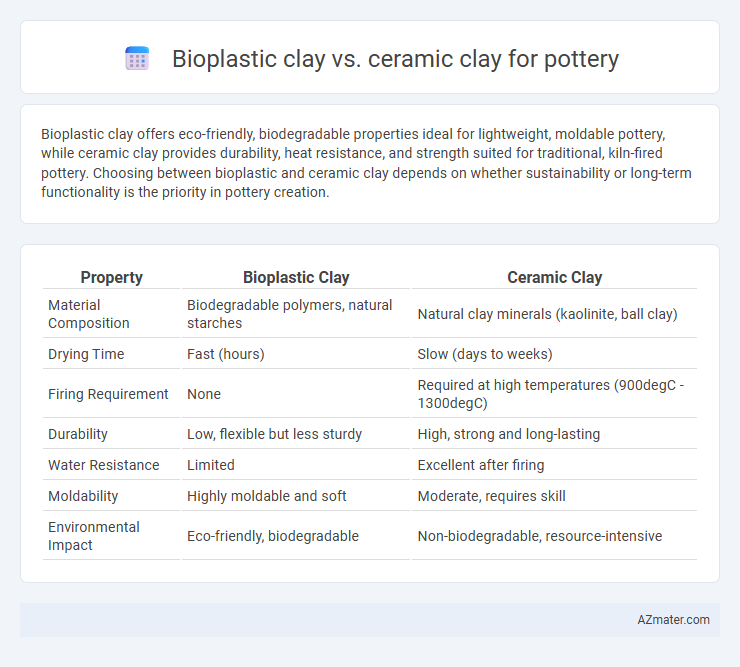
Bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly, biodegradable properties ideal for lightweight, moldable pottery, while ceramic clay provides durability, heat resistance, and strength suited for traditional, kiln-fired pottery. Choosing between bioplastic and ceramic clay depends on whether sustainability or long-term functionality is the priority in pottery creation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioplastic Clay | Ceramic Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Biodegradable polymers, natural starches | Natural clay minerals (kaolinite, ball clay) |
| Drying Time | Fast (hours) | Slow (days to weeks) |
| Firing Requirement | None | Required at high temperatures (900degC - 1300degC) |
| Durability | Low, flexible but less sturdy | High, strong and long-lasting |
| Water Resistance | Limited | Excellent after firing |
| Moldability | Highly moldable and soft | Moderate, requires skill |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Non-biodegradable, resource-intensive |
Introduction to Bioplastic Clay and Ceramic Clay
Bioplastic clay is a modern, eco-friendly material made from biodegradable polymers that offers flexibility, lightweight properties, and easy molding, making it ideal for sustainable pottery projects. Ceramic clay, derived from natural minerals like kaolinite, is a traditional, fire-hardened material known for its durability, high heat resistance, and suitability for functional pottery. Both clays have unique chemical compositions and physical characteristics that influence their shaping, drying, and firing processes in ceramic arts.
Composition and Material Differences
Bioplastic clay is primarily composed of biodegradable polymers derived from renewable sources such as cornstarch or cellulose, making it lightweight and flexible for sculpting, whereas ceramic clay consists of natural minerals like kaolin, ball clay, and quartz that are dense and require high-temperature firing. The organic polymers in bioplastic clay enable air-drying without kiln firing, contrasting with ceramic clay's transformation through vitrification during kiln firing to achieve hardness and durability. Materially, bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly properties and ease of use for decorative pieces, while ceramic clay provides structural strength and longevity suited for functional pottery.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioplastic clay offers a renewable alternative to traditional ceramic clay by utilizing biodegradable starch-based materials that reduce reliance on non-renewable resources and minimize landfill waste. Ceramic clay, while abundant and recyclable in some cases, requires high-temperature kiln firing that consumes significant energy and releases carbon emissions, impacting sustainability. The biodegradability and lower carbon footprint of bioplastic clay make it a more environmentally sustainable choice for eco-conscious pottery artisans.
Workability and Handling in Pottery
Bioplastic clay offers superior workability with its lightweight and pliable texture, making it ideal for intricate detailing and quick prototyping in pottery. Ceramic clay generally requires more skill to handle due to its heavier, denser consistency, but it provides better structural strength and durability once fired. Potters often prefer bioplastic clay for ease of shaping and modification, while ceramic clay is favored for creating lasting, functional pottery pieces.
Firing and Curing Processes
Bioplastic clay does not require firing and cures at room temperature or with minimal heat, making it ideal for quick projects and non-durable items. Ceramic clay undergoes a high-temperature kiln firing process, typically between 1,000degC and 1,300degC, which vitrifies the material, enhancing strength, durability, and water resistance. The firing process in ceramic clay also enables glazing and ensures the final product withstands functional use, unlike bioplastic clay which remains more flexible and less heat resistant.
Durability and Longevity of Finished Pieces
Bioplastic clay offers limited durability and longevity compared to ceramic clay, as it tends to be more flexible but less resistant to wear and environmental factors. Ceramic clay, once fired at high temperatures, becomes vitrified and highly durable, making finished pieces resistant to chipping, cracking, and moisture damage. Therefore, pottery made from ceramic clay is better suited for long-lasting functional and decorative items.
Artistic Potential and Aesthetic Outcomes
Bioplastic clay offers greater flexibility and vibrant color possibilities, enabling artists to create highly detailed, lightweight, and non-toxic sculptures often suited for decorative art. Ceramic clay, by contrast, provides superior durability and a natural, earthy texture that enhances traditional pottery with a classic, tactile aesthetic ideal for functional and artistic pieces. The choice between bioplastic and ceramic clay significantly influences the artistic potential and aesthetic outcomes, with bioplastic favoring intricate, colorful designs and ceramic clay excelling in structural strength and timeless beauty.
Health and Safety Considerations
Bioplastic clay is non-toxic, biodegradable, and emits minimal dust, making it a safer choice for indoor use and reducing respiratory risks during pottery activities. Ceramic clay often contains silica dust, which can be hazardous when inhaled over time, necessitating proper ventilation and protective masks to minimize health risks. Both materials require careful handling, but bioplastic clay offers a lower risk of exposure to harmful particles and heavy metals commonly found in traditional ceramic clays.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Bioplastic clay typically costs more than ceramic clay, reflecting its eco-friendly and biodegradable properties but remains less widely available in mainstream pottery supply stores. Ceramic clay is more affordable and widely accessible due to its long-established manufacturing processes and extensive distribution network. Both materials serve different purposes, but for budget-conscious potters, ceramic clay offers greater availability and lower cost.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Pottery Projects
Bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly and lightweight options ideal for small, detailed pottery projects, while ceramic clay provides durability and versatility suited for functional, heat-resistant pottery. Consider bioplastic clay for craft-based, non-fired creations and ceramic clay for wheel throwing or kiln-fired items that require strength and permanence. Selecting the right clay depends on the project's purpose, firing process, and desired finish quality.
Infographic: Bioplastic clay vs Ceramic clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com