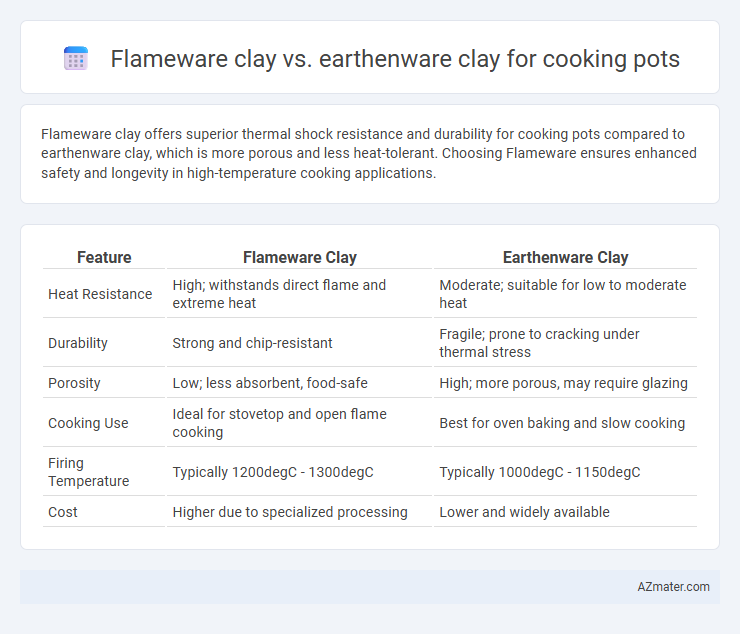
Flameware clay offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability for cooking pots compared to earthenware clay, which is more porous and less heat-tolerant. Choosing Flameware ensures enhanced safety and longevity in high-temperature cooking applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flameware Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | High; withstands direct flame and extreme heat | Moderate; suitable for low to moderate heat |
| Durability | Strong and chip-resistant | Fragile; prone to cracking under thermal stress |
| Porosity | Low; less absorbent, food-safe | High; more porous, may require glazing |
| Cooking Use | Ideal for stovetop and open flame cooking | Best for oven baking and slow cooking |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 1200degC - 1300degC | Typically 1000degC - 1150degC |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized processing | Lower and widely available |
Introduction to Flameware and Earthenware Clays
Flameware clay is a high-fire, durable ceramic material designed to withstand direct exposure to open flames and intense heat, making it ideal for cooking pots used on stovetops or campfires. Earthenware clay, typically low-fired and porous, requires glazing to be heat-resistant and is better suited for gentle cooking applications or serving dishes rather than direct flame use. Understanding the thermal properties and firing temperatures--Flameware clay fires at approximately 1200-1300degC, while Earthenware fires at 1000-1150degC--helps determine their suitability for heat-exposed cookware.
Composition Differences: Flameware vs Earthenware
Flameware clay is composed of a dense, refractory mixture with high silica and alumina content, designed to withstand direct flame and high temperatures without cracking, making it ideal for cooking pots used on stovetops or open flames. Earthenware clay contains higher levels of iron oxide and has a more porous, less vitrified composition, resulting in lower thermal resistance and increased absorption, which suits it better for decorative pottery but limits its direct cooking applications. The distinct composition differences mean Flameware offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability compared to the more porous, heat-sensitive earthenware clay.
Thermal Shock Resistance Compared
Flameware clay exhibits superior thermal shock resistance compared to earthenware clay, allowing cooking pots made from flameware to endure sudden temperature changes without cracking. The dense, vitrified nature of flameware clay enhances its ability to withstand direct flame and rapid heating, making it ideal for stovetop use. In contrast, earthenware clay, being more porous and less vitrified, is more prone to thermal shock and thus better suited for oven or slow cooking applications rather than direct flame exposure.
Heat Distribution and Retention Properties
Flameware clay exhibits superior heat distribution and retention properties compared to earthenware clay, enabling more even cooking temperatures and prolonged heat holding. Its dense composition reduces hot spots and ensures consistent heat transfer throughout the cooking pot. Earthenware clay, while more porous and prone to uneven heating, cools faster and may require lower cooking temperatures to prevent cracking.
Safety and Health Considerations
Flameware clay is specifically formulated to withstand direct heat without cracking, making it a safer option for cooking pots used on stovetops and open flames. Earthenware clay, while porous and often more affordable, requires thorough glazing to prevent the absorption of bacteria and toxins, which can pose health risks if improperly sealed. Choosing flameware clay enhances durability and reduces potential contamination, ensuring safer cooking practices and better food safety outcomes.
Durability and Longevity in Cookware
Flameware clay offers superior durability and thermal shock resistance compared to traditional Earthenware clay, making it ideal for high-heat cooking applications such as stove-top pots. Its vitrified, denser composition reduces the risk of cracking and chipping, significantly extending the lifespan of cookware under frequent use. Earthenware clay, while aesthetically pleasing and porous, is more prone to wear and requires careful handling to maintain longevity in cooking pots.
Cooking Performance and Results
Flameware clay outperforms earthenware clay in cooking pots due to its superior heat retention and even heat distribution, resulting in more consistent cooking temperatures and reduced hotspots. Its vitrified structure prevents absorption of flavors and odors, enhancing the purity of food taste compared to the more porous nature of earthenware clay. Consequently, flameware clay pots offer improved durability and better performance for slow-cooked dishes and high-temperature cooking.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Flameware clay, designed for direct heat exposure, requires minimal maintenance due to its heat-resistant glaze that prevents cracking and chipping during cooking. Earthenware clay, being more porous and less heat-tolerant, demands careful seasoning and gradual temperature changes to avoid damage and stains, thus needing more frequent upkeep. Proper cleaning and drying are essential for both, but Flameware's durability makes it more suitable for heavy use in cooking pots with lower maintenance effort.
Cost and Accessibility for Home Cooks
Flameware clay offers high heat resistance and durability, but it tends to be more expensive and less accessible for home cooks compared to earthenware clay. Earthenware clay is widely available, more affordable, and easier to work with, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious home cooks seeking traditional cooking pots. While Flameware's advanced properties benefit long-term use, earthenware's accessibility and cost-effectiveness make it ideal for everyday kitchen use.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Cooking Needs
Flameware clay offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for cooking pots that require direct flame exposure and high-temperature endurance. Earthenware clay provides excellent porosity and heat retention, suitable for slow-cooked dishes and steady simmering in traditional cooking methods. Selecting the right clay depends on your cooking style, with Flameware best for intense heat and Earthenware favored for gentle, gradual cooking.
Infographic: Flameware clay vs Earthenware clay for Cooking-pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com