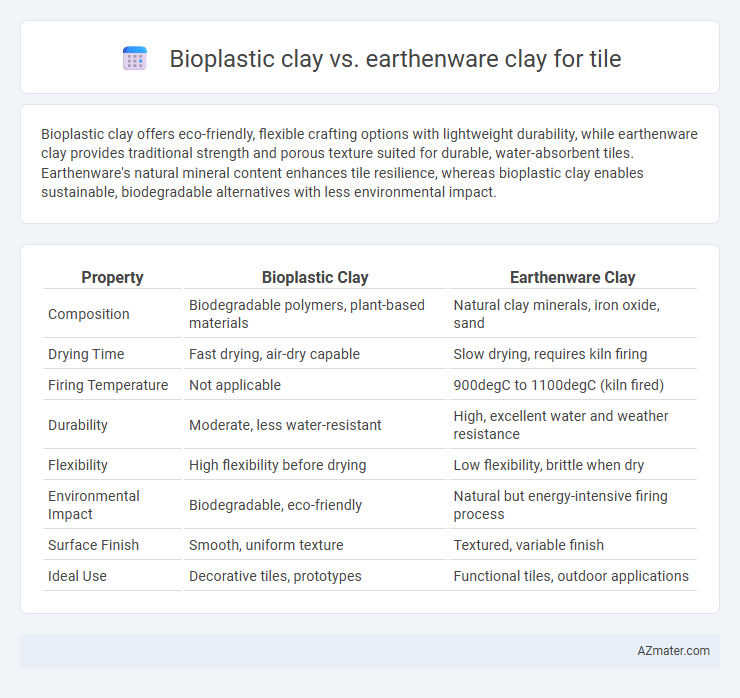
Bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly, flexible crafting options with lightweight durability, while earthenware clay provides traditional strength and porous texture suited for durable, water-absorbent tiles. Earthenware's natural mineral content enhances tile resilience, whereas bioplastic clay enables sustainable, biodegradable alternatives with less environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioplastic Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Biodegradable polymers, plant-based materials | Natural clay minerals, iron oxide, sand |
| Drying Time | Fast drying, air-dry capable | Slow drying, requires kiln firing |
| Firing Temperature | Not applicable | 900degC to 1100degC (kiln fired) |
| Durability | Moderate, less water-resistant | High, excellent water and weather resistance |
| Flexibility | High flexibility before drying | Low flexibility, brittle when dry |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Natural but energy-intensive firing process |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, uniform texture | Textured, variable finish |
| Ideal Use | Decorative tiles, prototypes | Functional tiles, outdoor applications |
Understanding Bioplastic Clay and Earthenware Clay
Bioplastic clay is a lightweight, non-toxic modeling material composed primarily of biodegradable polymers, offering flexibility and ease of shaping ideal for intricate tile designs. Earthenware clay, derived from natural clay minerals, is porous and fired at lower temperatures, providing durable and water-absorbent tiles suitable for rustic or traditional finishes. Understanding the material properties reveals bioplastic clay's advantage in eco-friendly, detailed projects, while earthenware clay excels in structural strength and thermal insulation for practical tile applications.
Key Material Properties of Bioplastic Clay
Bioplastic clay features lightweight, flexible, and water-resistant properties, making it ideal for intricate tile designs that require durability and minimal shrinkage. Earthenware clay, by contrast, is porous and brittle, necessitating glazing for water resistance and exhibiting higher shrinkage rates during firing. The key advantage of bioplastic clay lies in its eco-friendly composition and improved dimensional stability, which enhances tile longevity and reduces production defects.
Distinct Characteristics of Earthenware Clay
Earthenware clay is characterized by its porous nature and lower firing temperature, typically between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, which results in a more porous and less durable tile compared to bioplastic clay. It contains natural impurities like iron oxide, giving it a distinct reddish or brown color after firing, and is generally softer and more brittle than bioplastic alternatives. Earthenware tiles are favored for their rustic aesthetic and ease of shaping but lack the strength and water resistance provided by bioplastic clay tiles.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Bioplastic clay offers significant sustainability advantages over earthenware clay due to its biodegradable properties and lower resource consumption during production. Earthenware clay, while natural, involves high-energy firing processes that contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Using bioplastic clay for tiles reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste and relying on renewable materials, aligning with eco-friendly construction practices.
Workability: Shaping and Molding Tiles
Bioplastic clay offers superior flexibility and plasticity, allowing for intricate shaping and precise molding of tiles with less risk of cracking during manipulation. Earthenware clay, while traditional and robust, tends to be stiffer and may require more skill to shape tiles without deformation or damage. The enhanced workability of bioplastic clay facilitates detailed designs and smoother surfaces, making it preferable for complex tile patterns.
Drying and Firing Differences
Bioplastic clay, a synthetic material, dries faster than earthenware clay due to its polymer base, which can reduce the risk of cracking during drying. Earthenware clay requires slower, more controlled drying to avoid warping and cracking because of its higher water content and natural composition. Firing temperatures also differ, as earthenware typically needs lower kiln temperatures (around 1,000-1,150degC) compared to bioplastic-based clay materials, which may not require traditional firing or can be cured with heat rather than high-temperature kilns.
Tile Durability and Strength Comparison
Bioplastic clay offers enhanced tile durability with increased resistance to cracking under pressure due to its flexible polymer composition, making it less prone to brittle failure compared to earthenware clay. Earthenware clay tiles, while traditional and aesthetically prized, typically exhibit lower strength and higher porosity, leading to decreased durability and greater susceptibility to chipping or erosion over time. When evaluating tile strength, bioplastic clay outperforms earthenware in impact resistance and long-term structural integrity, especially in environments with variable moisture and mechanical stress.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finish
Bioplastic clay offers vibrant color consistency and smooth, polished surfaces ideal for intricate tile designs, while earthenware clay provides a warm, rustic aesthetic with natural texture variations that enhance handcrafted appeal. Earthenware tiles often display a matte or semi-gloss finish, reflecting organic imperfections, whereas bioplastic clay can achieve glossy or custom finishes through controlled curing processes. Choosing between the two depends on the desired visual effect, with bioplastic clay favoring precision and brightness, and earthenware emphasizing traditional, earthy character.
Use Cases: Ideal Applications for Each Clay Type
Bioplastic clay, known for its lightweight and flexible properties, is ideal for detailed decorative tiles, custom shapes, and quick prototyping in interior design. Earthenware clay, with its durability and porosity, suits functional applications such as floor and wall tiles in residential and commercial spaces, offering long-lasting performance and water resistance when glazed. Both clays cater to specific tile production needs based on aesthetic requirements and structural demands.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Bioplastic clay generally incurs higher production costs than earthenware clay due to the use of renewable materials and advanced processing techniques, impacting the overall price of tiles. Earthenware clay remains more affordable and widely available in global markets, benefiting from established supply chains and lower raw material expenses. Market availability favors earthenware clay with extensive distribution networks, while bioplastic clay tile options are still emerging, often found in niche or eco-conscious sectors.
Infographic: Bioplastic clay vs Earthenware clay for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com