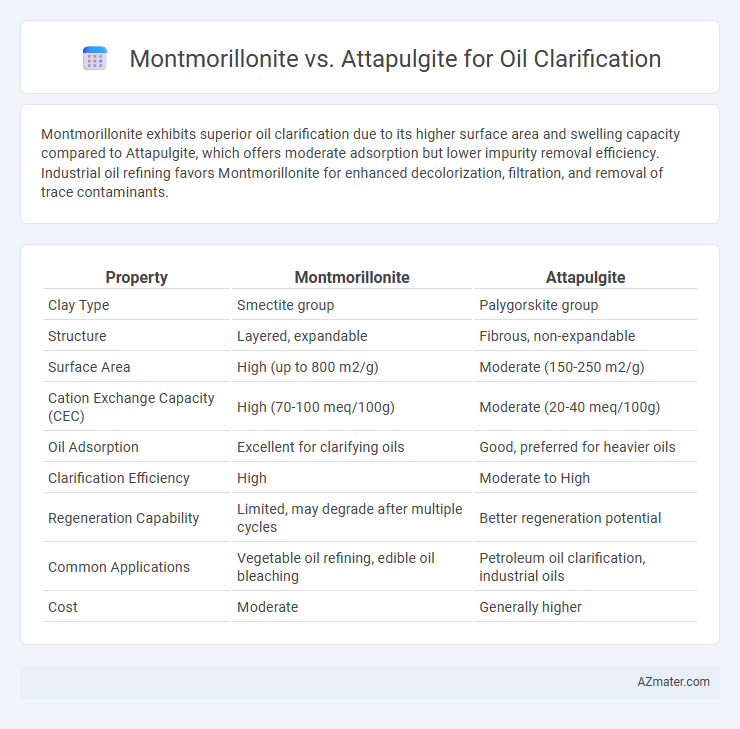
Montmorillonite exhibits superior oil clarification due to its higher surface area and swelling capacity compared to Attapulgite, which offers moderate adsorption but lower impurity removal efficiency. Industrial oil refining favors Montmorillonite for enhanced decolorization, filtration, and removal of trace contaminants.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Montmorillonite | Attapulgite |
|---|---|---|
| Clay Type | Smectite group | Palygorskite group |
| Structure | Layered, expandable | Fibrous, non-expandable |
| Surface Area | High (up to 800 m2/g) | Moderate (150-250 m2/g) |
| Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) | High (70-100 meq/100g) | Moderate (20-40 meq/100g) |
| Oil Adsorption | Excellent for clarifying oils | Good, preferred for heavier oils |
| Clarification Efficiency | High | Moderate to High |
| Regeneration Capability | Limited, may degrade after multiple cycles | Better regeneration potential |
| Common Applications | Vegetable oil refining, edible oil bleaching | Petroleum oil clarification, industrial oils |
| Cost | Moderate | Generally higher |
Introduction to Oil Clarification
Oil clarification is essential for improving the purity and quality of edible and industrial oils by removing impurities such as free fatty acids, pigments, and residual solids. Montmorillonite and Attapulgite are two types of clay adsorbents commonly used in this process due to their high surface area and adsorption capacity. Montmorillonite offers superior swelling properties and cation exchange capacity, while Attapulgite provides enhanced porosity and thermal stability, influencing their effectiveness in oil clarification.
Overview of Montmorillonite
Montmorillonite is a highly absorbent clay mineral composed primarily of smectite group minerals, known for its expansive properties and large surface area ideal for oil clarification. Its unique layered structure allows effective adsorption of impurities, suspended solids, and pigments in crude and edible oils, enhancing transparency and stability. Compared to attapulgite, montmorillonite offers superior swelling capacity and adsorption efficiency, making it a preferred choice in industrial oil refining processes.
Overview of Attapulgite
Attapulgite, a naturally occurring clay mineral composed of hydrated magnesium aluminum silicate, exhibits high adsorption capacity and unique fibrous structure, making it highly effective for oil clarification by removing impurities and contaminants. Its porous network enhances oil filtration efficiency and improves clarity without significantly altering oil properties. Compared to Montmorillonite, Attapulgite offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for refining and purifying various oil types in industrial applications.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Montmorillonite and Attapulgite are both clay minerals used in oil clarification, but they differ significantly in chemical composition. Montmorillonite primarily consists of a 2:1 layered silicate structure composed of silica (SiO2), alumina (Al2O3), and varying amounts of magnesium and iron oxides, which contribute to its high cation exchange capacity and swelling properties. In contrast, Attapulgite features a chain-like silicate structure rich in magnesium oxide (MgO) and lower alumina content, resulting in higher porosity and adsorption capacity favorable for absorbing impurities during oil clarification.
Adsorption Mechanisms
Montmorillonite and attapulgite are both effective clay minerals used for oil clarification due to their high adsorption capacities. Montmorillonite exhibits swelling properties and a layered structure, enabling it to trap polar contaminants through cation exchange and surface adsorption. Attapulgite, characterized by its fibrous morphology and high surface area, adsorbs impurities primarily via physical adsorption and pore entrapment, making it particularly efficient in removing color bodies and organic compounds from oils.
Efficiency in Oil Clarification
Montmorillonite exhibits superior efficiency in oil clarification due to its high adsorption capacity and expansive surface area, which effectively remove impurities and contaminants. Attapulgite, while also used in oil clarification, has a denser structure and lower surface area, resulting in slower adsorption rates and less overall impurity removal. Comparative studies highlight Montmorillonite's faster performance and higher clarity outcomes, making it the preferred choice for industrial oil purification processes.
Impact on Oil Quality
Montmorillonite enhances oil clarification by effectively adsorbing impurities and reducing color and odor, leading to higher oil purity and stability. Attapulgite improves oil quality by selectively removing suspended solids and moisture, which minimizes oil degradation and extends shelf life. The choice between Montmorillonite and Attapulgite directly influences oil clarity, oxidative stability, and overall sensory attributes crucial for consumer acceptance.
Environmental Considerations
Montmorillonite and Attapulgite clays differ significantly in environmental impact during oil clarification, with Montmorillonite often favored for its higher natural abundance and biodegradability. Attapulgite's fibrous structure provides effective adsorption but may pose challenges in disposal due to slower degradation rates and potential accumulation in ecosystems. Selecting Montmorillonite can reduce ecological footprints by promoting faster mineral recovery and minimizing hazardous waste generation in oil purification processes.
Cost and Availability
Montmorillonite clay offers a lower cost-per-unit for oil clarification applications due to its abundant natural deposits and widespread availability, making it an economically favorable choice in large-scale operations. Attapulgite, while slightly more expensive, provides specialized adsorption properties but is less common globally, resulting in higher procurement costs and limited supply chains. The cost-efficiency of Montmorillonite combined with its accessibility often outweighs Attapulgite's niche performance advantages in oil clarification processes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clay
Montmorillonite offers superior oil clarification due to its higher surface area and enhanced adsorption capacity, making it ideal for refining and purification processes. Attapulgite's fibrous structure provides effective filtration and contaminant trapping, suitable for applications requiring rapid sediment removal. Selecting the right clay depends on the specific oil type and clarification goals, with Montmorillonite favored for deep purification and Attapulgite preferred for quicker, bulk removal tasks.
Infographic: Montmorillonite vs Attapulgite for Oil Clarification
 azmater.com
azmater.com