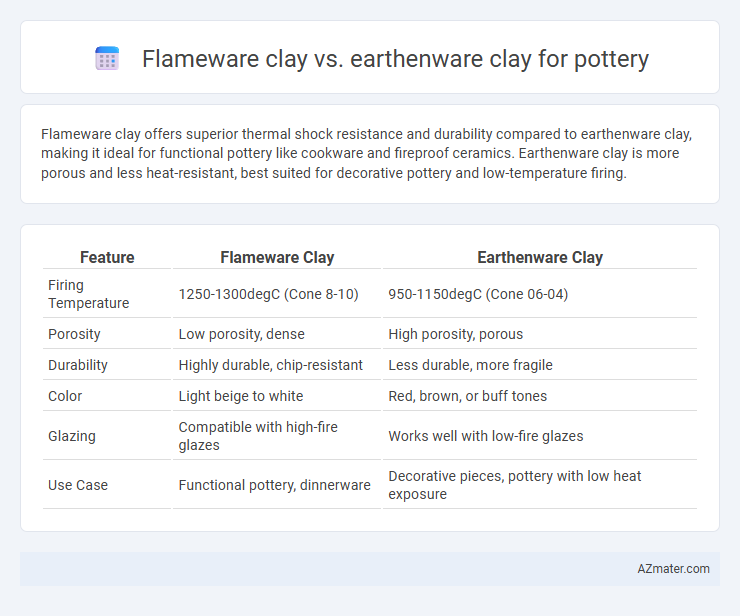
Flameware clay offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability compared to earthenware clay, making it ideal for functional pottery like cookware and fireproof ceramics. Earthenware clay is more porous and less heat-resistant, best suited for decorative pottery and low-temperature firing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flameware Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Firing Temperature | 1250-1300degC (Cone 8-10) | 950-1150degC (Cone 06-04) |
| Porosity | Low porosity, dense | High porosity, porous |
| Durability | Highly durable, chip-resistant | Less durable, more fragile |
| Color | Light beige to white | Red, brown, or buff tones |
| Glazing | Compatible with high-fire glazes | Works well with low-fire glazes |
| Use Case | Functional pottery, dinnerware | Decorative pieces, pottery with low heat exposure |
Introduction to Flameware and Earthenware Clay
Flameware clay is a high-fire clay body designed to withstand extreme heat, making it ideal for functional pottery like cookware and mugs that handle direct flame exposure. Earthenware clay, fired at lower temperatures, is porous and often used for decorative pottery and terracotta, offering a rustic and earthy appearance. Flameware provides superior durability and thermal shock resistance compared to the more brittle and porous earthenware.
Composition and Material Differences
Flameware clay contains higher levels of refractory materials such as alumina and silica, enabling it to withstand direct flame and rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it ideal for functional pottery like cookware. Earthenware clay is composed mainly of natural clay minerals with a higher iron content, resulting in a more porous, lower-fired ceramic that is softer and less durable under heat exposure. The material differences influence firing temperatures, with flameware clays typically firing between 1220-1300degC and earthenware clays firing at lower temperatures around 1000-1150degC.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
Flameware clay exhibits superior thermal properties with a higher heat resistance, typically enduring temperatures above 1200degC, making it ideal for functional pottery subjected to direct flames or high heat, such as cooking vessels. Earthenware clay, by contrast, has a lower firing temperature range, around 1000degC to 1150degC, resulting in less thermal shock resistance and making it more suitable for decorative pottery rather than high-heat applications. The vitrification level in flameware clay enhances its durability and reduces porosity, providing enhanced thermal stability compared to the more porous and fragile structure of earthenware.
Suitability for Cooking and Functional Pottery
Flameware clay, specifically formulated to withstand high temperatures and direct flame exposure, excels in cooking applications such as casseroles and pizza stones due to its thermal shock resistance and durability. Earthenware clay, while porous and less heat-resistant, is better suited for decorative or functional pottery that doesn't require direct contact with intense heat, like serving dishes or storage containers. Choosing the right clay depends on the intended use: flameware is optimal for cookware performance, whereas earthenware serves well in non-cooking functional and aesthetic pottery.
Firing Temperatures and Kiln Requirements
Flameware clay typically fires at higher temperatures, ranging from cone 6 to cone 10 (2232degF to 2345degF), requiring a kiln capable of withstanding and maintaining these intense heat levels for durability and vitrification. Earthenware clay fires at lower temperatures, usually between cone 06 and cone 04 (1828degF to 1940degF), suitable for kilns with lower temperature capabilities, often resulting in a more porous final product unless glazed. Kiln selection depends on the clay type: flameware demands a high-fire kiln with reliable temperature control, whereas earthenware can be fired in an electric or gas kiln with moderate heat settings.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
Flameware clay exhibits superior durability and long-term performance compared to earthenware clay, as it withstands high temperatures without cracking or breaking. Flameware is typically fired at higher temperatures, around 1200degC to 1300degC, resulting in a denser, more vitrified structure that enhances strength and resistance to thermal shock. Earthenware, fired at lower temperatures (typically 1000degC to 1150degC), remains more porous and fragile, making it less suitable for functional pottery exposed to heat and frequent use.
Glazing Options and Surface Finishes
Flameware clay offers higher thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for intricate glazing techniques that require multiple firings without cracking. Earthenware clay, known for its porous surface, absorbs glazes differently, often resulting in softer, matte finishes that highlight rustic textures. Glazes on Flameware tend to be more vibrant and durable, while Earthenware glazes provide a wider range of matte and satin surface finishes favored in traditional pottery.
Safety Considerations for Food Use
Flameware clay is formulated to withstand higher temperatures and is typically more durable and non-toxic, making it safer for food use compared to standard earthenware clay, which can be porous and may absorb liquids, leading to potential bacterial growth. Earthenware clay often requires a food-safe glaze and proper firing to ensure it is non-porous and safe for food contact. Potters must verify that both clays and glazes are certified lead-free and meet FDA or equivalent food safety standards to ensure safe use in functional pottery.
Cost and Accessibility for Potters
Flameware clay typically costs more than earthenware clay due to its enhanced heat resistance and durability, making it a preferred choice for functional pottery like cookware. Earthenware clay is widely accessible and budget-friendly, favored by beginners and hobbyists for its ease of use and abundant availability. Potters selecting between the two must weigh the higher price of Flameware against the affordability and convenience of earthenware to fit their project needs and skill level.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Pottery Project
Flameware clay offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for pottery that requires functional use such as cooking or baking vessels. Earthenware clay, known for its porous texture and lower firing temperature, is better suited for decorative or non-functional pottery projects that prioritize aesthetic appeal. Selecting the right clay depends on the intended purpose, with Flameware clay chosen for practicality and Earthenware for artistic expression.
Infographic: Flameware clay vs Earthenware clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com