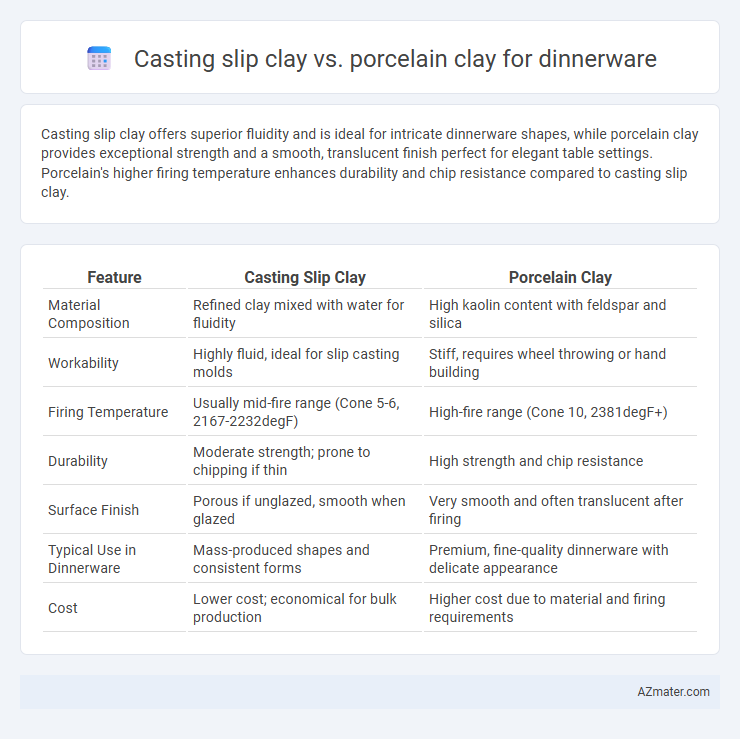
Casting slip clay offers superior fluidity and is ideal for intricate dinnerware shapes, while porcelain clay provides exceptional strength and a smooth, translucent finish perfect for elegant table settings. Porcelain's higher firing temperature enhances durability and chip resistance compared to casting slip clay.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Casting Slip Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Refined clay mixed with water for fluidity | High kaolin content with feldspar and silica |
| Workability | Highly fluid, ideal for slip casting molds | Stiff, requires wheel throwing or hand building |
| Firing Temperature | Usually mid-fire range (Cone 5-6, 2167-2232degF) | High-fire range (Cone 10, 2381degF+) |
| Durability | Moderate strength; prone to chipping if thin | High strength and chip resistance |
| Surface Finish | Porous if unglazed, smooth when glazed | Very smooth and often translucent after firing |
| Typical Use in Dinnerware | Mass-produced shapes and consistent forms | Premium, fine-quality dinnerware with delicate appearance |
| Cost | Lower cost; economical for bulk production | Higher cost due to material and firing requirements |
Introduction to Casting Slip Clay and Porcelain Clay
Casting slip clay offers a fluid consistency ideal for creating detailed and uniform dinnerware through slip casting, providing excellent mold reproduction and smooth surface finishes. Porcelain clay, known for its high firing temperature and strength, produces translucent, non-porous dinnerware with a refined, white appearance and superior durability. Comparing these materials highlights casting slip clay's ease of forming complex shapes versus porcelain's elegance and resilience in finished ceramic dinnerware.
Composition Differences: Casting Slip vs Porcelain
Casting slip clay for dinnerware typically contains a higher percentage of water and finer particles to improve fluidity and workability in molds, whereas porcelain clay features a denser composition with kaolin, feldspar, and silica, offering greater strength and translucency after firing. Casting slip's composition emphasizes plasticity and shrinkage control for seamless casting, contrasting with porcelain's formulation designed for durability and a smooth, white finish. The higher flux content in casting slip promotes faster vitrification, while porcelain's balanced mineral mix ensures thermal resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Workability and Forming Methods
Casting slip clay offers superior fluidity and ease of pouring into detailed molds, making it ideal for complex and thin-walled dinnerware pieces, while porcelain clay demands more skill in hand-building or wheel-throwing due to its stiff consistency. Porcelain's fine particle size allows for smooth surfaces and high translucency, but its reduced plasticity challenges workability compared to the more malleable slip clay. Selecting between slip and porcelain clays depends on desired dinnerware form complexity and production scale, with slip casting excelling in mass production and porcelain favored for artisanal craftsmanship.
Firing Temperatures and Kiln Requirements
Casting slip clay for dinnerware typically fires at cone 5-6 (2167-2232degF), requiring standard electric or gas kilns with consistent temperature control to ensure durability and vitrification. Porcelain clay demands higher firing temperatures, usually cone 10-11 (2381-2400degF), necessitating more advanced kiln types capable of reaching and maintaining these elevated temperatures without thermal shock. The choice between casting slip and porcelain profoundly impacts kiln fuel efficiency, firing schedules, and the final strength and translucency of the dinnerware.
Strength and Durability of Finished Dinnerware
Casting slip clay and porcelain clay differ significantly in strength and durability for dinnerware applications; porcelain clay typically offers higher mechanical strength and greater resistance to chipping due to its dense, vitrified structure after firing. Slip casting produces thinner, more uniform pieces but may result in increased fragility compared to porcelain slabs which are often denser and less porous. Porcelain dinnerware's enhanced durability makes it preferable for everyday use and long-term retention of aesthetic qualities.
Surface Texture and Finish Quality
Casting slip clay for dinnerware produces a slightly porous surface texture that can enhance glaze adhesion, resulting in a durable, matte or satin finish ideal for rustic or handmade aesthetics. Porcelain clay offers a smoother, denser surface texture due to its fine particle size and high firing temperature, delivering a glass-like, glossy finish favored for elegant and refined dinnerware. The choice between slip cast and porcelain clay impacts the final finish quality, with slip casting providing more textural variety and porcelain ensuring a consistently sleek, polished appearance.
Color and Translucency Comparisons
Casting slip clay typically offers a more muted color palette with softer, matte finishes compared to porcelain clay, which is prized for its bright whiteness and subtle translucency. Porcelain clay's high kaolin content allows light to pass through thin areas, creating a delicate, translucent effect that enhances the visual appeal of dinnerware. In contrast, slip-cast earthenware tends to be more opaque and less vibrant, making porcelain the preferred choice for fine, elegant table settings where color brilliance and translucency are desired.
Glaze Compatibility and Results
Casting slip clay offers superior glaze compatibility for dinnerware due to its higher plasticity and lower firing temperature, resulting in a smoother, more uniform surface that enhances glaze adherence and reduces defects like crazing. Porcelain clay, while prized for its translucency and strength after firing at higher temperatures, requires carefully formulated glazes to prevent issues such as blistering or shivering, as its low porosity can challenge glaze bonding. Selecting the appropriate clay and glaze combination directly impacts the durability and aesthetic quality of finished dinnerware, with casting slip clay generally providing easier and more predictable glaze outcomes.
Suitability for Various Dinnerware Designs
Casting slip clay offers excellent fluidity and finer particle size, making it highly suitable for intricate and delicate dinnerware designs with detailed patterns or thin walls. Porcelain clay provides a stronger, more durable finish with a smoother, glass-like surface, ideal for minimalist or elegant dinnerware that emphasizes strength and translucency. Both materials enable diverse aesthetic finishes, but casting slip is preferred for complex molds, while porcelain clay is favored for durability and refined textures.
Cost and Accessibility for Makers
Casting slip clay offers a more affordable and accessible option for makers due to its lower material costs and easier availability in bulk compared to porcelain clay. Porcelain clay, while prized for its fine texture and translucency, tends to be more expensive and less accessible, often requiring specialized suppliers and higher skill levels for successful firing. Makers prioritizing cost-efficiency and ease of sourcing typically prefer casting slip clay for dinnerware production.
Infographic: Casting slip clay vs Porcelain clay for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com